TPS54160 60-V, Step-Down LED Driver Design Guide Application Report ..............................................................
... The TPS54160 is normally used as a buck voltage regulator. In these applications, a lower dc voltage is derived from a higher input voltage. The output voltage is regulated by the internal current mode control circuitry to maintain a constant voltage over varying line and load conditions. The TPS541 ...
... The TPS54160 is normally used as a buck voltage regulator. In these applications, a lower dc voltage is derived from a higher input voltage. The output voltage is regulated by the internal current mode control circuitry to maintain a constant voltage over varying line and load conditions. The TPS541 ...
2SB1197K
... third party's intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights, and further, assumes no liability of whatsoever nature in the event of any such infringement, or arising from or connected with or related to the use of such devices. Upon the sale of any such devices, other than for buyer's rig ...
... third party's intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights, and further, assumes no liability of whatsoever nature in the event of any such infringement, or arising from or connected with or related to the use of such devices. Upon the sale of any such devices, other than for buyer's rig ...
RHRP8120 - Intranet
... characteristics (trr < 55ns). It has half the recovery time of ultrafast diodes and is of silicon nitride passivated ion-implanted epitaxial planar construction. ...
... characteristics (trr < 55ns). It has half the recovery time of ultrafast diodes and is of silicon nitride passivated ion-implanted epitaxial planar construction. ...
TRANSFORMERLESS STEP UP ALTERNATING VOLTAGE
... Conclusion 1. The transformerless alternating voltage regulators with a practically sinusoidal input and output currents are offered with the capability to increase per unit the voltage conversion coefficient. In the case when the load or independent three-phase source are executed with divided phas ...
... Conclusion 1. The transformerless alternating voltage regulators with a practically sinusoidal input and output currents are offered with the capability to increase per unit the voltage conversion coefficient. In the case when the load or independent three-phase source are executed with divided phas ...
ee221_4a
... The kilowatt-hours (kWh) to a customer is measured with a kWh meter corresponding to the average power consumed over a period of time. The cost/rate of the kWh may very depending on when the power is used (high vs. low demand) and how much total power has been consumed (cost may go down after so man ...
... The kilowatt-hours (kWh) to a customer is measured with a kWh meter corresponding to the average power consumed over a period of time. The cost/rate of the kWh may very depending on when the power is used (high vs. low demand) and how much total power has been consumed (cost may go down after so man ...
Modelling of Nonlinear Loads and Estimation of Harmonics
... Fig. 6. (a). Current waveform obtained from simulation model of fluorescent lamp and (b). Harmonic spectrum of the current drawn by the lamp. ...
... Fig. 6. (a). Current waveform obtained from simulation model of fluorescent lamp and (b). Harmonic spectrum of the current drawn by the lamp. ...
... large current, then the maximum output power of the system determined by (7) can be plotted in Fig. 7 as C1 and C3 when the battery voltage ranges from 20 to 365 V. Consider the voltage fluctuation on the DC-bus, C1 and C3 are the cases when V1 ¼ 140 and 150 V, respectively. However, with the decreas ...
Applications in the Industrial Market
... pair consists of a HBridge High Side and Low Side driver ...
... pair consists of a HBridge High Side and Low Side driver ...
basic09LED_Jun22
... current more than 10 % of nominal value. 2. ERROR alert produces message to Alert Screen, changes FSM state to ERROR state and switches off an over current channel, when a power supply current more than 30 % of nominal value. For the correct settings of the alarm levels the nominal voltages and curr ...
... current more than 10 % of nominal value. 2. ERROR alert produces message to Alert Screen, changes FSM state to ERROR state and switches off an over current channel, when a power supply current more than 30 % of nominal value. For the correct settings of the alarm levels the nominal voltages and curr ...
DOEPFER MUSIKELEKTRONIK GMBH
... different frequency resp. phase comparators and a low pass. The basic principle is like this: one of the comparators compares the frequency of an external signal with the frequency of the internal VCO and generates a correction voltage that is smoothed by the low pass and that controls the frequency ...
... different frequency resp. phase comparators and a low pass. The basic principle is like this: one of the comparators compares the frequency of an external signal with the frequency of the internal VCO and generates a correction voltage that is smoothed by the low pass and that controls the frequency ...
display
... Due to large amounts of energy stored in the motor coils during operation, a voltage spike of several hundred volts is generated when the breaker is turned OFF. This diode surpresses this spike which protects the connected motor controller and DC-DC converters. Cathode (i.e. banded end) MUST face po ...
