Definition of the spin current: The angular spin current and its
... of the spin in the y direction and the angular velocity −z direction. 共3兲 From the linear spin current density js共r , t兲, one can calculate 共or say how much兲 the linear spin current ជIs flowing through a surface S 关see Fig. 2共d兲兴: ជIsS = 兰兰SdSជ · js. However, the behavior for the angular spin curr ...
... of the spin in the y direction and the angular velocity −z direction. 共3兲 From the linear spin current density js共r , t兲, one can calculate 共or say how much兲 the linear spin current ជIs flowing through a surface S 关see Fig. 2共d兲兴: ជIsS = 兰兰SdSជ · js. However, the behavior for the angular spin curr ...
Module P10.4 The Schrödinger equation
... also assumed that you are acquainted with the de Broglie hypothesis (λ dB = h/p), the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Planck–Einstein formula (E = hf1). In addition you must be familiar with the basic ideas of classical mechanics, in particular conservation of energy and the potential energ ...
... also assumed that you are acquainted with the de Broglie hypothesis (λ dB = h/p), the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and the Planck–Einstein formula (E = hf1). In addition you must be familiar with the basic ideas of classical mechanics, in particular conservation of energy and the potential energ ...
Chapter 11
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
Chapter 11 PPT
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
611: Electromagnetic Theory II
... The Lorentz transformations (1.26) are what are called the pure boosts. It is easy to check that they have the property of preserving the spherical light-front condition, in the sense that points on the expanding spherical shell given by r 2 = t2 of a light-pulse emitted at the origin at t = 0 in th ...
... The Lorentz transformations (1.26) are what are called the pure boosts. It is easy to check that they have the property of preserving the spherical light-front condition, in the sense that points on the expanding spherical shell given by r 2 = t2 of a light-pulse emitted at the origin at t = 0 in th ...
Quantum State Engineering and Information Processing with
... By coupling the ion’s motional and electronic degrees of freeedom, we can engineer entanglement between these systems. This allows us to study quantum mechanics, with all its pecularities, in a well-controlled environment. For example, we can study the interactions of superposition states with the i ...
... By coupling the ion’s motional and electronic degrees of freeedom, we can engineer entanglement between these systems. This allows us to study quantum mechanics, with all its pecularities, in a well-controlled environment. For example, we can study the interactions of superposition states with the i ...
Electronic structure of quantum dots
... metal cluster can be described in a simple model that assumes that the delocalized valence electrons experience a homogeneous positively charged background (‘‘jellium’’) of the atom ions. This approach has long been used in solid-state physics to describe, for example, metal surfaces (Lang and Kohn, ...
... metal cluster can be described in a simple model that assumes that the delocalized valence electrons experience a homogeneous positively charged background (‘‘jellium’’) of the atom ions. This approach has long been used in solid-state physics to describe, for example, metal surfaces (Lang and Kohn, ...
Elements of the wave-particle duality of light
... The famous double-slit experiment, different versions of which we will come back to in the course of the thesis, serves as the canonical illustration of the wave-particle duality. Let us here present its simplified description: A light beam emerges from a source, propagates through two very small sl ...
... The famous double-slit experiment, different versions of which we will come back to in the course of the thesis, serves as the canonical illustration of the wave-particle duality. Let us here present its simplified description: A light beam emerges from a source, propagates through two very small sl ...
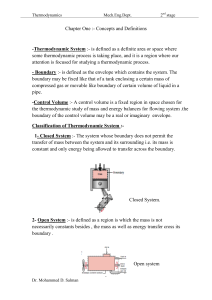
Chapter One :- Concepts and Definitions
... 1-Extensive Property :- The properties of a system whose value for the entire system is equal to the sum of their value for the individual parts of the system , these properties are related to the mass of the system. Like (volume, mass, all kinds of energy ). 2- Intensive Property :- the properties ...
... 1-Extensive Property :- The properties of a system whose value for the entire system is equal to the sum of their value for the individual parts of the system , these properties are related to the mass of the system. Like (volume, mass, all kinds of energy ). 2- Intensive Property :- the properties ...
AP Physics 1 Course Planning and Pacing Guide
... In pairs, students develop a way to predict where two battery-powered cars will collide if they are released from opposite ends of the lab table at different times. Students collect data and then make and test their predictions. In their lab journals, students include multiple representations of the ...
... In pairs, students develop a way to predict where two battery-powered cars will collide if they are released from opposite ends of the lab table at different times. Students collect data and then make and test their predictions. In their lab journals, students include multiple representations of the ...