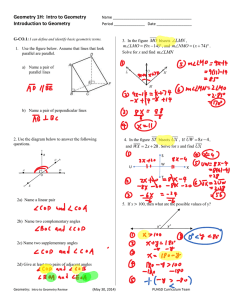
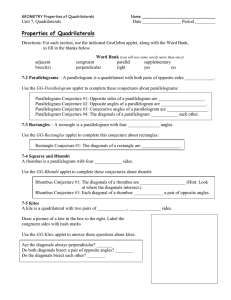
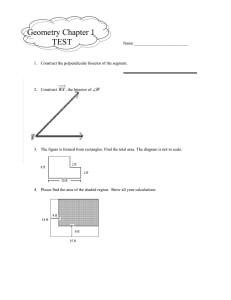
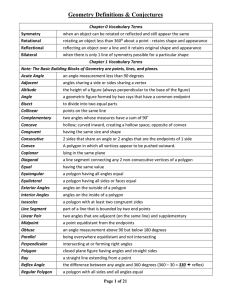
x - Greater Nanticoke Area School District
... 57. Apply basic rules of real numbers in problem solving 58. Select and justify appropriate methods needed in solving multi-step problems CS 2.5.11B: Use representations to communicate mathematically 59. Translate words to symbols and symbols to words 60. Use appropriate mathematical terminology 61. ...
... 57. Apply basic rules of real numbers in problem solving 58. Select and justify appropriate methods needed in solving multi-step problems CS 2.5.11B: Use representations to communicate mathematically 59. Translate words to symbols and symbols to words 60. Use appropriate mathematical terminology 61. ...
Geometry and Measurement
... To convert from one metric unit to another is a matter of moving the decimal point. For example, to convert from km to meters, we move three places right in the chart. Thus, to convert 73 km to meters, we move the decimal point in 73. three places right obtaining 73. km = 73,000 m. To convert 3847 m ...
... To convert from one metric unit to another is a matter of moving the decimal point. For example, to convert from km to meters, we move three places right in the chart. Thus, to convert 73 km to meters, we move the decimal point in 73. three places right obtaining 73. km = 73,000 m. To convert 3847 m ...
Mathematics Geometry
... The fundamental purpose of the course in Geometry is to formalize and extend students’ geometric experiences from the middle grades. Students explore more complex geometric situations and deepen their explanations of geometric relationships, moving towards formal mathematical arguments. Important di ...
... The fundamental purpose of the course in Geometry is to formalize and extend students’ geometric experiences from the middle grades. Students explore more complex geometric situations and deepen their explanations of geometric relationships, moving towards formal mathematical arguments. Important di ...