Summative – Geometry Grade 2 Summative for geometry Grade 2.
... 4. Choose two different pattern blocks. Put the pattern blocks together to make a new shape that has a line of symmetry. ...
... 4. Choose two different pattern blocks. Put the pattern blocks together to make a new shape that has a line of symmetry. ...
7-5
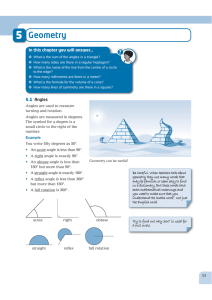
... 1. What are two angles whose sum is 90°? complementary angles 2. What are two angles whose sum is 180°? supplementary angles 3. A part of a line between two points is called a _________. segment 4. Two lines that intersect at 90° are ______________. perpendicular ...
... 1. What are two angles whose sum is 90°? complementary angles 2. What are two angles whose sum is 180°? supplementary angles 3. A part of a line between two points is called a _________. segment 4. Two lines that intersect at 90° are ______________. perpendicular ...
Geometry - Semester 2
... 1. Lay the paper across the circle so its corner lies on the circle. The points where the two edges of the paper cross the circle at the endpoints of the diameter. Mark those points and draw the diameter using the edge of the paper as a straight edge. Repeat to get a second diameter. Intersection of ...
... 1. Lay the paper across the circle so its corner lies on the circle. The points where the two edges of the paper cross the circle at the endpoints of the diameter. Mark those points and draw the diameter using the edge of the paper as a straight edge. Repeat to get a second diameter. Intersection of ...
Geometry Ch 2 and 3 Assignment Log Gordon
... a time before or after school to retake the target again, with teacher discretion. Target quizzes are not arranged for absent students since there will still be other opportunities in class for a student to retake the target even if they are absent. Learning Targets: “I can” … ...
... a time before or after school to retake the target again, with teacher discretion. Target quizzes are not arranged for absent students since there will still be other opportunities in class for a student to retake the target even if they are absent. Learning Targets: “I can” … ...
Euclidean geometry

Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to the Alexandrian Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the Elements. Euclid's method consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms, and deducing many other propositions (theorems) from these. Although many of Euclid's results had been stated by earlier mathematicians, Euclid was the first to show how these propositions could fit into a comprehensive deductive and logical system. The Elements begins with plane geometry, still taught in secondary school as the first axiomatic system and the first examples of formal proof. It goes on to the solid geometry of three dimensions. Much of the Elements states results of what are now called algebra and number theory, explained in geometrical language.For more than two thousand years, the adjective ""Euclidean"" was unnecessary because no other sort of geometry had been conceived. Euclid's axioms seemed so intuitively obvious (with the possible exception of the parallel postulate) that any theorem proved from them was deemed true in an absolute, often metaphysical, sense. Today, however, many other self-consistent non-Euclidean geometries are known, the first ones having been discovered in the early 19th century. An implication of Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity is that physical space itself is not Euclidean, and Euclidean space is a good approximation for it only where the gravitational field is weak.Euclidean geometry is an example of synthetic geometry, in that it proceeds logically from axioms to propositions without the use of coordinates. This is in contrast to analytic geometry, which uses coordinates.