Origins of Mass - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... of the electrons surrounding a nucleus, such as occur in chemical reactions or mechanical responses, do not bring anything approaching that energy into play. Thus the nuclei remain in their ground states, and effectively behave as ideal, structureless particles. In particular: Although they are not ...
... of the electrons surrounding a nucleus, such as occur in chemical reactions or mechanical responses, do not bring anything approaching that energy into play. Thus the nuclei remain in their ground states, and effectively behave as ideal, structureless particles. In particular: Although they are not ...
Is the Zero-Point Energy Real? - General Guide To Personal and
... the prediction of observable effects that were not in fact detected. Why was it thought to exist at all? The answer one often meets is that since light and electromagnetic forces propagate as waves, their must be a substratum which is in motion; something has to wave. But this answer is unedifying. ...
... the prediction of observable effects that were not in fact detected. Why was it thought to exist at all? The answer one often meets is that since light and electromagnetic forces propagate as waves, their must be a substratum which is in motion; something has to wave. But this answer is unedifying. ...
BARRIER PENETRATION AND INSTANTONS J. ZINN - IPhT
... at the end of section 1.1). The Euclidean formalism based on calculating the density matrix at thermal equilibrium e−βH , describes formally an evolution in imaginary time. We verify, in this chapter, that indeed it allows evaluating barrier penetration effects. Although the methods can be generaliz ...
... at the end of section 1.1). The Euclidean formalism based on calculating the density matrix at thermal equilibrium e−βH , describes formally an evolution in imaginary time. We verify, in this chapter, that indeed it allows evaluating barrier penetration effects. Although the methods can be generaliz ...
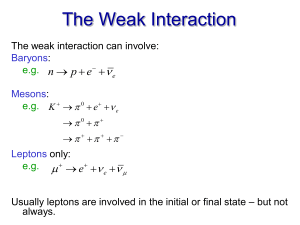
The Weak Interaction
... Therefore we see that a W or W+ must change the quark flavor at the vertex in order to conserve charge. Now we see why S 1 implies that the weak interaction is involved, but S 0 does not imply that the weak interaction is not involved. ...
... Therefore we see that a W or W+ must change the quark flavor at the vertex in order to conserve charge. Now we see why S 1 implies that the weak interaction is involved, but S 0 does not imply that the weak interaction is not involved. ...
Compact dimensions
... Q. Why is gravity so weak compared to the other interactions? Naturalness : Very large or very small numbers are unstable under quantum corrections Need some underlying symmetry to protect them ...
... Q. Why is gravity so weak compared to the other interactions? Naturalness : Very large or very small numbers are unstable under quantum corrections Need some underlying symmetry to protect them ...
Symmetry Violation of Time Reversal in Third Order Vertex Angle
... interaction. We will prove that when renormalization effect is considered, the third order vertex angles processes of electromagnetic interaction violate time reversal symmetry. The situation is similar to that the regularizations of some high order processes cause chirality’s anomalies and violates ...
... interaction. We will prove that when renormalization effect is considered, the third order vertex angles processes of electromagnetic interaction violate time reversal symmetry. The situation is similar to that the regularizations of some high order processes cause chirality’s anomalies and violates ...
STATISTICAL FIELD THEORY
... physics and in particular in the Standard Model of elementary particles [1]. A second reason is that soon after the development of the renormalization group methods for critical phenomena [2], it was realized that the same methods can in fact be used to describe the large-scale properties of manypar ...
... physics and in particular in the Standard Model of elementary particles [1]. A second reason is that soon after the development of the renormalization group methods for critical phenomena [2], it was realized that the same methods can in fact be used to describe the large-scale properties of manypar ...
An essay on condensed matter physics in the twentieth century
... subfield of physics. The writer estimates that at least a third of all American physicists identify themselves with CMP and with the closely related field of materials science. A look at the 1998 Bulletin of the March Meeting of the American Physical Society shows about 4500 papers in these fields. ...
... subfield of physics. The writer estimates that at least a third of all American physicists identify themselves with CMP and with the closely related field of materials science. A look at the 1998 Bulletin of the March Meeting of the American Physical Society shows about 4500 papers in these fields. ...
Electroweak Unification as Classical Field Theory
... only on subatomic scales. There are no macroscopic weak force phenomena for us to experience firsthand the way we can experience electromagnetic phenomena by handling magnets, circuit components, and so on. ...
... only on subatomic scales. There are no macroscopic weak force phenomena for us to experience firsthand the way we can experience electromagnetic phenomena by handling magnets, circuit components, and so on. ...
TWO-STATE SYSTEMS
... To adopt such practice would be to assign distinct physical dimension to every point on the a -sphere. Which would be fine and natural if we possessed only a limited collection of meters. Made attractive by the circumstance that they are addressable (if not, at the moment, by us) are some of the ques ...
... To adopt such practice would be to assign distinct physical dimension to every point on the a -sphere. Which would be fine and natural if we possessed only a limited collection of meters. Made attractive by the circumstance that they are addressable (if not, at the moment, by us) are some of the ques ...
