Ribosomes - 4J Blog Server
... • The nucleus contains most of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell. • Ribosomes use the information from the DNA to make proteins. ...
... • The nucleus contains most of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell. • Ribosomes use the information from the DNA to make proteins. ...
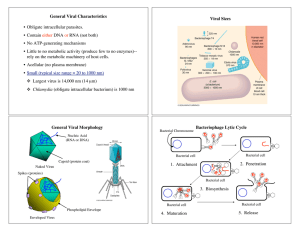
General Viral Characteristics • Obligate intracellular parasites
... Persistent Infections: Slow, but continuously increasing numbers of viral particles in infected person. May take many months or years for disease to become apparent (may have no initial acute illness). Example: HIV, measles, adenovirus diseases. ...
... Persistent Infections: Slow, but continuously increasing numbers of viral particles in infected person. May take many months or years for disease to become apparent (may have no initial acute illness). Example: HIV, measles, adenovirus diseases. ...
Biology_1_&_2_files/3 Cells ACADEMIC
... The ribosomes located on the rough ER make proteins which then cross into the membranes of the ER. The ER membrane then pinches off and forms a vesicle around the proteins. Vesicles transport the proteins from the rough ER to the Golgi apparatus, where they are modified by enzymes and repackaged ...
... The ribosomes located on the rough ER make proteins which then cross into the membranes of the ER. The ER membrane then pinches off and forms a vesicle around the proteins. Vesicles transport the proteins from the rough ER to the Golgi apparatus, where they are modified by enzymes and repackaged ...
Immunology Ambassador Guide Immunity and Disease We will talk
... genes – not enough to encode all of those 100 Billion different antibodies. And of course, most of those genes have to be making other proteins besides antibodies. So how do our B cells make so many different antibodies from a much smaller number of genes? Every Cell Has the Exact Same DNA First, it ...
... genes – not enough to encode all of those 100 Billion different antibodies. And of course, most of those genes have to be making other proteins besides antibodies. So how do our B cells make so many different antibodies from a much smaller number of genes? Every Cell Has the Exact Same DNA First, it ...
Osmotic, or Water Potential is simply a measure of the tendency for
... The cell is in dynamic equilibrium with its environment, and osmosis WILL occur, but no measureable difference on either side of the membrane will be noticed. ...
... The cell is in dynamic equilibrium with its environment, and osmosis WILL occur, but no measureable difference on either side of the membrane will be noticed. ...
Cell (biology)
... A human cell has genetic material contained in the cell nucleus (the nuclear genome) and in the mitochondria (the mitochondrial genome). In humans the nuclear genome is divided into 23 pairs of linear DNA molecules called chromosomes. The mitochondrial genome is a circular DNA molecule distinct from ...
... A human cell has genetic material contained in the cell nucleus (the nuclear genome) and in the mitochondria (the mitochondrial genome). In humans the nuclear genome is divided into 23 pairs of linear DNA molecules called chromosomes. The mitochondrial genome is a circular DNA molecule distinct from ...
Local interactions shape plant cells
... fucoid zygotes [16], but regional actin accumulation has also been observed in germinating pollen grains and root hairs embarking on tip growth [9,17], in leaf hair (trichome) initials [18] and in lobe-forming regions of leaf epidermal pavement cells [19]. Accordingly an inhibitorinduced interferenc ...
... fucoid zygotes [16], but regional actin accumulation has also been observed in germinating pollen grains and root hairs embarking on tip growth [9,17], in leaf hair (trichome) initials [18] and in lobe-forming regions of leaf epidermal pavement cells [19]. Accordingly an inhibitorinduced interferenc ...
Chapter 3
... Penicillin interferes with peptidoglycan synthesis • Prevents cross-linking of adjacent glycan chains • Usually more effective against Gram-positive bacteria than Gram-negative bacteria • Outer membrane of Gram-negatives blocks access • Derivatives have been developed that can cross ...
... Penicillin interferes with peptidoglycan synthesis • Prevents cross-linking of adjacent glycan chains • Usually more effective against Gram-positive bacteria than Gram-negative bacteria • Outer membrane of Gram-negatives blocks access • Derivatives have been developed that can cross ...
It is essential for students to know the three major tenets of the cell
... In the development of most multicellular organisms, a single cell (fertilized egg) gives rise to many different types of cells, each with a different structure and corresponding function. ○ The fertilized egg gives rise to a large number of cells through cell division, but the process of cell divi ...
... In the development of most multicellular organisms, a single cell (fertilized egg) gives rise to many different types of cells, each with a different structure and corresponding function. ○ The fertilized egg gives rise to a large number of cells through cell division, but the process of cell divi ...
1 The Diversity of Cells
... to survive. It also produces more waste. This means that more materials have to pass through the surface of a large cell than a small cell. ...
... to survive. It also produces more waste. This means that more materials have to pass through the surface of a large cell than a small cell. ...
SC.912.L14.3 Cell Structures
... The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a lipid bilayer, which gives cell membranes a flexible structure and forms a strong barrier between the cell and its surroundings. ...
