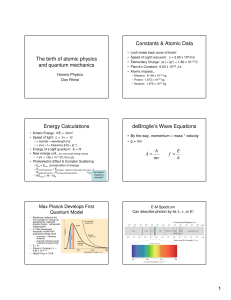
1. dia
... difference can be emitted as a photon. This may give a line in the visible spectrum. In the presence of an external magnetic field, these different states will have different energies due to having different orientations of the magnetic dipoles in the external field, so the atomic energy levels are ...
... difference can be emitted as a photon. This may give a line in the visible spectrum. In the presence of an external magnetic field, these different states will have different energies due to having different orientations of the magnetic dipoles in the external field, so the atomic energy levels are ...
763620S STATISTICAL PHYSICS Solution Set 8 Autumn
... (b) Black hole radiates like an (almost) perfect black body (why?). Calculate the radiation power P and the timescale associated with the loss of mass, τ = E/P . (c) Calculate the temperature T and lifetime τ in years for a black hole of mass 1012 kg. (d) Currently the Universe is filled with radiat ...
... (b) Black hole radiates like an (almost) perfect black body (why?). Calculate the radiation power P and the timescale associated with the loss of mass, τ = E/P . (c) Calculate the temperature T and lifetime τ in years for a black hole of mass 1012 kg. (d) Currently the Universe is filled with radiat ...
Discrete-continuous and classical-quantum
... applying: the quantum theory of Bohr (selection of discretness into continuum), the Heisenberg/Schrödinger quantum mechanics (differential equation against matrix theory), the return of Bohr conditions in constructing quantum solutions in the classical limit, and finally the trace formula where the ...
... applying: the quantum theory of Bohr (selection of discretness into continuum), the Heisenberg/Schrödinger quantum mechanics (differential equation against matrix theory), the return of Bohr conditions in constructing quantum solutions in the classical limit, and finally the trace formula where the ...
15-7 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... running backwards – what is it that gives it away? Both momentum and energy are conserved in the explosion, whether you view it forwards or backwards. What gives it away that you are viewing the film backwards is that the process of the million pieces coming together to form the spacecraft decreases ...
... running backwards – what is it that gives it away? Both momentum and energy are conserved in the explosion, whether you view it forwards or backwards. What gives it away that you are viewing the film backwards is that the process of the million pieces coming together to form the spacecraft decreases ...
Outline for Physics 2140 Exam 1
... field at a given point, or the force on a charge. • Identify the charge (sign and relative magnitude) of a source, given the field lines. • Identify the net charge on a collection of charges ...
... field at a given point, or the force on a charge. • Identify the charge (sign and relative magnitude) of a source, given the field lines. • Identify the net charge on a collection of charges ...
Single Photon Polarization
... • The Phase Modulators is sensitive to polarization. Solution: Plug and Play system? • The detection efficiency for the telecom wavelength photon is too low. ...
... • The Phase Modulators is sensitive to polarization. Solution: Plug and Play system? • The detection efficiency for the telecom wavelength photon is too low. ...
Byond Particle Physics
... The history of supersymmetry is exceptional. In the past, virtually all major conceptual breakthroughs have occurred because physicists were trying to understand some established aspect of nature. In contrast, the discovery of supersymmetry in the early 1970s was a purely intellectual achievement, d ...
... The history of supersymmetry is exceptional. In the past, virtually all major conceptual breakthroughs have occurred because physicists were trying to understand some established aspect of nature. In contrast, the discovery of supersymmetry in the early 1970s was a purely intellectual achievement, d ...
Measurement Problem - The Information Philosopher
... The radical treatments of macroscopic systems, by Schrödinger and Einstein and his colleagues, were intended to expose inconsistencies and incompleteness in quantum theory. The critics hoped to restore determinism and “local reality” to physics. They resulted in some strange and extremely popular “m ...
... The radical treatments of macroscopic systems, by Schrödinger and Einstein and his colleagues, were intended to expose inconsistencies and incompleteness in quantum theory. The critics hoped to restore determinism and “local reality” to physics. They resulted in some strange and extremely popular “m ...
Mechanics & Molecular Kinetic Theory
... • 6.02x1023 particles in 1 mole • e.g. 1 mole of He has a mass of 4 grams 1 mole of O2 has a mass of 32 grams Mass (g) = number of moles x molar mass ...
... • 6.02x1023 particles in 1 mole • e.g. 1 mole of He has a mass of 4 grams 1 mole of O2 has a mass of 32 grams Mass (g) = number of moles x molar mass ...
Syllabus - Department of Electrical Engineering
... lamp: The students will record the wavelengths of the Balmer lines of hydrogen. The measured values will be compared to the calculated wavelengths using the Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom. b) Sodium lamp: The students will record the yellow D-line from sodium and resolve its two components that are a ...
... lamp: The students will record the wavelengths of the Balmer lines of hydrogen. The measured values will be compared to the calculated wavelengths using the Bohr’s model of hydrogen atom. b) Sodium lamp: The students will record the yellow D-line from sodium and resolve its two components that are a ...
Abstract
... electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) [3], which is a technique for turning an opaque medium for a weak probe light into a transparent one with the help of an additional control light. There is a steep dispersion within the transparency window, so that the speed of the probe light pulse is ...
... electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) [3], which is a technique for turning an opaque medium for a weak probe light into a transparent one with the help of an additional control light. There is a steep dispersion within the transparency window, so that the speed of the probe light pulse is ...
primer notes
... time. That means that a particle prepared in a state of definite energy will stay in that energy if there are no perturbations. Its wavefunction does evolve as exp ( iEt/~), but this evolution is ‘unitary’ since its absolute value is unity. Notice the analogy with Newton’s first law, which states th ...
... time. That means that a particle prepared in a state of definite energy will stay in that energy if there are no perturbations. Its wavefunction does evolve as exp ( iEt/~), but this evolution is ‘unitary’ since its absolute value is unity. Notice the analogy with Newton’s first law, which states th ...
Chapter 3 The Statistical Theory of Thermodynamics 3.1 Macrostate
... (a) the microcanonical ensemble pertains to isolated systems (i.e., at fixed E, V, N); the copies in the ensemble are also isolated from each other (i.e., a single isolated system). The key state function is entropy S(E, V, N). (b) the canonical ensemble pertains to systems in contact with a heat ba ...
... (a) the microcanonical ensemble pertains to isolated systems (i.e., at fixed E, V, N); the copies in the ensemble are also isolated from each other (i.e., a single isolated system). The key state function is entropy S(E, V, N). (b) the canonical ensemble pertains to systems in contact with a heat ba ...
Is Classical Statistical Mechanics Self-Consistent? (A paper in honor of C. F. von Weizsäcker, 1912–2007)
... (in)distinguishability of particles that matters, but that of the states (e.g. [18], sects. 1 and 2.1; [19], sect. 4.1). Using Newton’s rather than Laplace’s notion of state, the statistical reasoning in [18, 19] can be physically-dynamically substantiated. It needs, perhaps, a congenial mixing of p ...
... (in)distinguishability of particles that matters, but that of the states (e.g. [18], sects. 1 and 2.1; [19], sect. 4.1). Using Newton’s rather than Laplace’s notion of state, the statistical reasoning in [18, 19] can be physically-dynamically substantiated. It needs, perhaps, a congenial mixing of p ...