Topic 2 The first law of thermodynamics
... If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. If A and C are each in thermal equilibrium with B, A is also in equilibrium with C. Temperature as a quality of heat, by Galileo and Newton The temperatures are equal for all systems ...
... If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. If A and C are each in thermal equilibrium with B, A is also in equilibrium with C. Temperature as a quality of heat, by Galileo and Newton The temperatures are equal for all systems ...
01. State of Physics - University of Central Florida
... We live in a Newtonian world, in an Einsteinian universe, where quantum effects are critically important and yet gravity, the weakest of all known forces, governs the ultimate fate of all that there is. We also live in a world in which science and technology are integral parts of our everyday lives. ...
... We live in a Newtonian world, in an Einsteinian universe, where quantum effects are critically important and yet gravity, the weakest of all known forces, governs the ultimate fate of all that there is. We also live in a world in which science and technology are integral parts of our everyday lives. ...
Full text in PDF form
... towards a more complete theory of quantum gravity [1]. In this framework the most important result is the thermal evaporation of black holes, whose temperature T is related to surface gravity κ by the relation κ ∼ T ∼ (GM )−1 , where M is the mass of the black hole [2]. Such a result has been obtain ...
... towards a more complete theory of quantum gravity [1]. In this framework the most important result is the thermal evaporation of black holes, whose temperature T is related to surface gravity κ by the relation κ ∼ T ∼ (GM )−1 , where M is the mass of the black hole [2]. Such a result has been obtain ...
chapter 7: atomic structure and periodicity
... Wave model of light cannot explain 1) The emission of light from hot object 2) Photoelectric effect – the emission of electrons from metal surfaces when light strikes it. Max Planck theorized that energy can either be released or absorbed by atoms in discrete “packets” of some minimum size (a quantu ...
... Wave model of light cannot explain 1) The emission of light from hot object 2) Photoelectric effect – the emission of electrons from metal surfaces when light strikes it. Max Planck theorized that energy can either be released or absorbed by atoms in discrete “packets” of some minimum size (a quantu ...
FORCE Matter
... us that “electrons repel because of the exchange of particles of light called photons” ...
... us that “electrons repel because of the exchange of particles of light called photons” ...
LOSS OF COHERENCE IN GATE-CONTROLLED QUBIT SYSTEMS
... ultrafast and very efficient counting capabilities of both visible-light and infrared photons. Superconducting single-photon detectors (SSPDs) are quantum photon counters. Their detection mechanism is based on photon-induced generation of a picosecond voltage transient across a nanostructured, 1010 ...
... ultrafast and very efficient counting capabilities of both visible-light and infrared photons. Superconducting single-photon detectors (SSPDs) are quantum photon counters. Their detection mechanism is based on photon-induced generation of a picosecond voltage transient across a nanostructured, 1010 ...
15. Crafting the Quantum.IV
... • Electron states in an atom are uniquely characterized by 4 quantum numbers: principle n, azimuthal k, and two magnetic numbers m1, m2. • These states obey an "Exclusion Principle": "There can never be two or more equivalent electrons in an atom for which, in strong fields, the values of all quantu ...
... • Electron states in an atom are uniquely characterized by 4 quantum numbers: principle n, azimuthal k, and two magnetic numbers m1, m2. • These states obey an "Exclusion Principle": "There can never be two or more equivalent electrons in an atom for which, in strong fields, the values of all quantu ...
Numerical Methods in Quantum Field Theories
... LDirac = ψ̄(iγ µ ∂µ − m)ψ This field describes a spin 1/2 particle and its corresponding antiparticle. A solution to the Dirac Field equation is automatically a solution to the Klein-Gordon equation, but not vice versa. These two fields give us the foundational tools to describe the interactions of ...
... LDirac = ψ̄(iγ µ ∂µ − m)ψ This field describes a spin 1/2 particle and its corresponding antiparticle. A solution to the Dirac Field equation is automatically a solution to the Klein-Gordon equation, but not vice versa. These two fields give us the foundational tools to describe the interactions of ...
Quantum computing
... based on NMR (Oxford; IBM, MIT, Stanford) 2000: quantum computer on 7 qubits, based on NMR ...
... based on NMR (Oxford; IBM, MIT, Stanford) 2000: quantum computer on 7 qubits, based on NMR ...
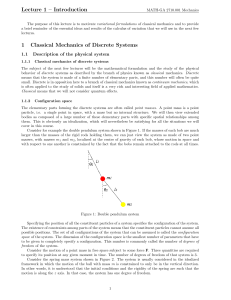
Lecture 1 – Introduction 1 Classical Mechanics of Discrete Systems
... coordinates, and to keep in mind, while setting up the equations describing the system, that there are constraints on the system that limit the possible configurations, since the masses m1 and m2 are not allowed to move independently from each other. With such an approach, the number of generalized ...
... coordinates, and to keep in mind, while setting up the equations describing the system, that there are constraints on the system that limit the possible configurations, since the masses m1 and m2 are not allowed to move independently from each other. With such an approach, the number of generalized ...
Quantum Mechanical Foundations of Causal Entropic Forces
... Theory of causal entropic forces is based on the idea of maximizing causal path entropy by evaluating path probabilities upto a finite time horizon τ instead of greedily maximizing instantaneous entropy production [1]. However, adhering to classical thermodynamics, one cannot fully explain the origi ...
... Theory of causal entropic forces is based on the idea of maximizing causal path entropy by evaluating path probabilities upto a finite time horizon τ instead of greedily maximizing instantaneous entropy production [1]. However, adhering to classical thermodynamics, one cannot fully explain the origi ...
Lesson 2 - The Bohr and Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... Bohr's model explains well: • how electrons occupy energy levels • maximum number of electrons at each level ...
... Bohr's model explains well: • how electrons occupy energy levels • maximum number of electrons at each level ...
Document
... of conservative forces that do not depend on time t explicitly. In this case there exists the energy integral H = T U = ε where U ( q1 , ..., qn ) is potential energy, q1 ,...,qk are coordinates, p1 ,..., pk are momenta, and 2T = aij pi p j the kinetic energy of the system. i, j The complete integ ...
... of conservative forces that do not depend on time t explicitly. In this case there exists the energy integral H = T U = ε where U ( q1 , ..., qn ) is potential energy, q1 ,...,qk are coordinates, p1 ,..., pk are momenta, and 2T = aij pi p j the kinetic energy of the system. i, j The complete integ ...
Epistemology_and_QM_v1
... status of the wavefunction in terms of an intermediate state whose properties cannot be adequately determined by measurement, remains ambiguous. The limitations imposed by the uncertainty principle require a probabilistic treatment, divorced from direct measurement except in terms of the initial st ...
... status of the wavefunction in terms of an intermediate state whose properties cannot be adequately determined by measurement, remains ambiguous. The limitations imposed by the uncertainty principle require a probabilistic treatment, divorced from direct measurement except in terms of the initial st ...