Parallel Circuit Lab
... segment of Electricity/Electronics. These concepts include, in parallel connected circuits current is additive, voltage drop is the same through-out the circuit, and total resistance is found by adding the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual legs of the circuits. Students will ...
... segment of Electricity/Electronics. These concepts include, in parallel connected circuits current is additive, voltage drop is the same through-out the circuit, and total resistance is found by adding the reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual legs of the circuits. Students will ...
18241 Demonstrate knowledge of basic electronic systems
... Providers must be granted consent to assess against standards (accredited) by NZQA, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQ ...
... Providers must be granted consent to assess against standards (accredited) by NZQA, before they can report credits from assessment against unit standards or deliver courses of study leading to that assessment. Industry Training Organisations must be granted consent to assess against standards by NZQ ...
How do they work?
... Since the phenomenon of mutual induction relies on changing magnetic fields, and direct current (DC) can only produce steady magnetic fields, transformers simply will not work with direct current. Of course, direct current may be interrupted (pulsed) through the primary winding of a transformer to c ...
... Since the phenomenon of mutual induction relies on changing magnetic fields, and direct current (DC) can only produce steady magnetic fields, transformers simply will not work with direct current. Of course, direct current may be interrupted (pulsed) through the primary winding of a transformer to c ...
Spirit 2
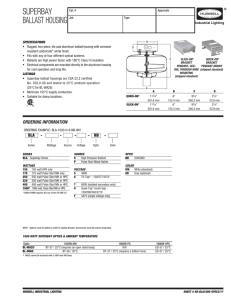
... “V” is the potential difference in volts and “R” the resistance of the material measured in Ohms. Within transformers ideally the ratio of voltage change to the change in the number of turns in the conducting wire is equal: where “V” is voltage, “N” number of turns, “p” for primary, and “s” for seco ...
... “V” is the potential difference in volts and “R” the resistance of the material measured in Ohms. Within transformers ideally the ratio of voltage change to the change in the number of turns in the conducting wire is equal: where “V” is voltage, “N” number of turns, “p” for primary, and “s” for seco ...
Document
... – Flicker is caused by load variations; for example arc welding, electrical smelters and klystron modulators ...
... – Flicker is caused by load variations; for example arc welding, electrical smelters and klystron modulators ...
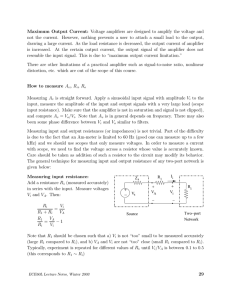
Maximum Output Current: Voltage amplifiers are designed to amplify
... and compute Av = Vo /Vi . Note that Av is in general depends on frequency. There may also been some phase difference between Vi and Vo similar to filters. Measuring input and output resistances (or impedances) is not trivial. Part of the difficulty is due to the fact that an Am-meter is limited to 6 ...
... and compute Av = Vo /Vi . Note that Av is in general depends on frequency. There may also been some phase difference between Vi and Vo similar to filters. Measuring input and output resistances (or impedances) is not trivial. Part of the difficulty is due to the fact that an Am-meter is limited to 6 ...
Identification Of Basic Electronic Components Their Characteristics
... change in voltages. It produces phase difference between voltage applied to it and the current, which passes through it. The current leads the voltage by 90º in the ideal capacitance with infinite resistance across the plates. (Fig. 3) Design of capacitor is connected with relation of the proper ele ...
... change in voltages. It produces phase difference between voltage applied to it and the current, which passes through it. The current leads the voltage by 90º in the ideal capacitance with infinite resistance across the plates. (Fig. 3) Design of capacitor is connected with relation of the proper ele ...
3 Phase Fully Controlled Rectifier
... changing constant ac input voltage to controlled dc output voltage. In phase controlled rectifiers, a thyristor is tuned off as AC supply voltage reverse biases it, provided anode current has fallen to level below the holding current. Controlled rectifiers have a wide range of applications, from sma ...
... changing constant ac input voltage to controlled dc output voltage. In phase controlled rectifiers, a thyristor is tuned off as AC supply voltage reverse biases it, provided anode current has fallen to level below the holding current. Controlled rectifiers have a wide range of applications, from sma ...
Electricity - PawPrints212
... Demonstrate that closed circuits allow current to flow and open circuits do not allow current to flow. Create and compare intensity of light produced by lamps in series and parallel circuits. Observe that a switch can turn a lamp on and off by completing a circuit or creating a short circuit. Se ...
... Demonstrate that closed circuits allow current to flow and open circuits do not allow current to flow. Create and compare intensity of light produced by lamps in series and parallel circuits. Observe that a switch can turn a lamp on and off by completing a circuit or creating a short circuit. Se ...
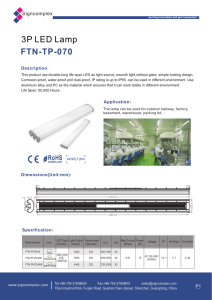
Electrical ballast

An electrical ballast is a device intended to limit the amount of current in an electric circuit. A familiar and widely used example is the inductive ballast used in fluorescent lamps, to limit the current through the tube, which would otherwise rise to destructive levels due to the tube's negative resistance characteristic.Ballasts vary in design complexity. They can be as simple as a series resistor or inductor, capacitors, or a combination thereof or as complex as electronic ballasts used with fluorescent lamps and high-intensity discharge lamps.