Electric Current
... A total of 20.0C of charge pass a given point in a conductor in 4.0 seconds. Determine the current in the conductor. I = Δq = 20.0C = 5A t 4.0s Conditions Necessary For An Electric Circuit A potential difference between two points. A voltage source for energy supplied by a battery (cell), power co ...
... A total of 20.0C of charge pass a given point in a conductor in 4.0 seconds. Determine the current in the conductor. I = Δq = 20.0C = 5A t 4.0s Conditions Necessary For An Electric Circuit A potential difference between two points. A voltage source for energy supplied by a battery (cell), power co ...
Technical Overview
... provide a broader spectrum and are a marked improvement on SOX lamps. The first mass produced lamp used in lighting schemes was the Mercury Discharge Lamp. Although this type of lamp is not as energy efficient as its sodium based counterparts it does provide better colour rendering properties in the ...
... provide a broader spectrum and are a marked improvement on SOX lamps. The first mass produced lamp used in lighting schemes was the Mercury Discharge Lamp. Although this type of lamp is not as energy efficient as its sodium based counterparts it does provide better colour rendering properties in the ...
Ohm`s Law Practice Problems (part of 1.2.3) The relationship
... developed by Georg Simon Ohm and is known today as Ohm’s law. Ohm’s law states that the direct current flowing in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the circuit. In other words, an electric circuit represents the flow of electrons along a conductive pathway betwee ...
... developed by Georg Simon Ohm and is known today as Ohm’s law. Ohm’s law states that the direct current flowing in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the voltage applied to the circuit. In other words, an electric circuit represents the flow of electrons along a conductive pathway betwee ...
POWER RATING OF RESISTOR Finding a resistor`s power rating
... important, and it’s a topic that’ll come up when selecting a resistor type. Power is the rate at which energy is transformed into something else. It’s calculated by multiplying the voltage difference across two points by the current running between them, and is measured in units of a watt (W). Light ...
... important, and it’s a topic that’ll come up when selecting a resistor type. Power is the rate at which energy is transformed into something else. It’s calculated by multiplying the voltage difference across two points by the current running between them, and is measured in units of a watt (W). Light ...
ExIIrev05ans
... In comparing the power (or brightness) of two light bulbs, you must first be clear whether the current or the voltage is the same for the two. It makes all the difference. If the two bulbs are in series, then the current is the same, and according to P = I2 R , the larger resistance bulb has more po ...
... In comparing the power (or brightness) of two light bulbs, you must first be clear whether the current or the voltage is the same for the two. It makes all the difference. If the two bulbs are in series, then the current is the same, and according to P = I2 R , the larger resistance bulb has more po ...
Rad Tech 110
... The autotransformer works on the principle of self-induction. It has a single core and is responsible for varying the voltage. Because of its ability to adjust voltage, the autotransformer can be either a stepup or step-down transformer. ...
... The autotransformer works on the principle of self-induction. It has a single core and is responsible for varying the voltage. Because of its ability to adjust voltage, the autotransformer can be either a stepup or step-down transformer. ...
Series and Parallel
... • Total resistance goes UP with each resistor since the current has must go through each resistor. • Total Resistance = Sum of all resistors in the series Req = R1+R2+ R3… ...
... • Total resistance goes UP with each resistor since the current has must go through each resistor. • Total Resistance = Sum of all resistors in the series Req = R1+R2+ R3… ...
EE3003-ModelPaper-2013
... (b) A separately excited 230V, 90kW dc generator has a field winding with 1000 turns per pole. To generate rated voltage at rated speed, the field current requirement is 4A on no-load and 5.3A on full load. Calculate the number of turns/pole of a series winding to be fitted in order to convert the m ...
... (b) A separately excited 230V, 90kW dc generator has a field winding with 1000 turns per pole. To generate rated voltage at rated speed, the field current requirement is 4A on no-load and 5.3A on full load. Calculate the number of turns/pole of a series winding to be fitted in order to convert the m ...
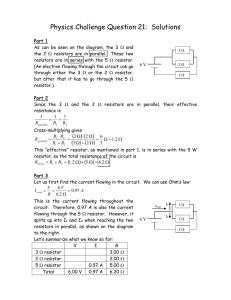
Physics Challenge Question 1: Solutions
... Looking at our table, we can use Ohm’s law to find the potential difference over the 5 resistor: V I R 5.0 0.97 A 4.84 V Since the 5 resistor is in series with the two others, that means the remaining voltage must be over the 3 and the 2 resistors. Notice that since the 3 ...
... Looking at our table, we can use Ohm’s law to find the potential difference over the 5 resistor: V I R 5.0 0.97 A 4.84 V Since the 5 resistor is in series with the two others, that means the remaining voltage must be over the 3 and the 2 resistors. Notice that since the 3 ...
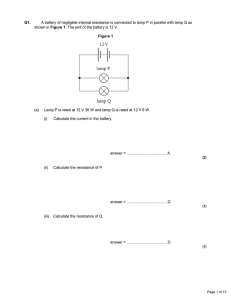
Q1. A battery of negligible internal resistance is connected to lamp P
... the lamps does not change significantly with temperature. ...
... the lamps does not change significantly with temperature. ...
Get Notes - Mindset Learn
... Explain the term internal resistance. Solve circuit problems using ε = Vload + Vinternal resistance and circuit problems, with internal resistance, involving series-parallel networks of resistors. Define power Solve circuit problems involving the concepts of power and electrical energy. Deduce that ...
... Explain the term internal resistance. Solve circuit problems using ε = Vload + Vinternal resistance and circuit problems, with internal resistance, involving series-parallel networks of resistors. Define power Solve circuit problems involving the concepts of power and electrical energy. Deduce that ...
DC-voltage doubler reaches 96% power efficiency
... protective subcircuit, is RL≤m2×(α/(1−α))×Rp, where the multiplication factor m=(VOUT/VIN) and α is a fraction of VOUT, at which the soft start turns off. For m=2, α=0.8, and Rp=10Ω, RL is 160Ω. Thus, loads of 160Ω or less will overload the circuit if you connect them to the circuit’s output before ...
... protective subcircuit, is RL≤m2×(α/(1−α))×Rp, where the multiplication factor m=(VOUT/VIN) and α is a fraction of VOUT, at which the soft start turns off. For m=2, α=0.8, and Rp=10Ω, RL is 160Ω. Thus, loads of 160Ω or less will overload the circuit if you connect them to the circuit’s output before ...
Basic DC Circuits - Ryerson Department of Physics
... Connect the parallel circuit shown below, with a 51 Ω resistor for R1 and a 68 Ω resistor for R2. As in the previous circuit, the Voltage Probe is used to measure the voltage applied to both ...
... Connect the parallel circuit shown below, with a 51 Ω resistor for R1 and a 68 Ω resistor for R2. As in the previous circuit, the Voltage Probe is used to measure the voltage applied to both ...
Electrical ballast

An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's negative resistance characteristic.Ballasts vary in design complexity. They can be as simple as a series resistor or inductor, capacitors, or a combination thereof or as complex as electronic ballasts used with fluorescent lamps and high-intensity discharge lamps.