
Definitions of reaction types (MT)
... Production a proton and an alpha particle, plus a residual. Production of a triton and 2 alpha particles, plus a residual. Production of a deuteron and 2 alpha particles, plus a residual. Production of proton and a deuteron, plus a residual. Production of proton and a triton, plus a residual. Produc ...
... Production a proton and an alpha particle, plus a residual. Production of a triton and 2 alpha particles, plus a residual. Production of a deuteron and 2 alpha particles, plus a residual. Production of proton and a deuteron, plus a residual. Production of proton and a triton, plus a residual. Produc ...
Particle sizing calibration with refractive index correction for light
... Particle sizing is only one aspect of the function of an OPC. The other is particle concentration measurement. Although this work does not deal directly with this aspect of calibration, it is useful to consider some of the problems which may be encountered with the data presented here. For a closed ...
... Particle sizing is only one aspect of the function of an OPC. The other is particle concentration measurement. Although this work does not deal directly with this aspect of calibration, it is useful to consider some of the problems which may be encountered with the data presented here. For a closed ...
ET2610101014
... approximation result after the first iteration. We have found that convergence can normally be achieved after only a few iterations for small electric fields. Once f 1 (k) has been evaluated to the required accuracy, it is possible to calculate quantities such as the drift mobility , which is give ...
... approximation result after the first iteration. We have found that convergence can normally be achieved after only a few iterations for small electric fields. Once f 1 (k) has been evaluated to the required accuracy, it is possible to calculate quantities such as the drift mobility , which is give ...
Chapter III. Scattering and Extinction of Evanescent waves by small
... to increased extinction in the range of shorter wavelengths and a double-peak structure, if the excitation is a p-polarized evanescent wave. The enhancement of the higher multipoles is not caused by an excitation-dependent susceptibility of the particles, but merely by the fact, that the ...
... to increased extinction in the range of shorter wavelengths and a double-peak structure, if the excitation is a p-polarized evanescent wave. The enhancement of the higher multipoles is not caused by an excitation-dependent susceptibility of the particles, but merely by the fact, that the ...
Introduction to Fluorescence Spectroscopies I. Theory
... suggested by A. Jablonski (1935) (see Fig. 1). The ground, first, and second electronic states are depicted by S0, S1, S2, …, respectively. The letter S (in this context) indicates a singlet excited state, in which the electrons remain paired (total spin = 0) during the excitation. In a triplet sta ...
... suggested by A. Jablonski (1935) (see Fig. 1). The ground, first, and second electronic states are depicted by S0, S1, S2, …, respectively. The letter S (in this context) indicates a singlet excited state, in which the electrons remain paired (total spin = 0) during the excitation. In a triplet sta ...
X-Ray Diffraction on Electrolyte Solutions in the Low Angle Range
... 2) The effect is complicated by ion-solvent and solvent-solvent interactions (see also [12]). 3) The concentration dependence of the peak positions is different for the different solutions. 4) In the case of the Pl^AsCl solutions no concentration dependence of the peak positions could be observed. 5 ...
... 2) The effect is complicated by ion-solvent and solvent-solvent interactions (see also [12]). 3) The concentration dependence of the peak positions is different for the different solutions. 4) In the case of the Pl^AsCl solutions no concentration dependence of the peak positions could be observed. 5 ...
MU2522002204
... mobility in III-V structures using the iterative technique. In the following sections electron-phonon and electron-impurity scattering mechanisms will be discussed. Deformation potential scattering The acoustic modes modulate the inter atomic spacing. Consequently, the position of the conduction and ...
... mobility in III-V structures using the iterative technique. In the following sections electron-phonon and electron-impurity scattering mechanisms will be discussed. Deformation potential scattering The acoustic modes modulate the inter atomic spacing. Consequently, the position of the conduction and ...
Plasma Process 5 col..
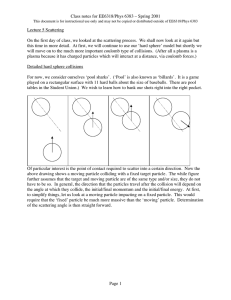
... This document is for instructional use only and may not be copied or distributed outside of EE6318/Phys 6383 ...
... This document is for instructional use only and may not be copied or distributed outside of EE6318/Phys 6383 ...
OpticalDiagnostics-ScatteringDiagnostics
... If a << 1 : then the scattering is from individual electron: Incoherent TS If a ≥ 1 : then scattering by electrons surrounding ions; (Ion) Coherent Thomson Scattering If a ~ 5-20 : Scattering by electron density fluctuations, or Bragg-scattering Coherent Thomson scattering Thomson Scattering Tutoria ...
... If a << 1 : then the scattering is from individual electron: Incoherent TS If a ≥ 1 : then scattering by electrons surrounding ions; (Ion) Coherent Thomson Scattering If a ~ 5-20 : Scattering by electron density fluctuations, or Bragg-scattering Coherent Thomson scattering Thomson Scattering Tutoria ...
Effect of pores on transmission properties of transparent ceramics
... yielding a fine grained polycrystalline microstructure. Optical transparency in ceramics is limited by the amount of light which is scattered and absorbed. The scattering centers in transparent ceramics include microstructure defects such as residual pores, second phase and grain boundaries. The gra ...
... yielding a fine grained polycrystalline microstructure. Optical transparency in ceramics is limited by the amount of light which is scattered and absorbed. The scattering centers in transparent ceramics include microstructure defects such as residual pores, second phase and grain boundaries. The gra ...
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics
... 12.6 Mass terms in : an attempted generalisation Experimental tests of the Weinberg–Salam theory 13.1 The search for the gauge bosons 13.2 The W± bosons 13.3 The Z boson 13.4 The number of lepton families 13.5 The measurement of partial widths 13.6 Left–right production cross-section asymmetry and l ...
