F 6 Biology - Ch 4: Cellular Organization Name: ( )
... 3 form a framework along which the cell wall is laid down 5 form centrioles of the spindle during cell division 4.2.14 Cilia and flagella ...
... 3 form a framework along which the cell wall is laid down 5 form centrioles of the spindle during cell division 4.2.14 Cilia and flagella ...
ACTIVITY: OSMOSIS AND DIFFUSION, IMPORTANCE OF CELL
... way that will change the weights as they were coming out of the beaker. 5. Analysis: If you have at least three groups of students in class, you can replicate the results 3 times for each treatment (note there are 6 treatments). Data can be plugged into the excel worksheet provided, or students can ...
... way that will change the weights as they were coming out of the beaker. 5. Analysis: If you have at least three groups of students in class, you can replicate the results 3 times for each treatment (note there are 6 treatments). Data can be plugged into the excel worksheet provided, or students can ...
HW1HeLaCellsHW2014
... Her cells would grow and divide, grow and divide. They quickly multiplied. This was remarkable. For 30 years scientists had been trying to grow “immortal cell lines: human cells that would reproduce endlessly in test tubes. These human cells could then provide a steady supply of cells for medical re ...
... Her cells would grow and divide, grow and divide. They quickly multiplied. This was remarkable. For 30 years scientists had been trying to grow “immortal cell lines: human cells that would reproduce endlessly in test tubes. These human cells could then provide a steady supply of cells for medical re ...
cell culture vessel
... • 1948: Earle isolated mouse L fibroblasts which formed clones from single cells. Fischer developed a chemically defined medium, CMRL 1066. • 1952: Gey established a continuous cell line from a human cervical carcinoma known as HeLa (Helen Lane) cells. Dulbecco developed plaque assay for animal viru ...
... • 1948: Earle isolated mouse L fibroblasts which formed clones from single cells. Fischer developed a chemically defined medium, CMRL 1066. • 1952: Gey established a continuous cell line from a human cervical carcinoma known as HeLa (Helen Lane) cells. Dulbecco developed plaque assay for animal viru ...
Slide ()
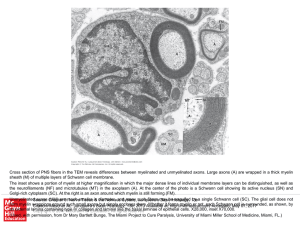
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
Lymphatic System
... to cell contact. May also be cells involved in the aging process – may be involved in apoptosis (programmed cell death). ...
... to cell contact. May also be cells involved in the aging process – may be involved in apoptosis (programmed cell death). ...
Chapter 5 Review Answers (1)
... Growth- When a cell surpasses a maximum size, the nucleus cannot control cell functions and material is unable to reach all parts of the cell. The cell must then divide if the organism is to grow. Reproduction- For some organisms, cell division is the mode in which they create more life (such as in ...
... Growth- When a cell surpasses a maximum size, the nucleus cannot control cell functions and material is unable to reach all parts of the cell. The cell must then divide if the organism is to grow. Reproduction- For some organisms, cell division is the mode in which they create more life (such as in ...
Cells B - Depoali
... Multiple Choice (1 point each) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
... Multiple Choice (1 point each) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ...
name date ______ period
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more lik ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE: Circle all that are TRUE. There may be MORE THAN ONE correct answer. 1. Which of the following is TRUE of a cell membranes? A. Cell membranes allow ALL substances to pass through easily B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more lik ...
Adult neural stem cells, which are commonly thought of as
... down very early during embryonic development. It’s almost as if the embryo is planning for the future.” The study was published on June 18 in Cell. Adult stem cells are found in organ systems throughout the body. Most are undifferentiated, meaning they have the potential to develop into several diff ...
... down very early during embryonic development. It’s almost as if the embryo is planning for the future.” The study was published on June 18 in Cell. Adult stem cells are found in organ systems throughout the body. Most are undifferentiated, meaning they have the potential to develop into several diff ...
Cell Organelle Chart
... c. Helps in digestion for cell by breaking down food particles into smaller pieces for the mitochondria d. Digests old and warn out cell parts so new ones can be made e. Pushes waste vacuoles out the cell membrane – takes out the trash 4. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE – Support and Protection & Doorway to nucleu ...
... c. Helps in digestion for cell by breaking down food particles into smaller pieces for the mitochondria d. Digests old and warn out cell parts so new ones can be made e. Pushes waste vacuoles out the cell membrane – takes out the trash 4. NUCLEAR MEMBRANE – Support and Protection & Doorway to nucleu ...
Cell Division Review Sheet
... 100 - This phase technically happens before mitosis. 200 - After cytokinesis, each cell has this many chromosomes in a healthy human. 300 - These are the products of mitosis. 400 - This is what would happen if a cell went through mitosis but not cytokinesis. 500 - After interphase, the cell contains ...
... 100 - This phase technically happens before mitosis. 200 - After cytokinesis, each cell has this many chromosomes in a healthy human. 300 - These are the products of mitosis. 400 - This is what would happen if a cell went through mitosis but not cytokinesis. 500 - After interphase, the cell contains ...
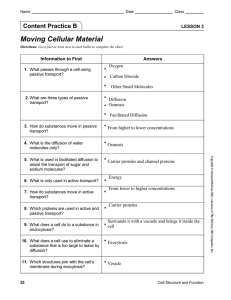
Moving Cellular Material
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
... 6. What is only used in active transport? 7. How do substances move in active transport? 8. Which proteins are used in active and passive transport? 9. What does a cell do to a substance in endocytosis? 10. What does a cell use to eliminate a substance that is too large to leave by diffusion? 11. Wh ...
