The Five Kingdoms
... Fish – live in water, breathe through gills, are covered by scales, and are cold-blooded ...
... Fish – live in water, breathe through gills, are covered by scales, and are cold-blooded ...
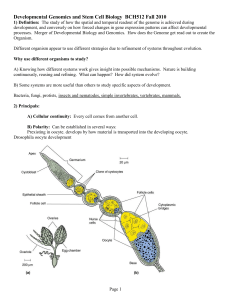
Developmental Genomics
... Many biochemical and molecular biological assays are performed in homogenous solutions. In contrast, within cells, tissues and organs there is often restriction of diffusion and organization of materials in defined spatial patterns. Many of the terms below are used to describe such patterns and will ...
... Many biochemical and molecular biological assays are performed in homogenous solutions. In contrast, within cells, tissues and organs there is often restriction of diffusion and organization of materials in defined spatial patterns. Many of the terms below are used to describe such patterns and will ...
Human body
... Relate some common diseases (i.e., cold, influenza, strep throat, dysentery, fungal infections) to the organisms that cause them (bacteria, viruses, protests, fungi) Differentiate between infectious and noninfectious diseases Explain the role of antibiotics and vaccines in the treatment and preventi ...
... Relate some common diseases (i.e., cold, influenza, strep throat, dysentery, fungal infections) to the organisms that cause them (bacteria, viruses, protests, fungi) Differentiate between infectious and noninfectious diseases Explain the role of antibiotics and vaccines in the treatment and preventi ...
Big Idea 14 : Organization and Development of Living Organisms
... 1. Why is a cell compared to a city? 2. What are two differences between an animal and a plant cell? 3. What is the smallest building block of matter? 4. What is the smallest building block of life? ...
... 1. Why is a cell compared to a city? 2. What are two differences between an animal and a plant cell? 3. What is the smallest building block of matter? 4. What is the smallest building block of life? ...
Some Background Concerning Life Science Content Standards for
... bundles; the xylem is the wood, and the phloem is part of the inner bark. Xylem cells in the sapwood (light colored wood) of trees are like open straws that transport mineral-water (sap). Xylem cells in the heartwood (dark-colored wood in the center) of trees no longer transport mineralwater. Note t ...
... bundles; the xylem is the wood, and the phloem is part of the inner bark. Xylem cells in the sapwood (light colored wood) of trees are like open straws that transport mineral-water (sap). Xylem cells in the heartwood (dark-colored wood in the center) of trees no longer transport mineralwater. Note t ...
4.2 Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell
... *Cytoplasm = cell goo • Cytosol = fluid (water, salts, minerals, biochemicals…) • All cellular interactions and most life interactions occur in watery fluid ...
... *Cytoplasm = cell goo • Cytosol = fluid (water, salts, minerals, biochemicals…) • All cellular interactions and most life interactions occur in watery fluid ...
Pset 5 Solutions
... the embryonic stem cells? Provide a brief explanation for the choice that you made. Since you make the iPS cells from the adult differentiated cells of the patient the iPS cells are genotypically the same as the host, unlike the embryonic cells and they will not be rejected by the immune system of t ...
... the embryonic stem cells? Provide a brief explanation for the choice that you made. Since you make the iPS cells from the adult differentiated cells of the patient the iPS cells are genotypically the same as the host, unlike the embryonic cells and they will not be rejected by the immune system of t ...
lec1
... phospholipid bilayer and thus has all of the general functions of a cell membrane such as acting as a permeability barrier for most molecules and serving as the location for the transport of molecules into the cell. In addition to these functions, prokaryotic membranes also function in energy conser ...
... phospholipid bilayer and thus has all of the general functions of a cell membrane such as acting as a permeability barrier for most molecules and serving as the location for the transport of molecules into the cell. In addition to these functions, prokaryotic membranes also function in energy conser ...
Cell Cycle Lab Instructions
... 2. Place the chromosomes within the nuclear membrane in a pile because they are not visible yet. This represents the chromatin (unwound chromosomes) 3. Put the centrioles (pennies) in the correct area of the cell. 4. With chalk, label he following things: cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear membra ...
... 2. Place the chromosomes within the nuclear membrane in a pile because they are not visible yet. This represents the chromatin (unwound chromosomes) 3. Put the centrioles (pennies) in the correct area of the cell. 4. With chalk, label he following things: cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear membra ...
Internal Environment
... As we saw in chapter 2 (pages 52-56), cells have connections with other cells and in some cases, small molecules can pass from one cell to another through those connections.this provides only limited communication. In addition, communication between cells can take place by means of chemical messenge ...
... As we saw in chapter 2 (pages 52-56), cells have connections with other cells and in some cases, small molecules can pass from one cell to another through those connections.this provides only limited communication. In addition, communication between cells can take place by means of chemical messenge ...
Plasma Membrane Discussion
... Molecules are moved out of the cell by vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve ...
... Molecules are moved out of the cell by vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve ...
Supplemental File S3. Acting Transport-Think-pair
... If you are an ion, consider whether you are “inclined” to cross the membrane under current conditions. Why or why not? If allowed, Na+ would flow into the cell down its electrochemical gradient. The possible movement of K + is less straightforward as the concentration gradient of K+ would make it li ...
... If you are an ion, consider whether you are “inclined” to cross the membrane under current conditions. Why or why not? If allowed, Na+ would flow into the cell down its electrochemical gradient. The possible movement of K + is less straightforward as the concentration gradient of K+ would make it li ...