... Due to large amounts of energy stored in the motor coils during operation, a voltage spike of several hundred volts is generated when the breaker is turned OFF. This diode surpresses this spike which protects the connected motor controller and DC-DC converters. Cathode (i.e. banded end) MUST face po ...
Chapter 5 Switching Function, Circuit Models, and Simulation
... Chapter 5 Switching Function, Circuit Models, and Simulation • Switching Function – Use “0” and “1” to express a switch: switching function – Use switching function to express voltage and current ...
... Chapter 5 Switching Function, Circuit Models, and Simulation • Switching Function – Use “0” and “1” to express a switch: switching function – Use switching function to express voltage and current ...
Pulse and Exponential Waveforms in PSPICE
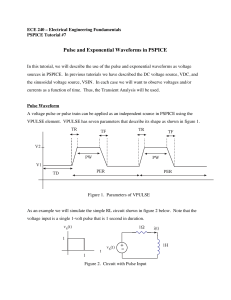
... Figure 3. PSPICE Schematic Note that the pulse parameters are set to be: TD = 0 (no delay, start the pulse train at t = 0) TR = TF = 1n (10-9 makes the rise and fall times almost zero) V1 = 0 (pulse starts at zero) V2 = 1 (rises to one volt) PW = 1 (pulse width is 1 second) PER = 10 (the pulse will ...
... Figure 3. PSPICE Schematic Note that the pulse parameters are set to be: TD = 0 (no delay, start the pulse train at t = 0) TR = TF = 1n (10-9 makes the rise and fall times almost zero) V1 = 0 (pulse starts at zero) V2 = 1 (rises to one volt) PW = 1 (pulse width is 1 second) PER = 10 (the pulse will ...
AMP03 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The differential amplifier topology of the AMP03 both amplifies the difference between two signals and provides extremely high rejection of the common-mode input voltage. By providing common-mode rejection (CMR) of 100 dB typical, the AMP03 solves common problems encountered in instrumentation desig ...
... The differential amplifier topology of the AMP03 both amplifies the difference between two signals and provides extremely high rejection of the common-mode input voltage. By providing common-mode rejection (CMR) of 100 dB typical, the AMP03 solves common problems encountered in instrumentation desig ...
Testing Power Sources for Stability
... In the case of boost and buck-boost converters, a sudden increase in duty cycle causes a momentary reduction in output since power flows to the output a smaller percentage of the time. Once the current level builds up, which may take several cycles, the duty cycle will revert to normal and the highe ...
... In the case of boost and buck-boost converters, a sudden increase in duty cycle causes a momentary reduction in output since power flows to the output a smaller percentage of the time. Once the current level builds up, which may take several cycles, the duty cycle will revert to normal and the highe ...
EEEE 482 Lab0_Rev2015_1 - RIT
... supply voltage. For example, if your supply voltage is 14 V, your output voltage must be able to swing 4.5 V, for a total peak-to-peak output swing of 14 – 5 = 9 V. Each student will design the amplifier by selection of R1, R2, RC, Re1 and Re2 using standard 10% tolerance resistor values (no paral ...
... supply voltage. For example, if your supply voltage is 14 V, your output voltage must be able to swing 4.5 V, for a total peak-to-peak output swing of 14 – 5 = 9 V. Each student will design the amplifier by selection of R1, R2, RC, Re1 and Re2 using standard 10% tolerance resistor values (no paral ...
BB4103331337
... It may be mentioned that the effectiveness of the DSTATCOM in correcting voltage sag depends on the value of ZTH or fault level of the load bus. When the shunt injected current Ir is kept in quadrature with V, the desired voltage correction can be achieved without injecting any active power into the ...
... It may be mentioned that the effectiveness of the DSTATCOM in correcting voltage sag depends on the value of ZTH or fault level of the load bus. When the shunt injected current Ir is kept in quadrature with V, the desired voltage correction can be achieved without injecting any active power into the ...
Study of Excitation Control System Responses
... power flow. The generator excitation of older systems may be provided through slip rings and brushes by means of dc generators mounted on the same shaft of the rotor of the synchronous machine. However, modern excitation systems usually use ac generators with rotating rectifiers, and are known as br ...
... power flow. The generator excitation of older systems may be provided through slip rings and brushes by means of dc generators mounted on the same shaft of the rotor of the synchronous machine. However, modern excitation systems usually use ac generators with rotating rectifiers, and are known as br ...
Power inverter
A power inverter, or inverter, is an electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source.A power inverter can be entirely electronic or may be a combination of mechanical effects (such as a rotary apparatus) and electronic circuitry.Static inverters do not use moving parts in the conversion process.