AMO-1: Table of Contents Fall 2004, C. D. Lin
... Exercise 5. You can learn a lot about hydrogen atom using Bohr model. Go over the derivation and use atomic units. Now remember to use reduced mass to go from two-body system to one-body problem. Let the total energy of the ground state of H is -13.6 eV. (1) What is the energy difference between th ...
... Exercise 5. You can learn a lot about hydrogen atom using Bohr model. Go over the derivation and use atomic units. Now remember to use reduced mass to go from two-body system to one-body problem. Let the total energy of the ground state of H is -13.6 eV. (1) What is the energy difference between th ...
J - Laboratory of Molecular Interactions
... fluorine coupling constants. • Very accurate calculations for small molecules can be carried out by means of MCSCF i CC. (In such calculations also rovibrational effects should be accounted for.) • Standard basis sets of atomic orbitals are not suitable for calculations of spin-spin coupling constan ...
... fluorine coupling constants. • Very accurate calculations for small molecules can be carried out by means of MCSCF i CC. (In such calculations also rovibrational effects should be accounted for.) • Standard basis sets of atomic orbitals are not suitable for calculations of spin-spin coupling constan ...
Theory of ferromagnetism in planar heterostructures of Mn,III
... ferromagnetism in planar heterostructures of ferromagnetic III-V semiconductors. The model combines the standard procedure to calculate the electronic structure of planar semiconductor heterostructures in the envelope-function formalism with a mean-field theory for the ferromagnetic state. Our goal ...
... ferromagnetism in planar heterostructures of ferromagnetic III-V semiconductors. The model combines the standard procedure to calculate the electronic structure of planar semiconductor heterostructures in the envelope-function formalism with a mean-field theory for the ferromagnetic state. Our goal ...
PHYS4210 Electromagnetic Theory Quiz 1 Feb 2010
... 2. What is the magnetic dipole moment for a square loop of wire of side L and carrying a current I? A. IL2 /c B. πIL2 /c C. IL2 /4c D. 4πIL2 /c E. πIL2 /4c 3. A charge q moves with constant velocity v through a region of electric field E and magnetic field B. The vectors v, E, and B are all mutually ...
... 2. What is the magnetic dipole moment for a square loop of wire of side L and carrying a current I? A. IL2 /c B. πIL2 /c C. IL2 /4c D. 4πIL2 /c E. πIL2 /4c 3. A charge q moves with constant velocity v through a region of electric field E and magnetic field B. The vectors v, E, and B are all mutually ...
Theoretical Studies of Magnetic Monopole
... The theory of electromagnetism (EM) was one of the most profound and fruitful theories in modern physics. From a theoretical respective, the ideas used to construct the theory had laid down the foundations of some much more fundamental theories. Among them, there are the theory of quantum electrodyn ...
... The theory of electromagnetism (EM) was one of the most profound and fruitful theories in modern physics. From a theoretical respective, the ideas used to construct the theory had laid down the foundations of some much more fundamental theories. Among them, there are the theory of quantum electrodyn ...
Here
... by an all-pervading medium that had inertia and elasticity but no specified mechanism. In what seemed like a conjuring trick, he used Joseph Louis Lagrange’s method, which treated a dynamic system like a ‘black box’: by specifying the system’s general characteristics it was possible to derive the ou ...
... by an all-pervading medium that had inertia and elasticity but no specified mechanism. In what seemed like a conjuring trick, he used Joseph Louis Lagrange’s method, which treated a dynamic system like a ‘black box’: by specifying the system’s general characteristics it was possible to derive the ou ...
Grand unification and enhanced quantum gravitational effects
... be described by a grand unified gauge theory at sufficiently high energy scales has intrigued physicists for many years [1]. There are hints that the renormalization group evolution of the coupling constants of the standard model of particle physics, or possibly of its supersymmetric version, causes ...
... be described by a grand unified gauge theory at sufficiently high energy scales has intrigued physicists for many years [1]. There are hints that the renormalization group evolution of the coupling constants of the standard model of particle physics, or possibly of its supersymmetric version, causes ...
QCD --- Quantum Chromodynamics
... Don’t carry colour, “zero colour charge” Î Don’t participate in strong interaction ...
... Don’t carry colour, “zero colour charge” Î Don’t participate in strong interaction ...
Electromagnetic Fields
... When Up = (mc2), then relativistic behavior must occur. Failure of the dipole approximation: • Upper limit on frequency (lower limit on wavelength): Dipole approximation requires >> size of bound system. • Lower limit on frequency (upper limit on wavelength): Dipole approximation limited by magnet ...
... When Up = (mc2), then relativistic behavior must occur. Failure of the dipole approximation: • Upper limit on frequency (lower limit on wavelength): Dipole approximation requires >> size of bound system. • Lower limit on frequency (upper limit on wavelength): Dipole approximation limited by magnet ...