... 12.6 Mass terms in : an attempted generalisation Experimental tests of the Weinberg–Salam theory 13.1 The search for the gauge bosons 13.2 The W± bosons 13.3 The Z boson 13.4 The number of lepton families 13.5 The measurement of partial widths 13.6 Left–right production cross-section asymmetry and l ...
11.2 - Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection
... Sometimes when you look out a window, you see what is outside as well as your own reflection This is because some light reflects and some light refracts at a surface between two media that have different indices of refraction This phenomenon is called partial reflection and refraction ...
... Sometimes when you look out a window, you see what is outside as well as your own reflection This is because some light reflects and some light refracts at a surface between two media that have different indices of refraction This phenomenon is called partial reflection and refraction ...
Coulomb deceleration of fast protons in a strong magnetic field
... electron to another Landau level to be possible. Therefore, in the cross section (15) and the functions F, Q, and G only the terms with n= playa role. Such a cross section differs from the Rutherford cross section only by the presence of the exponential function and in the argument of the delta-func ...
... electron to another Landau level to be possible. Therefore, in the cross section (15) and the functions F, Q, and G only the terms with n= playa role. Such a cross section differs from the Rutherford cross section only by the presence of the exponential function and in the argument of the delta-func ...
Polarization - Manchester HEP
... • Light then passed through a crossed polarizer, only that part of each of the components in the transmission plane emerges two coplanar components with a phase difference (dependent on wavelength) • Some colors undergo destructive interference and some constructive, giving an interference patte ...
... • Light then passed through a crossed polarizer, only that part of each of the components in the transmission plane emerges two coplanar components with a phase difference (dependent on wavelength) • Some colors undergo destructive interference and some constructive, giving an interference patte ...
[pdf]
... In single-scattering experiments, all observed photons travel nearly the same distance to the detector, and the scattering angle is well known. In DWS, however, photon path lengths are typically distributed over several centimeters. The detected photons have scattered many times, through all possibl ...
... In single-scattering experiments, all observed photons travel nearly the same distance to the detector, and the scattering angle is well known. In DWS, however, photon path lengths are typically distributed over several centimeters. The detected photons have scattered many times, through all possibl ...
Nonlinear matter wave optics
... matter wave solitons can be observed if the nonlinear dynamics compensates the linear dispersion of matter waves. Nonlinearity is given by the interaction between the particles in a Bose-Einstein condensate, the dispersion acts on every material particle even in vacuum. These effects are shown in tw ...
... matter wave solitons can be observed if the nonlinear dynamics compensates the linear dispersion of matter waves. Nonlinearity is given by the interaction between the particles in a Bose-Einstein condensate, the dispersion acts on every material particle even in vacuum. These effects are shown in tw ...
Strongly Interacting Fermi Gases
... of the ground state of three Fermions in a harmonic trap with frequency ω precisely at infinite scattering length, which has l = 1. For a detailed discussion of these connections, see Nishida and Son (2012). The issue of inelastic collisions has an additional aspect, which is is crucial for the eve ...
... of the ground state of three Fermions in a harmonic trap with frequency ω precisely at infinite scattering length, which has l = 1. For a detailed discussion of these connections, see Nishida and Son (2012). The issue of inelastic collisions has an additional aspect, which is is crucial for the eve ...
Optical resonances in electrically charged particles
... optical signatures of the electrically charged particles differ from the signatures of neutral particles. Furthermore, we have shown that the parameters such as the surface conductivity or kB T=ℏ work as modulators of the optical response (see e.g. [18,14,11]; and also [4,22]). It is only in the las ...
... optical signatures of the electrically charged particles differ from the signatures of neutral particles. Furthermore, we have shown that the parameters such as the surface conductivity or kB T=ℏ work as modulators of the optical response (see e.g. [18,14,11]; and also [4,22]). It is only in the las ...
Why is the propagation velocity of a photon in a... reduced?
... understand, in terms of scattering and nothing but scattering, the propagation of a photon through a medium of variable refraction index... How many wonderful aspects of physics came together (in this enterprise): ...refractive index as a cumulative consequence of many individual scattering processe ...
... understand, in terms of scattering and nothing but scattering, the propagation of a photon through a medium of variable refraction index... How many wonderful aspects of physics came together (in this enterprise): ...refractive index as a cumulative consequence of many individual scattering processe ...
Reflection of X-rays with change of frequency
... pulsations of optical density in the crystal should not be of identical phase throughout, but should appear as stratifications having the appropriate wavelength and inclination to the incident light-waves and thus satisfying the condition for a coherent reflection. In our present case, the spacing o ...
... pulsations of optical density in the crystal should not be of identical phase throughout, but should appear as stratifications having the appropriate wavelength and inclination to the incident light-waves and thus satisfying the condition for a coherent reflection. In our present case, the spacing o ...
Cross section (physics)
The cross section is an effective area that quantifies the intrinsic likelihood of a scattering event when an incident beam strikes a target object, made of discrete particles. The cross section of a particle is the same as the cross section of a hard object, if the probabilities of hitting them with a ray are the same. It is typically denoted σ and measured in units of area.In scattering experiments, one is often interested in knowing how likely a given event occurs. However, the rate depends strongly on experimental variables such as the density of the target material, the intensity of the beam, or the area of overlap between the beam and the target material. To control for these mundane differences, one can factor out these variables, resulting in an area-like quantity known as the cross section.

















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852311_1-a80c01e7dd06bde7495e825ae8833165-300x300.png)




