Geometry Module 1, Topic B, Lesson 11: Student
... A proof of a mathematical statement is a detailed explanation of how that statement follows logically from other statements already accepted as true. A theorem is a mathematical statement with a proof. ...
... A proof of a mathematical statement is a detailed explanation of how that statement follows logically from other statements already accepted as true. A theorem is a mathematical statement with a proof. ...
Geometry
... Proving the Congruent Supplements Theorem Given: Angle 1 and Angle 2 are supplements Angle 3 and Angle 4 are supplements Angle 1 ≅ Angle 4 Prove: Angle 2 ≅ Angle 3 ...
... Proving the Congruent Supplements Theorem Given: Angle 1 and Angle 2 are supplements Angle 3 and Angle 4 are supplements Angle 1 ≅ Angle 4 Prove: Angle 2 ≅ Angle 3 ...
Chapter 8
... Parallelogram: opposite sides are parallel and congruent. Opposite angles are congruent. Rectangle: Parallelogram with four right angles Rhombus: Parallelogram with four congruent sides, opposite angles are congruent Square: Parallelogram with four congruent sides and four right angles. Trapezoid: O ...
... Parallelogram: opposite sides are parallel and congruent. Opposite angles are congruent. Rectangle: Parallelogram with four right angles Rhombus: Parallelogram with four congruent sides, opposite angles are congruent Square: Parallelogram with four congruent sides and four right angles. Trapezoid: O ...
Geometry - Grade 4 Common Core Math
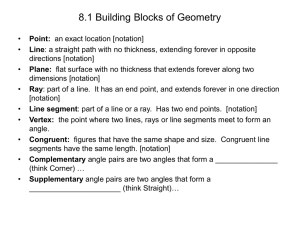
... Angles An angle is formed when two rays have the same endpoint. This endpoint is called the vertex. The two rays that form the angle are called sides. ...
... Angles An angle is formed when two rays have the same endpoint. This endpoint is called the vertex. The two rays that form the angle are called sides. ...