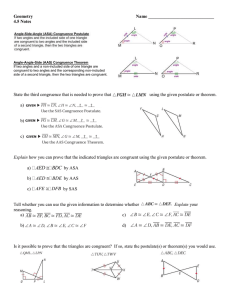
7-1 - MathPlease
... Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
... Copyright © by Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All Rights Reserved. ...
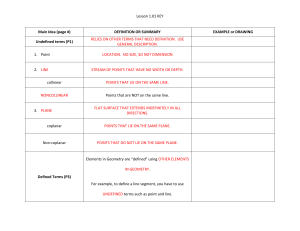
Lesson 1.01 KEY Main Idea (page #) DEFINITION OR SUMMARY
... UNDEFINED TERMS, DEFINED TERMS, and postulates will Print Theorems from Lesson 1.06 Page 5 help you prove theorems in Geometry. ...
... UNDEFINED TERMS, DEFINED TERMS, and postulates will Print Theorems from Lesson 1.06 Page 5 help you prove theorems in Geometry. ...
Connecting the Data: Geometry and Measurement
... width of 10 feet. The length was increased by 50%, and the width was decreased by 50% to form a new garden. How does the area of the new garden compare to the area of the original garden? The area of the new garden is ...
... width of 10 feet. The length was increased by 50%, and the width was decreased by 50% to form a new garden. How does the area of the new garden compare to the area of the original garden? The area of the new garden is ...
Geometry 9 - SH - Willmar Public Schools
... geometry, including proofs by contradiction. Express proofs in a form that clearly justifies the reasoning, such as two-column proofs, paragraph proofs, flow charts or illustrations. 9.3.2.5 (p. 126) Use technology tools to examine theorems, make and test conjectures, perform constructions and devel ...
... geometry, including proofs by contradiction. Express proofs in a form that clearly justifies the reasoning, such as two-column proofs, paragraph proofs, flow charts or illustrations. 9.3.2.5 (p. 126) Use technology tools to examine theorems, make and test conjectures, perform constructions and devel ...
MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Structure Determination by VSEPR
... 3rd period and higher. Consider boron trifluoride, BF3 The B atom is surrounded by only 3 electron pairs. Bond angles are 120o ...
... 3rd period and higher. Consider boron trifluoride, BF3 The B atom is surrounded by only 3 electron pairs. Bond angles are 120o ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)