INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE EDUCATION AND RESEARCH
... Sociality (altruism, cooperation, kin selection, reciprocal altruism, etc.); Optimal foraging theory; Mating systems, Parental care. F. Conservation Biology: Taxonomy and Systematics; Measuring diversity; Global change; Biodiversity of India. In-situ and ex-situ conservation, Invasive Species, Islan ...
... Sociality (altruism, cooperation, kin selection, reciprocal altruism, etc.); Optimal foraging theory; Mating systems, Parental care. F. Conservation Biology: Taxonomy and Systematics; Measuring diversity; Global change; Biodiversity of India. In-situ and ex-situ conservation, Invasive Species, Islan ...
Dielectric Polarization
... To see the connection between the dielectric constant and the polarization we perform an experiment. We charge up the capacitor in vacuum. The field is E0 = σ/ε0. Then we add an insulating medium with dielectric constant εr leaving the charges constant. Now the field is E = σ/ε = σ/εrε0. The field i ...
... To see the connection between the dielectric constant and the polarization we perform an experiment. We charge up the capacitor in vacuum. The field is E0 = σ/ε0. Then we add an insulating medium with dielectric constant εr leaving the charges constant. Now the field is E = σ/ε = σ/εrε0. The field i ...
Silicon-based Quantum Computation
... donor electron spin state is determined. There are different schemes to determine the electron spin, including charge-based or spin-dependent transport based. The former is accomplished by exploiting the difference in symmetry of the orbital wavefunction of an exchange-coupled two-electron system [6 ...
... donor electron spin state is determined. There are different schemes to determine the electron spin, including charge-based or spin-dependent transport based. The former is accomplished by exploiting the difference in symmetry of the orbital wavefunction of an exchange-coupled two-electron system [6 ...
Quantum Algorithms for Estimating Gauss Sums and Calculating
... of this ‘chi state’ should be viewed as a form of preprocessing because the state does not get destroyed during the computation (see Section 3). The Gauss sum estimation algorithm over finite fields can be used to estimate Jacobi sums and Gauss sums over finite rings Z/nZ. This is done in Section 7. ...
... of this ‘chi state’ should be viewed as a form of preprocessing because the state does not get destroyed during the computation (see Section 3). The Gauss sum estimation algorithm over finite fields can be used to estimate Jacobi sums and Gauss sums over finite rings Z/nZ. This is done in Section 7. ...
Identifying student and teacher difficulties in interpreting
... corresponding electronic transitions between stationary orbits with well-defined energy. These students explained that the emission or absorption of radiation occurs when the electron moves from one state to another, and they established a relationship of proportionality between the radiation freque ...
... corresponding electronic transitions between stationary orbits with well-defined energy. These students explained that the emission or absorption of radiation occurs when the electron moves from one state to another, and they established a relationship of proportionality between the radiation freque ...
Outline Introduction Introduction Gibbs Free Energy
... G = H – TS Equilibrium is a tradeoff between enthalpy and entropy • A change to a lower enthalpy state (H < 0, exothermic) usually decreases the randomness (S < 0). (e.g. solidification and oxidation) • A change to a higher entropy state (S > 0) usually increases the enthalpy (H > 0, endothermic). ( ...
... G = H – TS Equilibrium is a tradeoff between enthalpy and entropy • A change to a lower enthalpy state (H < 0, exothermic) usually decreases the randomness (S < 0). (e.g. solidification and oxidation) • A change to a higher entropy state (S > 0) usually increases the enthalpy (H > 0, endothermic). ( ...
Maximal Newton polygons via the quantum Bruhat graph
... F -crystals are indexed by combinatorial objects called Newton polygons, a family of lattice polygons in the plane. Kottwitz used the theory of algebraic groups to explicitly study the set of Newton polygons associated to any connected reductive group G over a discretely valued field. In particular, ...
... F -crystals are indexed by combinatorial objects called Newton polygons, a family of lattice polygons in the plane. Kottwitz used the theory of algebraic groups to explicitly study the set of Newton polygons associated to any connected reductive group G over a discretely valued field. In particular, ...
