Case 3
... Focally the lesion extends into the testis invading in between seminiferous tubules. Elsewhere the lesion shows central infarction. Discussion One of the keys to recognizing this entity is its paratesticular as opposed to intratesticular location. Relatively few entities involved the paratesticular ...
... Focally the lesion extends into the testis invading in between seminiferous tubules. Elsewhere the lesion shows central infarction. Discussion One of the keys to recognizing this entity is its paratesticular as opposed to intratesticular location. Relatively few entities involved the paratesticular ...
Biology Monday, October 16
... • Selectively Permeable – only certain things can pass through • Only small molecules can fit between the phospholipids. • The nonpolar tails of the phospholipids prevent charged molecules from passing between them. • Proteins help certain larger molecules to enter ...
... • Selectively Permeable – only certain things can pass through • Only small molecules can fit between the phospholipids. • The nonpolar tails of the phospholipids prevent charged molecules from passing between them. • Proteins help certain larger molecules to enter ...
Unicellular Organisms - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Bacteria (singular form is bacterium) are among the most primitive and also the most plentiful organisms on the planet. They are said to be very successful because they have survived and changed little over several billion years (Figure 2). Some, like plants, can make their own food. Others are para ...
... Bacteria (singular form is bacterium) are among the most primitive and also the most plentiful organisms on the planet. They are said to be very successful because they have survived and changed little over several billion years (Figure 2). Some, like plants, can make their own food. Others are para ...
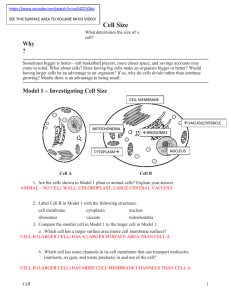
Model 1 – Investigating Cell Size
... Sometimes bigger is better—tall basketball players, more closet space, and savings accounts may come to mind. What about cells? Does having big cells make an organism bigger or better? Would having larger cells be an advantage to an organism? If so, why do cells divide rather than continue growing? ...
... Sometimes bigger is better—tall basketball players, more closet space, and savings accounts may come to mind. What about cells? Does having big cells make an organism bigger or better? Would having larger cells be an advantage to an organism? If so, why do cells divide rather than continue growing? ...
Golgi Body
... many substances are dissolved in it, such as nucleotides, for replication of DNA & enzymes, direct activities that take place in the nucleus. It also contains & carries some important structure inside it. Extracurricular Activities: Nucleoplasm is found in all eukaryotic cells which are cells that h ...
... many substances are dissolved in it, such as nucleotides, for replication of DNA & enzymes, direct activities that take place in the nucleus. It also contains & carries some important structure inside it. Extracurricular Activities: Nucleoplasm is found in all eukaryotic cells which are cells that h ...
The Specificity of cell signaling
... may function as a transcription factor. Often a transcription factor regulates several different genes. ...
... may function as a transcription factor. Often a transcription factor regulates several different genes. ...
Cell Membrane
... tunnels across the membrane to move materials Channel proteins may always be open or have gates that open & close to control the movement of materials; called gated channels Gates open & close in response to concentration inside & outside the cell Ion Channel is a transport protein with a polar ...
... tunnels across the membrane to move materials Channel proteins may always be open or have gates that open & close to control the movement of materials; called gated channels Gates open & close in response to concentration inside & outside the cell Ion Channel is a transport protein with a polar ...
Cell Organelles
... Cells May be Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Prokaryotes include bacteria which lack of nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles. ...
... Cells May be Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Prokaryotes include bacteria which lack of nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles. ...
Chapter 1
... 8. The Golgi complex functions in processing of lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins formed by the ER. The golgi produces gylcoproteins and glycolipids, and also enzymes. The golgi forms lysosomes. 9. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes (or hydrolytic enzyme) in the cell. 10. The plant cell has a cel ...
... 8. The Golgi complex functions in processing of lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins formed by the ER. The golgi produces gylcoproteins and glycolipids, and also enzymes. The golgi forms lysosomes. 9. Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes (or hydrolytic enzyme) in the cell. 10. The plant cell has a cel ...
Effect of ±5ºC difference from physiologic temperature on surface
... activity in a dose-dependent manner up to 44°C. However, the temperature increase did not induce widespread transport increase of all other nutrients tested [15]. In human, promonocytic U937 heat-treated cells displayed a lower intracellular pH (pHi) than untreated cells [14]. On the other hand, hyp ...
... activity in a dose-dependent manner up to 44°C. However, the temperature increase did not induce widespread transport increase of all other nutrients tested [15]. In human, promonocytic U937 heat-treated cells displayed a lower intracellular pH (pHi) than untreated cells [14]. On the other hand, hyp ...
Cell Membrane and Transport
... Placing plant cells in a hypertonic solution causes the plant cell membranes to shrink away from the cell wall. This process is called plasmolysis. Plasmolysis can result in plant cell death due to water loss. A wilted plant is showing signs of plasmolysis. Placing a plant in a hypotonic solution h ...
... Placing plant cells in a hypertonic solution causes the plant cell membranes to shrink away from the cell wall. This process is called plasmolysis. Plasmolysis can result in plant cell death due to water loss. A wilted plant is showing signs of plasmolysis. Placing a plant in a hypotonic solution h ...
