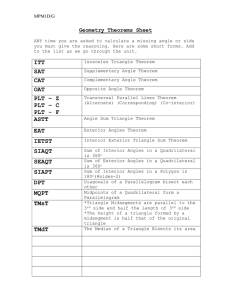
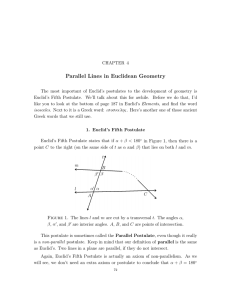
3-2 - Plainfield Public Schools
... to the measures of the angles in each pair. Then find the unknown angle measures. 1. m1 = 120°, m2 = (60x)° Alt. Ext. s Thm.; m2 = 120° 2. m2 = (75x – 30)°, m3 = (30x + 60)° Corr. s Post.; m2 = 120°, m3 = 120° 3. m3 = (50x + 20)°, m4= (100x – 80)° Alt. Int. s Thm.; m3 = 120°, m4 =120° ...
... to the measures of the angles in each pair. Then find the unknown angle measures. 1. m1 = 120°, m2 = (60x)° Alt. Ext. s Thm.; m2 = 120° 2. m2 = (75x – 30)°, m3 = (30x + 60)° Corr. s Post.; m2 = 120°, m3 = 120° 3. m3 = (50x + 20)°, m4= (100x – 80)° Alt. Int. s Thm.; m3 = 120°, m4 =120° ...
Mathematical problem solving or mathematical modeling
... physical world) Layman (Using mathematics for daily use) ...
... physical world) Layman (Using mathematics for daily use) ...
ACT Geometry Review Sheet
... Parallel lines: notation The big three 1) Alternate interior angles 2) Corresponding angles 3) Same side interior angles ...
... Parallel lines: notation The big three 1) Alternate interior angles 2) Corresponding angles 3) Same side interior angles ...
6.5 - mrstynercartervillehighschool
... Theorem 6.10 Triangle Larger Angle Theorem If one angle of a triangle is larger than another angle, then the side opposite the larger angle is longer than the side opposite the smaller angle. ...
... Theorem 6.10 Triangle Larger Angle Theorem If one angle of a triangle is larger than another angle, then the side opposite the larger angle is longer than the side opposite the smaller angle. ...
Unit 2
... Counting Mat Activities The focus in Unit 2 is on activities that show a 5-group and numbers 6 through 10. Pennies, Nickel Strips, and 5-square tiles enable children to make numbers quickly with a 5-group. Children use the new ⴙ tile to show 5 ⴙ 1, 5 ⴙ 2, 5 ⴙ 3, 5 ⴙ 4, 5 ⴙ 5, and ⴝ and ⴝ are introdu ...
... Counting Mat Activities The focus in Unit 2 is on activities that show a 5-group and numbers 6 through 10. Pennies, Nickel Strips, and 5-square tiles enable children to make numbers quickly with a 5-group. Children use the new ⴙ tile to show 5 ⴙ 1, 5 ⴙ 2, 5 ⴙ 3, 5 ⴙ 4, 5 ⴙ 5, and ⴝ and ⴝ are introdu ...
Geometry 15.10.23 CP1
... Is the conclusion a result of inductive or deductive reasoning? There is a myth that the Great Wall of China is the only man-made object visible from the Moon. The Great Wall is barely visible in photographs taken from 180 miles above Earth. The Moon is about 237,000 miles from Earth. Therefore, the ...
... Is the conclusion a result of inductive or deductive reasoning? There is a myth that the Great Wall of China is the only man-made object visible from the Moon. The Great Wall is barely visible in photographs taken from 180 miles above Earth. The Moon is about 237,000 miles from Earth. Therefore, the ...
History of geometry

Geometry (from the Ancient Greek: γεωμετρία; geo- ""earth"", -metron ""measurement"") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic).Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, The Elements is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century.In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.)