File
... double the momentum) b) p = 60 000 units (tripling the velocity will triple the momentum) c) p = 40 000 units (doubling the mass will double the momentum) d) p = 80 000 units (doubling the velocity will double the momentum and doubling the mass will also double the momentum; the combined result is t ...
... double the momentum) b) p = 60 000 units (tripling the velocity will triple the momentum) c) p = 40 000 units (doubling the mass will double the momentum) d) p = 80 000 units (doubling the velocity will double the momentum and doubling the mass will also double the momentum; the combined result is t ...
Q1. As shown In Figure 1 four particles form a square of side length
... Determine the angle between the electric field E at point P and the positive x axis. The coordinates of the point P are x=1.00 m and y=2.00 m. A) B) C) D) E) ...
... Determine the angle between the electric field E at point P and the positive x axis. The coordinates of the point P are x=1.00 m and y=2.00 m. A) B) C) D) E) ...
Extra Dimensions, no kidding
... Van-der-Waals and Casimir forces which are well known to scientists for quite some time As far as experiment is concerned these extra dimensions are there and experimentalists cannot wait to measure them. The paradigm of extra dimensions does much more that excite our imagination. It solves the so c ...
... Van-der-Waals and Casimir forces which are well known to scientists for quite some time As far as experiment is concerned these extra dimensions are there and experimentalists cannot wait to measure them. The paradigm of extra dimensions does much more that excite our imagination. It solves the so c ...
Physics 2220 - University of Utah
... Electrostatic equilibrium in a conductor: The net motion of charges within the conductor is zero. Properties of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium: E = 0 inside the conductor (hollow or solid). Charged conductors: Charge is on the surface. Just outside the surface of the conductor: ...
... Electrostatic equilibrium in a conductor: The net motion of charges within the conductor is zero. Properties of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium: E = 0 inside the conductor (hollow or solid). Charged conductors: Charge is on the surface. Just outside the surface of the conductor: ...
Introduction toElementary Particle Phenomenology
... angular-momentum conservation is rather simple since pions too have spin zero: the total orbital angular momentum of the final state must then also be zero. With zero orbital contribution to the total angular momentum of the system, the overall parity is just the product of the intrinsic parities of ...
... angular-momentum conservation is rather simple since pions too have spin zero: the total orbital angular momentum of the final state must then also be zero. With zero orbital contribution to the total angular momentum of the system, the overall parity is just the product of the intrinsic parities of ...
Counting energy packets in the electromagnetic
... 2. The concept of wave energy packet in the classic approach The synchronous oscillations of the electric and magnetic fields result in periodical oscillations of wave energy density. An observer using an electric antenna and a wire loop to probe these fields detects short time windows when either p ...
... 2. The concept of wave energy packet in the classic approach The synchronous oscillations of the electric and magnetic fields result in periodical oscillations of wave energy density. An observer using an electric antenna and a wire loop to probe these fields detects short time windows when either p ...
Critical flow and dissipation in a quasi–one
... velocity vc via a mechanism that unwinds the phase of the order parameter in quanta of 2p. Such “phase slips,” occurring at rate G, correspond to a process whereby the amplitude of the order parameter is instantaneously suppressed to zero at some point along the channel and can be driven by either t ...
... velocity vc via a mechanism that unwinds the phase of the order parameter in quanta of 2p. Such “phase slips,” occurring at rate G, correspond to a process whereby the amplitude of the order parameter is instantaneously suppressed to zero at some point along the channel and can be driven by either t ...
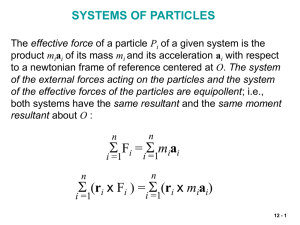
Lec12
... which expresses that the moment resultant about G of the external forces is equal to the rate of change of the angular momentum about G of the system of particles. When no external force acts on a system of particles, the linear momentum L and the angular momentum Ho of the system are conserved. In ...
... which expresses that the moment resultant about G of the external forces is equal to the rate of change of the angular momentum about G of the system of particles. When no external force acts on a system of particles, the linear momentum L and the angular momentum Ho of the system are conserved. In ...