Name: ANIMAL Cell Form and Function Problem: How does the form
... contrast the forms of these cells and understand how those forms fit well the each cell’s function in your body Cheek Cells: To prepare this slide, a small stick was used to gently scrape the inside of a human cheek and swirl it in a drop of methylene blue to stain the cells (otherwise they will be ...
... contrast the forms of these cells and understand how those forms fit well the each cell’s function in your body Cheek Cells: To prepare this slide, a small stick was used to gently scrape the inside of a human cheek and swirl it in a drop of methylene blue to stain the cells (otherwise they will be ...
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Results The recombinant Lmdd
... TILs, the cytotoxic activity of TILs and MPFG-specific CTL against various targets ...
... TILs, the cytotoxic activity of TILs and MPFG-specific CTL against various targets ...
Unit 1: Biology - science physics
... • Only present in eukaryotes • An Intracellular (inside cell) transport system. • A system of membranous channels, allows substances to move through the cell. • Small sacs (vesicles) can be pinched off, allowing molecules to be transported around the cell to other organelles ...
... • Only present in eukaryotes • An Intracellular (inside cell) transport system. • A system of membranous channels, allows substances to move through the cell. • Small sacs (vesicles) can be pinched off, allowing molecules to be transported around the cell to other organelles ...
1 Cell Organelles in Plant and Animal Cells
... 8. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) makes lipids, breaks down drugs, and acts as the internal delivery system for the cell. It is a network of membranes that run throughout the cell. There are two types of ER: rough and smooth. Rough ER is covered with ribosomes and smooth ER is not. ER is found in bo ...
... 8. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) makes lipids, breaks down drugs, and acts as the internal delivery system for the cell. It is a network of membranes that run throughout the cell. There are two types of ER: rough and smooth. Rough ER is covered with ribosomes and smooth ER is not. ER is found in bo ...
Chapter 4 Cell Structure
... chloro- = green; -plast = molded (chloroplast: the site of photosynthesis in plants and algae) cili- = hair (cilium: a short hairlike cellular appendage with a microtubule core, specialized for locomotion) cyto- = cell; -plasm = fluid (cytoplasm: everything inside a cell between the plasma membrane ...
... chloro- = green; -plast = molded (chloroplast: the site of photosynthesis in plants and algae) cili- = hair (cilium: a short hairlike cellular appendage with a microtubule core, specialized for locomotion) cyto- = cell; -plasm = fluid (cytoplasm: everything inside a cell between the plasma membrane ...
Plants, Animals, and other Weird Cells
... 1. Obtain a slide, cover slip. Clean both the slide and the cover slip. 2. Drop one small drop of water on the slide. 3. Using a clean toothpick, gently scrape the toothpick inside your mouth along the cheek wall. 4. Smear the toothpick across the slide where the water drop is. 5. Add one drop of me ...
... 1. Obtain a slide, cover slip. Clean both the slide and the cover slip. 2. Drop one small drop of water on the slide. 3. Using a clean toothpick, gently scrape the toothpick inside your mouth along the cheek wall. 4. Smear the toothpick across the slide where the water drop is. 5. Add one drop of me ...
Types of Programmed Cell Death The mechanisms by which cells
... aging and contribute to aging-related loss of function in various adult tissues. This accumulation may result from the fact that senescent cells are resistant to apoptosis due to repressed activity of PCD pathway components such as caspase 3 and cell cycle factors that function in both cell division ...
... aging and contribute to aging-related loss of function in various adult tissues. This accumulation may result from the fact that senescent cells are resistant to apoptosis due to repressed activity of PCD pathway components such as caspase 3 and cell cycle factors that function in both cell division ...
2.1 Plant and Animal Cells pg. 29 Biology – The study of living
... Interphase: is the phase of the cell cycle during which the cell performs its normal functions and its genetic material is copied in preparation for cell division. It is the longest stage of the cell cycle, and performs all the life functions; growth, cellular reproduction and specialized functions. ...
... Interphase: is the phase of the cell cycle during which the cell performs its normal functions and its genetic material is copied in preparation for cell division. It is the longest stage of the cell cycle, and performs all the life functions; growth, cellular reproduction and specialized functions. ...
Week 11
... Homework: Complete Eukaryotic Cell packet and cell diagrams. Objective: Students will gain an understanding of the cellular structure common to all eukaryotic cells and how these structures work together to allow the all of the cellular reactions to occur. Activity: Five minute review. Check and go ...
... Homework: Complete Eukaryotic Cell packet and cell diagrams. Objective: Students will gain an understanding of the cellular structure common to all eukaryotic cells and how these structures work together to allow the all of the cellular reactions to occur. Activity: Five minute review. Check and go ...
3.5 Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis KEY CONCEPT
... that cannot diffuse across a membrane. ...
... that cannot diffuse across a membrane. ...
Cell Processes Notes as a “PowerPoint
... of a large particle out of the cell by first surrounding it with a vesicle and then moving it to the cell membrane where it is expelled. ...
... of a large particle out of the cell by first surrounding it with a vesicle and then moving it to the cell membrane where it is expelled. ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.