... The composition of nearly all cell membranes is a double-layered sheet called a lipid bilayer, which gives cell membranes a flexible structure and forms a strong barrier between the cell and its surroundings. ...
Standard B-2
... • In the development of most multicellular organisms, a single cell (fertilized egg) gives rise to many different types of cells, each with a different structure and corresponding function. ○ The fertilized egg gives rise to a large number of cells through cell division, but the process of cell divi ...
... • In the development of most multicellular organisms, a single cell (fertilized egg) gives rise to many different types of cells, each with a different structure and corresponding function. ○ The fertilized egg gives rise to a large number of cells through cell division, but the process of cell divi ...
BARTH SYNDROME: CARDIOLIPIN ALTERATIONS LINKED TO
... respiratory activities. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the cause of mitochondrial dysfunction in Barth syndrome remain poorly understood. Taking into account recent findings, i.e. bioenergetic perturbations1, ROS production1, cell cycle dysregulation2, that accompagnied tafazzin gene m ...
... respiratory activities. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the cause of mitochondrial dysfunction in Barth syndrome remain poorly understood. Taking into account recent findings, i.e. bioenergetic perturbations1, ROS production1, cell cycle dysregulation2, that accompagnied tafazzin gene m ...
Control of Cell Shape in Bacteria: Helical, Actin-like
... (B) Field of cells (unprocessed images) showing typical localization of MreB. (C) Optical sections through cell marked “a” in (B), at three different levels in the z axis after deconvolution. (D) 3D reconstruction of the same cell shown from above and during rotation through to 45⬚. (E) Cells prepar ...
... (B) Field of cells (unprocessed images) showing typical localization of MreB. (C) Optical sections through cell marked “a” in (B), at three different levels in the z axis after deconvolution. (D) 3D reconstruction of the same cell shown from above and during rotation through to 45⬚. (E) Cells prepar ...
Sample Chapter - Viva Online Learning
... 2. Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. 3. Cell was discovered by the research and observation of many scientists like Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann and Rudolph Virchow. Their work also led to the formulation of cell ...
... 2. Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. 3. Cell was discovered by the research and observation of many scientists like Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, Robert Hooke, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann and Rudolph Virchow. Their work also led to the formulation of cell ...
Chapter Test B
... are bacteria that contain chlorophyll, which is used to produce food through photosynthesis. The bacteria could make food while the cell provided the bacteria with an environment in which to live. Eventually, this combination may have allowed cells to produce food, giving rise to the first plants on ...
... are bacteria that contain chlorophyll, which is used to produce food through photosynthesis. The bacteria could make food while the cell provided the bacteria with an environment in which to live. Eventually, this combination may have allowed cells to produce food, giving rise to the first plants on ...
Retinoic Acid - Wesleyan College Faculty
... Treating Neurula Embryos with Retinoic Acid? To study global changes in gene expression patterns we use DNA microarrays Large numbers of genes (from 5-10K) represented on small coated glass slides (chips) Assess changes in gene expression patterns in normal vs treated embryos (work in progress) ...
... Treating Neurula Embryos with Retinoic Acid? To study global changes in gene expression patterns we use DNA microarrays Large numbers of genes (from 5-10K) represented on small coated glass slides (chips) Assess changes in gene expression patterns in normal vs treated embryos (work in progress) ...
Effects of deuterium oxide on cell growth and vesicle speed
... was observed after five days compared to cells cultured in 0 moles/L D2 O (closed circles). Cell viability also dropped by 20% for cells cultured in D2 O (open circles) as shown in Fig. 1B. These results are qualitatively consistent with studies on human pancreatic tumor cells (Hartmann et al., 2005 ...
... was observed after five days compared to cells cultured in 0 moles/L D2 O (closed circles). Cell viability also dropped by 20% for cells cultured in D2 O (open circles) as shown in Fig. 1B. These results are qualitatively consistent with studies on human pancreatic tumor cells (Hartmann et al., 2005 ...
ABSORPTION DEGRADATION OF MONO-Si AND POLY
... Throughout the history of solar cell development, an efficiency increase has been a major priority because a low efficiency is one of the chief disadvantages in Photovoltaic (PV) industries [1-3]. Such improvement includes the development of a better model for increasing the absorbance of the solar ...
... Throughout the history of solar cell development, an efficiency increase has been a major priority because a low efficiency is one of the chief disadvantages in Photovoltaic (PV) industries [1-3]. Such improvement includes the development of a better model for increasing the absorbance of the solar ...
Chapter 4: Tour of the Cell
... and repeat this time after time – This “walking” causes the microtubules to bend ...
... and repeat this time after time – This “walking” causes the microtubules to bend ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes
... For the following questions, use the lettered answers to match the structure to its proper cell type. Choose the most inclusive category. Each answer may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. B. C. D. E. ...
... For the following questions, use the lettered answers to match the structure to its proper cell type. Choose the most inclusive category. Each answer may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. B. C. D. E. ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.