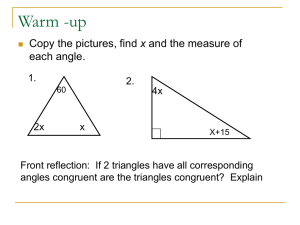
Chapter 3
... • Now draw median CF, intersecting BE at G’ • Draw parallels as before • Note similar triangles and the fact that G’ is two-thirds the way along BE • Thus G’ = G and all three medians concurrent ...
... • Now draw median CF, intersecting BE at G’ • Draw parallels as before • Note similar triangles and the fact that G’ is two-thirds the way along BE • Thus G’ = G and all three medians concurrent ...
Right Triangle Trigonometry
... Use trigonometric ratios to find the unknown sides and angles in the right triangle below: c = .92 mB = 49.9° ...
... Use trigonometric ratios to find the unknown sides and angles in the right triangle below: c = .92 mB = 49.9° ...
Full text
... In the study of a combinatorial minimization problem related to multimodule computer memory organizations [ 5 ] , a triangle of numbers is constructed, which enjoys many of the pleasant properties of Pascal's triangle [1,2]. These numbers originate from counting a set of points in the /r-dimensional ...
... In the study of a combinatorial minimization problem related to multimodule computer memory organizations [ 5 ] , a triangle of numbers is constructed, which enjoys many of the pleasant properties of Pascal's triangle [1,2]. These numbers originate from counting a set of points in the /r-dimensional ...
HW: Module 1, Topic D, Lesson 22 - Congruence Criteria for Triangles
... D. two sides and the excluded angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and the excluded angle of the other triangle. ...
... D. two sides and the excluded angle of one triangle are equal to two sides and the excluded angle of the other triangle. ...
math8_breakout_aug_24_v1
... 8.G.B Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.G.B.6 Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. 8.G.B.7 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. 8.G.B.8 Apply the P ...
... 8.G.B Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.G.B.6 Explain a proof of the Pythagorean Theorem and its converse. 8.G.B.7 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine unknown side lengths in right triangles in real-world and mathematical problems in two and three dimensions. 8.G.B.8 Apply the P ...
Definitions, Postulates, Properties and Theorems – and the Pictures
... Any time you “plug in” angle measures or side lengths for other angles or side lengths you are using Substitution. This only works with =, not . The Transitive property is like substitution but only when it fits the pattern like the one shown (can use with .) Any time 2 triangles share a side. C ( ...
... Any time you “plug in” angle measures or side lengths for other angles or side lengths you are using Substitution. This only works with =, not . The Transitive property is like substitution but only when it fits the pattern like the one shown (can use with .) Any time 2 triangles share a side. C ( ...
Indirect Proof and Inequalities in One Triangle
... In Exercises 1–3, write the first step in an indirect proof of the statement. 1. Not all the students in a given class can be above average. 2. No number equals another number divided by zero. 3. The square root of 2 is not equal to the quotient of any two integers. In Exercises 4 and 5, determine w ...
... In Exercises 1–3, write the first step in an indirect proof of the statement. 1. Not all the students in a given class can be above average. 2. No number equals another number divided by zero. 3. The square root of 2 is not equal to the quotient of any two integers. In Exercises 4 and 5, determine w ...