CHAPTER 5 – HOMEOSTASIS + TRANSPORT
... substances go in or out of cells. Some substances can cross the cell membrane without any input of energy – known as passive transport Let’s look at some types of passive transport… ...
... substances go in or out of cells. Some substances can cross the cell membrane without any input of energy – known as passive transport Let’s look at some types of passive transport… ...
Chapter 8 Cells and Their Environment Section 1 : Cell Membrane
... environment. Individual cells, as well as organisms, must maintain homeostasis in order to live. • Cells are suspended in a fluid environment. Even the cell membrane is fluid. It is made up of a “sea” of lipids in which proteins float. • By allowing some materials but not others to enter the cell, t ...
... environment. Individual cells, as well as organisms, must maintain homeostasis in order to live. • Cells are suspended in a fluid environment. Even the cell membrane is fluid. It is made up of a “sea” of lipids in which proteins float. • By allowing some materials but not others to enter the cell, t ...
No Slide Title
... What might this suggest about the structure of the cell membrane? Answer: This suggests that the cell membrane’s inner and outer layers have essentially the same structure and are, therefore, interchangeable. ...
... What might this suggest about the structure of the cell membrane? Answer: This suggests that the cell membrane’s inner and outer layers have essentially the same structure and are, therefore, interchangeable. ...
DESKTOP YARN MITOSIS/MEIOSIS SET UP AHEAD OF TIME: Cut
... Walk students through the phases of mitosis and have them move the yarn pieces on their desks as each step is discussed. After they have practiced all the phases, quiz them by naming different phases and have them create them on their desks. Activity can be repeated when learning about meiosis so st ...
... Walk students through the phases of mitosis and have them move the yarn pieces on their desks as each step is discussed. After they have practiced all the phases, quiz them by naming different phases and have them create them on their desks. Activity can be repeated when learning about meiosis so st ...
The Road Not Taken
... • heterotrophic because they were unable to synthesize organic compounds from inorganic precursors ,but instead had to obtain preformed organic compounds from ...
... • heterotrophic because they were unable to synthesize organic compounds from inorganic precursors ,but instead had to obtain preformed organic compounds from ...
Notes - Brookings School District
... Indicator 1: Understand the fundamental structures, functions, classifications, and mechanisms found in living things. 9-12.L.1.1. Students are able to relate cellular functions and processes to specialized structures within cells. Transport ...
... Indicator 1: Understand the fundamental structures, functions, classifications, and mechanisms found in living things. 9-12.L.1.1. Students are able to relate cellular functions and processes to specialized structures within cells. Transport ...
Cell Transport - Effingham County Schools
... gradient with the aid of a protein molecule. • Most glucose moves this way ...
... gradient with the aid of a protein molecule. • Most glucose moves this way ...
Immune System lecture
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
... higher temperature helps defense inhibits bacterial growth stimulates phagocytosis speeds up repair of tissues causes liver & spleen to store ...
Sci 14_Unit C_
... 1. Describe, in general terms, the exchange of matter by the digestive and circulatory systems, the functional relationship between the two systems and the need for a healthy diet and lifestyle • assess the nutrient components of prepared foods by reading labels, and evaluate a variety of popular di ...
... 1. Describe, in general terms, the exchange of matter by the digestive and circulatory systems, the functional relationship between the two systems and the need for a healthy diet and lifestyle • assess the nutrient components of prepared foods by reading labels, and evaluate a variety of popular di ...
Poultry Biology - Central Web Server 2
... provide a chamber, separated from the rest of the cell=s metabolic processes, for the chemical modification of some of the proteins made by ribosomes. Ribosomes make some proteins for immediate use in the open liquid of the cell (cytoplasm). But if the protein is one whose function inside the cell c ...
... provide a chamber, separated from the rest of the cell=s metabolic processes, for the chemical modification of some of the proteins made by ribosomes. Ribosomes make some proteins for immediate use in the open liquid of the cell (cytoplasm). But if the protein is one whose function inside the cell c ...
Transport across the Plasma Membrane
... Solution- a liquid with one or more substances dissolved in it Solvent- the liquid that the solute is dissolved in Solute- the substance dissolved in a solution Concentration- how strong it is the solute/volume (percentage) ...
... Solution- a liquid with one or more substances dissolved in it Solvent- the liquid that the solute is dissolved in Solute- the substance dissolved in a solution Concentration- how strong it is the solute/volume (percentage) ...
Submission - Provisions of the Research Involving Embryos and
... use? The first concern is a practical one: adult stem cells are more difficult than embryonic ones to grow in culture and may not be able to produce the very large numbers of cells required to treat large numbers of patients. This is a relatively trivial objection for at least two reasons. First, im ...
... use? The first concern is a practical one: adult stem cells are more difficult than embryonic ones to grow in culture and may not be able to produce the very large numbers of cells required to treat large numbers of patients. This is a relatively trivial objection for at least two reasons. First, im ...
Transport across the Plasma Membrane
... Solution- a liquid with one or more substances dissolved in it Solvent- the liquid that the solute is dissolved in Solute- the substance dissolved in a solution Concentration- how strong it is the solute/volume (percentage) ...
... Solution- a liquid with one or more substances dissolved in it Solvent- the liquid that the solute is dissolved in Solute- the substance dissolved in a solution Concentration- how strong it is the solute/volume (percentage) ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.