Name - Humble ISD
... Eukaryotic cells contain a _nucleus_______ and other membrane-bound structures. Eukaryotic organisms may be _unicellular (single-celled)_____ or _multicellular____. In multicellular organisms, cells become _specialized______. II. DISCOVERY OF CELLS (pp.169-172) A. History of Microscopes The inventio ...
... Eukaryotic cells contain a _nucleus_______ and other membrane-bound structures. Eukaryotic organisms may be _unicellular (single-celled)_____ or _multicellular____. In multicellular organisms, cells become _specialized______. II. DISCOVERY OF CELLS (pp.169-172) A. History of Microscopes The inventio ...
Gametogenesis, Fertilization and Blastula Formation
... Continuous process in adult males; can make 100’s of millions of sperm per day For each cell that enters meiosis, 4 sperm cells are produced It is continuous for the reproductive life of a male and occurs in an uninterrupted sequence Sperm structure Head: contains the haploid nucleus and an acro ...
... Continuous process in adult males; can make 100’s of millions of sperm per day For each cell that enters meiosis, 4 sperm cells are produced It is continuous for the reproductive life of a male and occurs in an uninterrupted sequence Sperm structure Head: contains the haploid nucleus and an acro ...
Virtual Cell Worksheet
... The thick ropy strands are the _____________________________. The large solid spot is the _____________________. The nucleolus is a knot of __________________ chromatin. It manufactures __________________________. Dissolve and move to next page. The nucleolus is a spot of condensed _______________. ...
... The thick ropy strands are the _____________________________. The large solid spot is the _____________________. The nucleolus is a knot of __________________ chromatin. It manufactures __________________________. Dissolve and move to next page. The nucleolus is a spot of condensed _______________. ...
Chapter 3 - Crosby ISD
... NUCLEUS: the central core, control center or “brain” of the cell – The largest organelle of the cell – Filled with nucleoplasm – Contains 3 distinct regions A. Nuclear membrane (envelope) B. Nucleoli C. Chromatin ...
... NUCLEUS: the central core, control center or “brain” of the cell – The largest organelle of the cell – Filled with nucleoplasm – Contains 3 distinct regions A. Nuclear membrane (envelope) B. Nucleoli C. Chromatin ...
Animal and Plant Organelles
... Where Are They FoundRibosomes are found in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryote. ...
... Where Are They FoundRibosomes are found in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryote. ...
“differential reproductive advantage” within a population This is
... A person with type AB blood mates with a person with type O blood will produce these phenotypes in their offspring ...
... A person with type AB blood mates with a person with type O blood will produce these phenotypes in their offspring ...
Vocabulary Inventory
... On our planet Earth, life comes in a variety of forms. We have about 2 million species of animals (such as elephants), 270,000 types of plants (such as sunflowers), 4,000 kinds of bacteria (such as E. coli), 80,000 different protists (such as algae), and 72,000 assorted fungi (such as mushrooms). Wh ...
... On our planet Earth, life comes in a variety of forms. We have about 2 million species of animals (such as elephants), 270,000 types of plants (such as sunflowers), 4,000 kinds of bacteria (such as E. coli), 80,000 different protists (such as algae), and 72,000 assorted fungi (such as mushrooms). Wh ...
Name
... cell membrane cell wall chloroplast centrioles centrosome cytoplasm endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus lysosome mitochondria nuclear membrane nucleolus nucleus ribosomes vacuole 1. liquid inside the cell, mostly water 2. made of lipids & proteins, it is the boundary of the cell; it controls what ...
... cell membrane cell wall chloroplast centrioles centrosome cytoplasm endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus lysosome mitochondria nuclear membrane nucleolus nucleus ribosomes vacuole 1. liquid inside the cell, mostly water 2. made of lipids & proteins, it is the boundary of the cell; it controls what ...
Golgi apparatus
... • The basic processes necessary for living things to survive are the same for a single cell as they are for a more complex organism. • A single-celled organism has to conduct all life processes by itself. • A multi-cellular organism has groups of cells that specialize to perform specific functions. ...
