Document
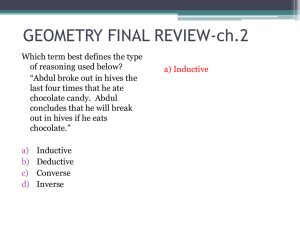
... Example 2: Given that 1 is a complement of 2, and m 1 = 35o, find the m 2. Example 3: Given that 1 is a complement of 2, and m 1= 73o, find the m 2. Example 4: Given that 3 is a supplement of 4, and m 4 = 37o, find the m 3. ...
... Example 2: Given that 1 is a complement of 2, and m 1 = 35o, find the m 2. Example 3: Given that 1 is a complement of 2, and m 1= 73o, find the m 2. Example 4: Given that 3 is a supplement of 4, and m 4 = 37o, find the m 3. ...
Non-Euclidean Geometries
... 1. To draw a straight line from any point to any other 2. Any straight line segment can be extended indefinitely in a straight line 3. To describe a circle with any center and distance 4. That all right angles are equal to each other 5. That, if a straight line falling on two straight lines makes th ...
... 1. To draw a straight line from any point to any other 2. Any straight line segment can be extended indefinitely in a straight line 3. To describe a circle with any center and distance 4. That all right angles are equal to each other 5. That, if a straight line falling on two straight lines makes th ...
Many Sorted First-order Logic
... it. That is, for every set of formulas Γ and formulas Φ , when every Γ|=Φ then also Φ can be deduced from Γ. Henkin’s theorem: Γ consistent → Γ has a model. ...
... it. That is, for every set of formulas Γ and formulas Φ , when every Γ|=Φ then also Φ can be deduced from Γ. Henkin’s theorem: Γ consistent → Γ has a model. ...