Why Life Exists?
... there is in fact a tremendous degree of coherence within all living systems. The accelerating electrons explain not only the Maxwell Equations and the Special Relativity, but the Heisenberg Uncertainty Relation, the Wave-Particle Duality and the electron’s spin also, building the Bridge between the ...
... there is in fact a tremendous degree of coherence within all living systems. The accelerating electrons explain not only the Maxwell Equations and the Special Relativity, but the Heisenberg Uncertainty Relation, the Wave-Particle Duality and the electron’s spin also, building the Bridge between the ...
Variational principle in the conservation operators deduction
... where is the certain constant which value dependent on our choice of this or that unit system only. One can notice that has the velocity dimension. It is easy to show (see the Appendix) that means the velocity of propagation of the studied object in the case of inertial movement. Thus we have ...
... where is the certain constant which value dependent on our choice of this or that unit system only. One can notice that has the velocity dimension. It is easy to show (see the Appendix) that means the velocity of propagation of the studied object in the case of inertial movement. Thus we have ...
Raadsel - MindMeister
... The basic geometric shape is a spiral form that is seen abundantly in nature in seashells and sunflowers. This design is called a toroid and can be seen in its 2 dimensional form on the Merkaba Repatterning cards. The 3 dimensional form looks like a donut and is called a tube torus. This design carr ...
... The basic geometric shape is a spiral form that is seen abundantly in nature in seashells and sunflowers. This design is called a toroid and can be seen in its 2 dimensional form on the Merkaba Repatterning cards. The 3 dimensional form looks like a donut and is called a tube torus. This design carr ...
First law
... Main article: Second law of thermodynamics The entropy of an isolated system consisting of two regions of space, isolated from one another, each in thermodynamic equilibrium in itself, but not in equilibrium with each other, will, when the isolation that separates the two regions is broken, so that ...
... Main article: Second law of thermodynamics The entropy of an isolated system consisting of two regions of space, isolated from one another, each in thermodynamic equilibrium in itself, but not in equilibrium with each other, will, when the isolation that separates the two regions is broken, so that ...
Overview
... canonical distribution and other probabilities based on the maxent principle. We will also develop other distributions that are useful for isolated systems and for systems that exchange particles with the environment (the micro canonical and grand canonical distributions). Basics of classical thermo ...
... canonical distribution and other probabilities based on the maxent principle. We will also develop other distributions that are useful for isolated systems and for systems that exchange particles with the environment (the micro canonical and grand canonical distributions). Basics of classical thermo ...
abstract,
... Join me and enjoy your pizza as I discuss our recent results found on the 1% and 5% Mn doped samples. The naive expectation of local insulating islands around the Mn impurities are not observed, instead several unexpected and exciting ordering phenomena emerge upon doping, including potential nemati ...
... Join me and enjoy your pizza as I discuss our recent results found on the 1% and 5% Mn doped samples. The naive expectation of local insulating islands around the Mn impurities are not observed, instead several unexpected and exciting ordering phenomena emerge upon doping, including potential nemati ...
PH4041 – Atomic, Nuclear, and Particle Physics
... Explain the electronic structure of alkali atoms. Building on time-dependent perturbation theory seen in PH3062 (Quantum Mechanics 2), explain aspects of atom-light interactions such as selection rules in optical transitions. Explain the effect of magnetic interactions on electronic energy lev ...
... Explain the electronic structure of alkali atoms. Building on time-dependent perturbation theory seen in PH3062 (Quantum Mechanics 2), explain aspects of atom-light interactions such as selection rules in optical transitions. Explain the effect of magnetic interactions on electronic energy lev ...
Section 1.1-1.6 Lecture Slides
... Second Law: A particle acted upon by an unbalanced force F experiences an acceleration a that has the same direction as the force and a magnitude that is directly proportional to the force. If F is applied to a particle of mass m, this law may be expressed mathematically as ...
... Second Law: A particle acted upon by an unbalanced force F experiences an acceleration a that has the same direction as the force and a magnitude that is directly proportional to the force. If F is applied to a particle of mass m, this law may be expressed mathematically as ...
PerturbationTheory
... Because of spin (2 possible orientations of each nucleon) any energy level n,ℓ accommodates 2ℓ+1 protons 2ℓ+1 neutrons ...
... Because of spin (2 possible orientations of each nucleon) any energy level n,ℓ accommodates 2ℓ+1 protons 2ℓ+1 neutrons ...
Homework
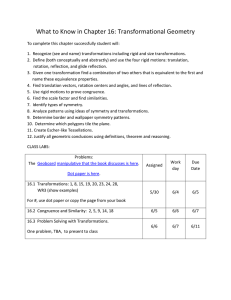
... 3. Given one transformation find a combination of two others that is equivalent to the first and name these equivalence properties. 4. Find translation vectors, rotation centers and angles, and lines of reflection. 5. Use rigid motions to prove congruence. 6. Find the scale factor and find similarit ...
... 3. Given one transformation find a combination of two others that is equivalent to the first and name these equivalence properties. 4. Find translation vectors, rotation centers and angles, and lines of reflection. 5. Use rigid motions to prove congruence. 6. Find the scale factor and find similarit ...
algebraic quantization and t
... charged particle moving in the field of a monopole is not that it moves in the field of a monopole, but that the location of the monopole (taken to be the origin) is excluded from its configuration space. To derive relevant aspects of the quantum mechanics of such a particle, we will therefore only ...
... charged particle moving in the field of a monopole is not that it moves in the field of a monopole, but that the location of the monopole (taken to be the origin) is excluded from its configuration space. To derive relevant aspects of the quantum mechanics of such a particle, we will therefore only ...
Confusions and questions about the information paradox 1 September 17, 2009
... There is no problem for an observer sitting at infinity, because in his Schwarzschild coordinates he sees an infinite temperature at the horizon, which will cause all infalling matter to burn up and radiate its information out. It is not all all clear how to complete such an argument. The Schwarzsch ...
... There is no problem for an observer sitting at infinity, because in his Schwarzschild coordinates he sees an infinite temperature at the horizon, which will cause all infalling matter to burn up and radiate its information out. It is not all all clear how to complete such an argument. The Schwarzsch ...
Problem Set 5 - 2004
... You should read Chapter 5 of Thermal Physics by C.B.P. Finn, if you have not already. (1) For each of the following processes, state whether the entropy is increasing, decreasing or staying the same. (i) A piston filled with an ideal gas is surrounded by very good thermal insulation. It is compresse ...
... You should read Chapter 5 of Thermal Physics by C.B.P. Finn, if you have not already. (1) For each of the following processes, state whether the entropy is increasing, decreasing or staying the same. (i) A piston filled with an ideal gas is surrounded by very good thermal insulation. It is compresse ...
ppt - ICTS
... function F that is meant to quantify the ability of the reference frame to perform a particular task. The quality measure should not be biased such that it favors a quantum reference frame that is pointed in any particular direction relative to some external frame. All directions must be equally v ...
... function F that is meant to quantify the ability of the reference frame to perform a particular task. The quality measure should not be biased such that it favors a quantum reference frame that is pointed in any particular direction relative to some external frame. All directions must be equally v ...