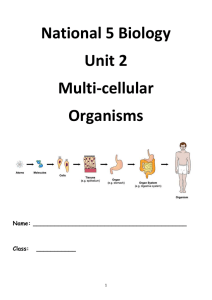
The cell is the basic unit of living things.
... when there was no mechanical refrigeration in homes. People were used to having foods spoil, like milk going sour. During this time, many people died from diseases such as typhoid fever, tuberculosis, and diphtheria. Pasteur’s work showed that microscopic organisms were involved both in the spoilage ...
... when there was no mechanical refrigeration in homes. People were used to having foods spoil, like milk going sour. During this time, many people died from diseases such as typhoid fever, tuberculosis, and diphtheria. Pasteur’s work showed that microscopic organisms were involved both in the spoilage ...
Histology PowerPoint Presentation
... May contain goblet cells and bear cilia Nuclei lie at varying heights within cells ...
... May contain goblet cells and bear cilia Nuclei lie at varying heights within cells ...
Functional role of c-Jun/PP2B in regulation of gene expression
... Microbiology and Immunology, College of Medicine, Nation Cheng Kung University The extracellular matrix (ECM) of tissue stroma affects the proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis of normal epithelial cells. Moreover, aberration of ECM components, as well as its interaction with epithelial ...
... Microbiology and Immunology, College of Medicine, Nation Cheng Kung University The extracellular matrix (ECM) of tissue stroma affects the proliferation, differentiation, and morphogenesis of normal epithelial cells. Moreover, aberration of ECM components, as well as its interaction with epithelial ...
How do cells position their division plane?
... In animal cells mitotic spindle organises both karyokinesis and cytokinesis Astral Microtubules play a key role in mediating position and orientation of spindle ...
... In animal cells mitotic spindle organises both karyokinesis and cytokinesis Astral Microtubules play a key role in mediating position and orientation of spindle ...
Study of Cells
... •There are three main types of fibers in the cytoskeleton: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. ...
... •There are three main types of fibers in the cytoskeleton: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. ...
chromosomes - sandsbiochem
... series of events that cells go through as they grow and develop cells alive cell cycle ...
... series of events that cells go through as they grow and develop cells alive cell cycle ...
Eukaryotic cell
... •There are three main types of fibers in the cytoskeleton: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. ...
... •There are three main types of fibers in the cytoskeleton: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. ...
HIV and the Immune System
... When antobodies have been produced and detected, then seroconversion has taken place. “Sero” is the latin word for blood, so the term means that the blood has changed/is changing. Seroconversion illness is an illness that can be experienced as a result of infection. Usually this takes the form of mi ...
... When antobodies have been produced and detected, then seroconversion has taken place. “Sero” is the latin word for blood, so the term means that the blood has changed/is changing. Seroconversion illness is an illness that can be experienced as a result of infection. Usually this takes the form of mi ...
Title: Cells, Tissues, and Organs (L201) Prelab Check:
... include muscle cells, nerve cells, and red blood cells. A bunch of cells that look alike and work together are called a tissue. Four types of tissue are muscle tissue, epithelial tissue, connective tissue, and nerve tissue. Each of these tissues has different functions. o Your bicep is made of muscl ...
... include muscle cells, nerve cells, and red blood cells. A bunch of cells that look alike and work together are called a tissue. Four types of tissue are muscle tissue, epithelial tissue, connective tissue, and nerve tissue. Each of these tissues has different functions. o Your bicep is made of muscl ...
APChapter11 2014 - Auburn School District
... Can you think of any examples of short and long distance messages sent in your body? Can you think of any cellular messages that are general information for the whole body and others that are specific to certain cell? How can information that is general get to all the cells in the body efficiently? ...
... Can you think of any examples of short and long distance messages sent in your body? Can you think of any cellular messages that are general information for the whole body and others that are specific to certain cell? How can information that is general get to all the cells in the body efficiently? ...
Cell Structure pdf
... Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the main energy transformers of cells • Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the organelles that convert energy to forms that cells can use for work. • Mitochondria are the sites of cellular respiration, generating ATP from the catabolism of sugars, fats, and other fue ...
... Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the main energy transformers of cells • Mitochondria and chloroplasts are the organelles that convert energy to forms that cells can use for work. • Mitochondria are the sites of cellular respiration, generating ATP from the catabolism of sugars, fats, and other fue ...
Review Facts for the Biology SOL
... offspring. Sex cells are produced through meiosis. This allows sexually reproducing organisms to produce genetically differing offspring. The many body cells of an individual organism can e specialized to perform different functions, even though they are all descended from a single cell and contain ...
... offspring. Sex cells are produced through meiosis. This allows sexually reproducing organisms to produce genetically differing offspring. The many body cells of an individual organism can e specialized to perform different functions, even though they are all descended from a single cell and contain ...
Cells, tissues and organs
... I can state that stem cells are involved in growth and repair. I can describe the role of meristems in plants. I can state that non-specialised cells can become any type of plants cell and they contribute to growth. Stem cells Stem cells are unspecialised cells that have the potential to divid ...
