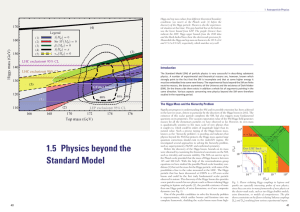
1.5 physics beyond the Standard Model
... These symmetries can be promoted to gauge symmetries that are spontaneously broken. Theoretical inconsistencies – so-called anomalies – that might arise in this case, can be resolved if leptoquarks, i. e., fields that carry both B and L, are introduced. A specific model of this type, consistent with ...
... These symmetries can be promoted to gauge symmetries that are spontaneously broken. Theoretical inconsistencies – so-called anomalies – that might arise in this case, can be resolved if leptoquarks, i. e., fields that carry both B and L, are introduced. A specific model of this type, consistent with ...
Are Quantum Objects Propensitons
... of what sort of entities electrons and atoms can be in view of their apparently contradictory particle and wave properties. It also fails to answer the other childishly elementary question: Is the quantum domain deterministic or probabilistic? The basic dynamic equation of OQT, Schrödinger’s time-de ...
... of what sort of entities electrons and atoms can be in view of their apparently contradictory particle and wave properties. It also fails to answer the other childishly elementary question: Is the quantum domain deterministic or probabilistic? The basic dynamic equation of OQT, Schrödinger’s time-de ...
Quantum Disentanglement Eraser
... Scattered photons γ and γ result from a → b transition. Decay of atoms from b′→ c results in Φ photon emission Elliptical cavities reflect Φ photons onto a common photodetector. Electrooptic shutter transmits Φ photons only when switch is open. Choice of switch position determines whether we emphasi ...
... Scattered photons γ and γ result from a → b transition. Decay of atoms from b′→ c results in Φ photon emission Elliptical cavities reflect Φ photons onto a common photodetector. Electrooptic shutter transmits Φ photons only when switch is open. Choice of switch position determines whether we emphasi ...
Quantum numbers for relative ground states of antiferromagnetic
... As mentioned above these quantum numbers are different unless N divides 2a + 1. Relative ground states can be chosen to be eigenstates ~ 2 . As we are going to show, the k-rule helps to underof S ...
... As mentioned above these quantum numbers are different unless N divides 2a + 1. Relative ground states can be chosen to be eigenstates ~ 2 . As we are going to show, the k-rule helps to underof S ...
Short-Lived Resonance States
... terms of energy changes arising from four basic types of physical force. All atomic and nuclear interactions can be described in terms of electromagnetic, strong and weak interactions or forces. Strong interactions involve particles of high energy whereas lepton decay processes are the result of wea ...
... terms of energy changes arising from four basic types of physical force. All atomic and nuclear interactions can be described in terms of electromagnetic, strong and weak interactions or forces. Strong interactions involve particles of high energy whereas lepton decay processes are the result of wea ...
Black Hole Entropy and Attractors
... (0) Zeroth Law: In thermal physics, the zeroth law states that the temperature T of body at thermal equilibrium is constant throughout the body. Otherwise heat will flow from hot spots to the cold spots. Correspondingly for black holes one can show that surface gravity κ is constant on the event hor ...
... (0) Zeroth Law: In thermal physics, the zeroth law states that the temperature T of body at thermal equilibrium is constant throughout the body. Otherwise heat will flow from hot spots to the cold spots. Correspondingly for black holes one can show that surface gravity κ is constant on the event hor ...
Miami-Dade College
... o. Calculating the ratio of components of a buffer, given the pH of the buffer. p. Calculating the pH of a buffer, when strong acids or bases are added. q. Predicting whether an aqueous salt solution is acidic, basic, or neutral. r. Illustrating the ionization of a soluble salt solution and subseque ...
... o. Calculating the ratio of components of a buffer, given the pH of the buffer. p. Calculating the pH of a buffer, when strong acids or bases are added. q. Predicting whether an aqueous salt solution is acidic, basic, or neutral. r. Illustrating the ionization of a soluble salt solution and subseque ...
Quantum Theory of Hydrogen
... Section 6.7 contains much of the “testable” material of chapter 6. The earlier sections are important (especially quantum numbers and angular momentum) but many of the problems come from 6.7, so be sure to study it well. Important ideas (quantum mechanics works very well for describing the hydrogen ...
... Section 6.7 contains much of the “testable” material of chapter 6. The earlier sections are important (especially quantum numbers and angular momentum) but many of the problems come from 6.7, so be sure to study it well. Important ideas (quantum mechanics works very well for describing the hydrogen ...
Chapter 31 Atomic Physics
... corresponding energy. Such integer number is called a quantum number. Quantum mechanics describes the hydrogen atom in terms of four quantum numbers: (1) the principal quantum number n, which can have the integer values n = 1, 2, 3, ...; (2) the orbital quantum number l, which can have values l = 0, ...
... corresponding energy. Such integer number is called a quantum number. Quantum mechanics describes the hydrogen atom in terms of four quantum numbers: (1) the principal quantum number n, which can have the integer values n = 1, 2, 3, ...; (2) the orbital quantum number l, which can have values l = 0, ...
P1710_MWF09
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: (1) Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and only if there is a net external force. (2) a = F/m [Note this is a vector eqn.] (3) The force exerted by a first object on a second is always equal and opposite the the force exerted by the second on the first. F12 = ...
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: (1) Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and only if there is a net external force. (2) a = F/m [Note this is a vector eqn.] (3) The force exerted by a first object on a second is always equal and opposite the the force exerted by the second on the first. F12 = ...
File
... 2) What is the type of light that we can see called? 3) Visible light is found on the _________ spectrum. 4) A particle of light that has zero mass and a quantum of energy is called a ________. 5) The distance between two peaks is called_____ 6) Name the model of an atom that said electrons circle a ...
... 2) What is the type of light that we can see called? 3) Visible light is found on the _________ spectrum. 4) A particle of light that has zero mass and a quantum of energy is called a ________. 5) The distance between two peaks is called_____ 6) Name the model of an atom that said electrons circle a ...
Astrophysics and Creation: Perceiving the Universe Through
... propose a convergence of physics and mysticism into a virtual identity (Talbot 1980). However, quantum mechanics is a mechanical description of the temporal evolution of a system’s physical parameters. It uses rigid mathematics. Quantum uncertainty rules in every atom and molecule of our brain, but ...
... propose a convergence of physics and mysticism into a virtual identity (Talbot 1980). However, quantum mechanics is a mechanical description of the temporal evolution of a system’s physical parameters. It uses rigid mathematics. Quantum uncertainty rules in every atom and molecule of our brain, but ...
m H - Indico
... • The “EW charge density” gives a contribution to the energy density of the universe 1056 times too large. (Part of an even bigger problem). Has gravity anything to do with EW breaking? • The puzzle of the hierarchy problem ...
... • The “EW charge density” gives a contribution to the energy density of the universe 1056 times too large. (Part of an even bigger problem). Has gravity anything to do with EW breaking? • The puzzle of the hierarchy problem ...
Matrix Product States and Tensor Network States
... with integer and half-integer spin at edge → inequivalent phases! ...
... with integer and half-integer spin at edge → inequivalent phases! ...