... • The basic processes necessary for living things to survive are the same for a single cell as they are for a more complex organism. • A single-celled organism has to conduct all life processes by itself. • A multi-cellular organism has groups of cells that specialize to perform specific functions. ...
What to know Chap 11
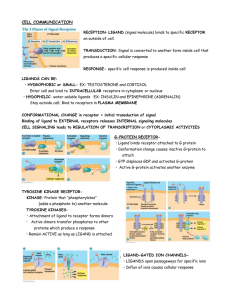
... TYROSINE KINASE RECEPTORKINASE- Protein that “phosphorylates” (adds a phosphate to) another molecule TYROSINE KINASES: • Attachment of ligand to receptor forms dimers • Active dimers transfer phosphates to other proteins which produce a response • Remain ACTIVE as long as LIGAND is attached ...
... TYROSINE KINASE RECEPTORKINASE- Protein that “phosphorylates” (adds a phosphate to) another molecule TYROSINE KINASES: • Attachment of ligand to receptor forms dimers • Active dimers transfer phosphates to other proteins which produce a response • Remain ACTIVE as long as LIGAND is attached ...
Cell Comparison *All in the Family*
... They have cell walls They use photosynthesis Are typically green from chlorophyll Contain a chloroplast structure Are square from the cell walls presence And have one large central vacuole ...
... They have cell walls They use photosynthesis Are typically green from chlorophyll Contain a chloroplast structure Are square from the cell walls presence And have one large central vacuole ...
1367057852.
... 7. Viruses can be classified as living things because (a) They have a genetic material on their own when left outside the living cell (b) They have a genetic material composed of either DNA or RNA (c) They crystalise when removed out of their natural medium (d) They have double membrane organelle 8. ...
... 7. Viruses can be classified as living things because (a) They have a genetic material on their own when left outside the living cell (b) They have a genetic material composed of either DNA or RNA (c) They crystalise when removed out of their natural medium (d) They have double membrane organelle 8. ...
Biology Study Guide: 7
... 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? ...
... 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? ...
Amoeba - Biology Resources
... cytoplasm; the living substance in which all the chemical reactions necessary for life are carried out. ectoplasm is a clear gel-like layer enclosing the endoplasm which is more fluid and contains granules and other inclusions. nucleus; controls most of the reactions taking place in the cell and pla ...
... cytoplasm; the living substance in which all the chemical reactions necessary for life are carried out. ectoplasm is a clear gel-like layer enclosing the endoplasm which is more fluid and contains granules and other inclusions. nucleus; controls most of the reactions taking place in the cell and pla ...
3.10 Practice Exam - Rocky View Schools
... (a) compound light microscope (b) scanning electron microscope (c) transmission electron microscope (d) scanning tunnelling microscope 8. A ribosome (a) does not have a cell wall (b) is not surrounded by a membrane (c) does not contain cytoplasm (d) all of the above 9. Which structure is found in ro ...
... (a) compound light microscope (b) scanning electron microscope (c) transmission electron microscope (d) scanning tunnelling microscope 8. A ribosome (a) does not have a cell wall (b) is not surrounded by a membrane (c) does not contain cytoplasm (d) all of the above 9. Which structure is found in ro ...
Induction MSS Cell City Participant
... Below is a list of parts of a cell and their general functions. You are to determine a part of a city that would perform a similar function and add it to the chart. Then you are to draw your city in the general shape of a cell. {Note: students would not be given the clues / descriptions or a picture ...
... Below is a list of parts of a cell and their general functions. You are to determine a part of a city that would perform a similar function and add it to the chart. Then you are to draw your city in the general shape of a cell. {Note: students would not be given the clues / descriptions or a picture ...
CELL (Introduction)
... • Consists of 4 to 5 layers of flat vesicles closely related to the ER. • Prominent in secretory cells.(those that secrete enzymes and ...
... • Consists of 4 to 5 layers of flat vesicles closely related to the ER. • Prominent in secretory cells.(those that secrete enzymes and ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.