... I can state that stem cells are involved in growth and repair. I can describe the role of meristems in plants. I can state that non-specialised cells can become any type of plants cell and they contribute to growth. Stem cells Stem cells are unspecialised cells that have the potential to divid ...
How are Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Alike and
... Prior Knowledge: What prior knowledge should students have for this lesson? 1. Students should have a basic understanding that all organisms are made of cells. 2. Cells provide structure and carry out the major functions of life. 3. There are different types of cells. ...
... Prior Knowledge: What prior knowledge should students have for this lesson? 1. Students should have a basic understanding that all organisms are made of cells. 2. Cells provide structure and carry out the major functions of life. 3. There are different types of cells. ...
sem2 wl2 - WordPress.com
... 25. Esophagus : the passageway from the pharynx until the stomach 26. Liver: an organ that makes bile (pH that digests fats), builds proteins, gets and makes glucose. It also gets nutrients from food. 27. Gallbladder : organ that stores bile and sends it to the duodenum to help it digest fat easier ...
... 25. Esophagus : the passageway from the pharynx until the stomach 26. Liver: an organ that makes bile (pH that digests fats), builds proteins, gets and makes glucose. It also gets nutrients from food. 27. Gallbladder : organ that stores bile and sends it to the duodenum to help it digest fat easier ...
Eph Receptors: Two Ways to Sharpen Boundaries
... boundary cells form at the interface of hindbrain segments [16,17], and recent work suggests that expression of Wnt signals and Notch activation at hindbrain boundaries in zebrafish regulates neurogenesis and the localisation of boundary cells [18,19]. As blocking or knockdown of EphA4 leads to a de ...
... boundary cells form at the interface of hindbrain segments [16,17], and recent work suggests that expression of Wnt signals and Notch activation at hindbrain boundaries in zebrafish regulates neurogenesis and the localisation of boundary cells [18,19]. As blocking or knockdown of EphA4 leads to a de ...
Embo conference series: At the joint edge of cellular microbiology
... Volker Heussler (Bernhard Nocht Inst. Tropical Medicine, Hamburg) Manipulation of host hepatocytes by the malaria parasite ...
... Volker Heussler (Bernhard Nocht Inst. Tropical Medicine, Hamburg) Manipulation of host hepatocytes by the malaria parasite ...
Development of Escherichia coli systemic infection model
... bacteria disseminated from IP liquid to all internal organs as well as to a bloodstream. Infection levels after 6, 24 and 48 h were all comparable (Fig. 4). Highest level of infection was obtained in spleen. ...
... bacteria disseminated from IP liquid to all internal organs as well as to a bloodstream. Infection levels after 6, 24 and 48 h were all comparable (Fig. 4). Highest level of infection was obtained in spleen. ...
interphase and cell division.
... consists of two main phases: one in which the cell carries out its functions, called interphase, and one in which the cell divides, which can include mitosis and cytokinesis. All cells divide, but only eukaryotes undergo mitosis. Each phase in the cell cycle requires a certain period of time-from ho ...
... consists of two main phases: one in which the cell carries out its functions, called interphase, and one in which the cell divides, which can include mitosis and cytokinesis. All cells divide, but only eukaryotes undergo mitosis. Each phase in the cell cycle requires a certain period of time-from ho ...
General Histopathology Practicals
... 2. How do you recognise the mtaplastic process histologically? Pseudostratified ciliated columnar with goblet replaced byh stratified squamous epithelium seen in the same slide. 3. What does it represent? It represents the replacement of an adult cell type with another adult cell type (native to har ...
... 2. How do you recognise the mtaplastic process histologically? Pseudostratified ciliated columnar with goblet replaced byh stratified squamous epithelium seen in the same slide. 3. What does it represent? It represents the replacement of an adult cell type with another adult cell type (native to har ...
The Cell Cycle - english for biology
... (beans, for example take 19 hours for the complete cycle; red blood cells must divide at a rate of 2.5 million per second). Others, such as nerve cells, lose their capability to divide once they reach maturity. Some cells, such as liver cells, retain but do not normally utilize their capacity for di ...
... (beans, for example take 19 hours for the complete cycle; red blood cells must divide at a rate of 2.5 million per second). Others, such as nerve cells, lose their capability to divide once they reach maturity. Some cells, such as liver cells, retain but do not normally utilize their capacity for di ...
The Cell Cycle - english for biology
... (beans, for example take 19 hours for the complete cycle; red blood cells must divide at a rate of 2.5 million per second). Others, such as nerve cells, lose their capability to divide once they reach maturity. Some cells, such as liver cells, retain but do not normally utilize their capacity for di ...
... (beans, for example take 19 hours for the complete cycle; red blood cells must divide at a rate of 2.5 million per second). Others, such as nerve cells, lose their capability to divide once they reach maturity. Some cells, such as liver cells, retain but do not normally utilize their capacity for di ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.