I. Evolution from unicellular to multicellular organisms II. Evolution
... Land plants have distinct developmental programs in haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte) generations. Although usually the two programs strictly alternate at fertilization and meiosis, one program can be induced during the other program. In a process called apogamy, cells of the gametophyt ...
... Land plants have distinct developmental programs in haploid (gametophyte) and diploid (sporophyte) generations. Although usually the two programs strictly alternate at fertilization and meiosis, one program can be induced during the other program. In a process called apogamy, cells of the gametophyt ...
NAME DATE ______ PERIOD _____
... 8. The molecule used by cells to store genetic information = DNA 9. An organism with a nuclear membrane and organelles surrounded by membranes = EUKARYOTES 10. The NUCLEUS is surrounded by a double membrane, contains the cells DNA, and acts as the control center. 11. One or two long, hair-like struc ...
... 8. The molecule used by cells to store genetic information = DNA 9. An organism with a nuclear membrane and organelles surrounded by membranes = EUKARYOTES 10. The NUCLEUS is surrounded by a double membrane, contains the cells DNA, and acts as the control center. 11. One or two long, hair-like struc ...
Mechanistic Ideas of Life: The Cell Theory
... – “This variety in the elementary parts seemed to hold some relation to their more diversified physiological function in animals, so that it might be established as a principle, that every diversity in the physiological signification of an organ requires a difference in its elementary particles; and ...
... – “This variety in the elementary parts seemed to hold some relation to their more diversified physiological function in animals, so that it might be established as a principle, that every diversity in the physiological signification of an organ requires a difference in its elementary particles; and ...
kaoshiung-talk-scrip..
... various energy-consuming cellular processes ) coupled to proton movement down the electrochemical gradient. It is also called the F0F1 complex. Other complexes include proteasome, ribosome (part of it being r-RNA), DNA and RNA polymerase, and so on. 3. Gene expression and Microarray. There are many ...
... various energy-consuming cellular processes ) coupled to proton movement down the electrochemical gradient. It is also called the F0F1 complex. Other complexes include proteasome, ribosome (part of it being r-RNA), DNA and RNA polymerase, and so on. 3. Gene expression and Microarray. There are many ...
Cells Pre-Test - ESC-2
... 1 The food that you eat travels from your mouth, down your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the followin ...
... 1 The food that you eat travels from your mouth, down your esophagus, into your stomach, and through your small and large intestines before your body rids itself of solid waste. As the food passes through your body, it is digested, and you get important nutrients from the food. Which of the followin ...
chapter28_Sections 1
... • Because it divides frequently, epithelium is the animal tissue most likely to become cancerous • An epithelial cell cancer is called a carcinoma • About 95% of skin cancers are carcinomas • Breast cancers are usually carcinomas of epithelial cells that line milk ducts, or of breast glandular epith ...
... • Because it divides frequently, epithelium is the animal tissue most likely to become cancerous • An epithelial cell cancer is called a carcinoma • About 95% of skin cancers are carcinomas • Breast cancers are usually carcinomas of epithelial cells that line milk ducts, or of breast glandular epith ...
Lymphatic System
... to cell contact. May also be cells involved in the aging process – may be involved in apoptosis (programmed cell death). ...
... to cell contact. May also be cells involved in the aging process – may be involved in apoptosis (programmed cell death). ...
Life is Cellular
... 1838: Schleiden concluded that plants are made of cells. 1839: Schwann concluded that animals are made of cells. 1858: Virchow concluded that new cells came only from ...
... 1838: Schleiden concluded that plants are made of cells. 1839: Schwann concluded that animals are made of cells. 1858: Virchow concluded that new cells came only from ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... 1st Item Specification: Identify major cell structures and their functions. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. Which organelles are most directly involved in transporting materials out of the cell? A. Nucleus and Ribosomes B. Chloroplast and Mitochondria C. Cell Membrane and Cell wall D. Golgi apparatus ...
... 1st Item Specification: Identify major cell structures and their functions. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. Which organelles are most directly involved in transporting materials out of the cell? A. Nucleus and Ribosomes B. Chloroplast and Mitochondria C. Cell Membrane and Cell wall D. Golgi apparatus ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... a. the ratio between the size of the image produced by the microscope and the actual size of the object. b. the degree to which a particular structure looks different from other structures around it. c. how well a structure takes up certain dyes. d. clarity of an image. e. the degree to which the im ...
... a. the ratio between the size of the image produced by the microscope and the actual size of the object. b. the degree to which a particular structure looks different from other structures around it. c. how well a structure takes up certain dyes. d. clarity of an image. e. the degree to which the im ...
Cell Notes
... Endosymbiosis theory: All organelles seem to share many properties with bacteria. Lynn Margulis proposed endosymbiont hypothesis: that organelles derived from ancient colonization of large bacteria (became the eukaryotic cell) by smaller bacteria (became the mitochondria, chloroplast, etc.) Symbiosi ...
... Endosymbiosis theory: All organelles seem to share many properties with bacteria. Lynn Margulis proposed endosymbiont hypothesis: that organelles derived from ancient colonization of large bacteria (became the eukaryotic cell) by smaller bacteria (became the mitochondria, chloroplast, etc.) Symbiosi ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.