Miss Gilchrist Newton High School Honors Geometry Lesson Plans
... To use congruent chords, arc, and central angles To use perpendicular bisectors to chords Homework: None Tuesday, May 17 Objectives: 12.2: Chords and Arcs To use congruent chords, arc, and central angles To use perpendicular bisectors to chords Homework: Page 776 #6-25, 27, 29-34 Wednesday, May 18 O ...
... To use congruent chords, arc, and central angles To use perpendicular bisectors to chords Homework: None Tuesday, May 17 Objectives: 12.2: Chords and Arcs To use congruent chords, arc, and central angles To use perpendicular bisectors to chords Homework: Page 776 #6-25, 27, 29-34 Wednesday, May 18 O ...
Powerpoint - Math Sciences Computing Facility
... crossing line (we did not get to this) Follow up with GeoGebra explorations and explanations – with GeoGebra and drawn figures we were able to see how the result of reflecting first in one line and then in a parallel line was a translation in the perpendicular direction from the first line towards t ...
... crossing line (we did not get to this) Follow up with GeoGebra explorations and explanations – with GeoGebra and drawn figures we were able to see how the result of reflecting first in one line and then in a parallel line was a translation in the perpendicular direction from the first line towards t ...
LSU College Readiness Program COURSE
... 5.5 Indirect Proofs and Inequalities in One Triangle (41) Use indirect reasoning to write proofs Learn the triangle relationship between length of a side and size of its opposite angle Use the triangle inequality theorem 5.6 Inequalities in Two Triangles (21) Use the Hinge Theorem and its converse t ...
... 5.5 Indirect Proofs and Inequalities in One Triangle (41) Use indirect reasoning to write proofs Learn the triangle relationship between length of a side and size of its opposite angle Use the triangle inequality theorem 5.6 Inequalities in Two Triangles (21) Use the Hinge Theorem and its converse t ...
geometry unit 2 workbook
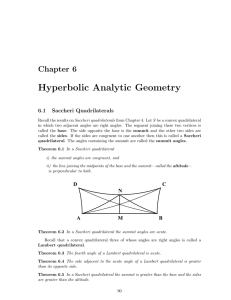
... square given the coordinates of the vertices. Example 1: Quadrilateral JKLM has vertices J(–2, 3), K(1, 4), L(3, –2), and M(0, –3). Determine whether JKLM is a rectangle using the Distance Formula. ...
... square given the coordinates of the vertices. Example 1: Quadrilateral JKLM has vertices J(–2, 3), K(1, 4), L(3, –2), and M(0, –3). Determine whether JKLM is a rectangle using the Distance Formula. ...
Board Members - Township of Union Public Schools
... Justify the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged (the dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the s ...
... Justify the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor. A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged (the dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the s ...
Answers to Geometry Unit 1 Practice
... 65. Sample answer: It is true that if A and B are both complementary to T, then A > B. However, the reason the student gives, the definition of complementary angles, is not the correct reason for this statement. The definition of complementary angles states only that complementary angles are ...
... 65. Sample answer: It is true that if A and B are both complementary to T, then A > B. However, the reason the student gives, the definition of complementary angles, is not the correct reason for this statement. The definition of complementary angles states only that complementary angles are ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)