CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL
... • The nucleus contains DNA organized with proteins into a complex called chromatin: • In non-dividing cell chromatin appear as diffuse mass. • when the cell prepares to divide, the chromatin fibers coil up to be seen as separate structures, chromosomes. • Each eukaryotic species has a characteristi ...
... • The nucleus contains DNA organized with proteins into a complex called chromatin: • In non-dividing cell chromatin appear as diffuse mass. • when the cell prepares to divide, the chromatin fibers coil up to be seen as separate structures, chromosomes. • Each eukaryotic species has a characteristi ...
5 Homeostasis and Transport adn Cell Structure
... ◦ Include cells from plants, animals, fungi and protists ...
... ◦ Include cells from plants, animals, fungi and protists ...
2. a) Protein channels help to move material across the cell
... 2. a) Protein channels help to move material across the cell membrane. b) Carbohydrates act like chemical identification cards allowing cells to identify one another 3. The plasma membrane is described to be fluid because of its lipids and membrane proteins that move laterally or sideways ...
... 2. a) Protein channels help to move material across the cell membrane. b) Carbohydrates act like chemical identification cards allowing cells to identify one another 3. The plasma membrane is described to be fluid because of its lipids and membrane proteins that move laterally or sideways ...
CSP_7-16-01_outline.rtf
... the mosaic of proteins allowing for flexibility and movement. Think about the balls on top of a pool. 2. The interior of the cell is filled with a fluid called cytoplasm. a. This fluid consists of mostly water, salts and organic molecules such as nucleotides, sugars and proteins that are important i ...
... the mosaic of proteins allowing for flexibility and movement. Think about the balls on top of a pool. 2. The interior of the cell is filled with a fluid called cytoplasm. a. This fluid consists of mostly water, salts and organic molecules such as nucleotides, sugars and proteins that are important i ...
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Worksheet
... The first cells to appear on Earth were prokaryotic cells. A prokaryote is an organism made of a single prokaryotic cell. The earliest prokaryotes may have arisen more than 2.5 billion years ago. Bacteria are prokaryotes. They are very small cells with a simple structure. Prokaryotes do not have a n ...
... The first cells to appear on Earth were prokaryotic cells. A prokaryote is an organism made of a single prokaryotic cell. The earliest prokaryotes may have arisen more than 2.5 billion years ago. Bacteria are prokaryotes. They are very small cells with a simple structure. Prokaryotes do not have a n ...
What are cells?
... • Direct all cell’s activities • Surrounded by a membrane • Cells with a nuclear membrane: Eukaryotic cells • Those without a nuclear membrane: prokaryotic cells – Ex. One-celled organism; bacteria BACK ...
... • Direct all cell’s activities • Surrounded by a membrane • Cells with a nuclear membrane: Eukaryotic cells • Those without a nuclear membrane: prokaryotic cells – Ex. One-celled organism; bacteria BACK ...
plant_and_animal_Cells
... has many smaller parts that have specific functions. Those smaller parts are called Organelles. Plant cells are different from animal cells because they have 3 organelles that are only found within the plant. Cell wall, Vacuole, and Chloroplasts are only found in Plant cells. The plant needs these o ...
... has many smaller parts that have specific functions. Those smaller parts are called Organelles. Plant cells are different from animal cells because they have 3 organelles that are only found within the plant. Cell wall, Vacuole, and Chloroplasts are only found in Plant cells. The plant needs these o ...
Chapter 4
... Cells are the smallest living units of life • Two types of cells exist on earth: 1. Prokaryotic cells 2. Eukaryotic cells • All cells are surrounded by a phospholipid bilayermade barrier called the plasma membrane. • The semifluid substance within the membrane is the cytosol, containing the organel ...
... Cells are the smallest living units of life • Two types of cells exist on earth: 1. Prokaryotic cells 2. Eukaryotic cells • All cells are surrounded by a phospholipid bilayermade barrier called the plasma membrane. • The semifluid substance within the membrane is the cytosol, containing the organel ...
Cell Organelles - Mr. Brown`s RCMS Seventh Grade Science
... of life • Organelles - small structures inside a cell with specific functions. ...
... of life • Organelles - small structures inside a cell with specific functions. ...
Cells Last minute sheet
... Things to remember in the last hour before the exam: Life processes at the cellular level (This is not a revision sheet – you’ve done that by now - it’s a list of things you might want to remind yourself about …) ...
... Things to remember in the last hour before the exam: Life processes at the cellular level (This is not a revision sheet – you’ve done that by now - it’s a list of things you might want to remind yourself about …) ...
Cell Analogy Rubric
... Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a ½ poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your analogy relates to the organ ...
... Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a ½ poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your analogy relates to the organ ...
Lazar Life Lab- Roles in the Garden Name After working in the
... garden successful. The job of the garden is to produce ___proteins__. How do the jobs in the garden relate to the jobs that are necessary for cells to operate successfully? A cell is the smallest unit of _life_. Your body is made up of trillions of cells with each one working hard to produce _pr ...
... garden successful. The job of the garden is to produce ___proteins__. How do the jobs in the garden relate to the jobs that are necessary for cells to operate successfully? A cell is the smallest unit of _life_. Your body is made up of trillions of cells with each one working hard to produce _pr ...
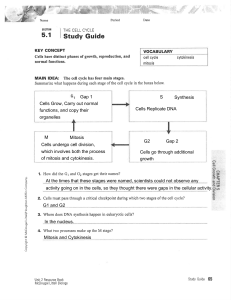
The Cell Cycle and Mitosis:
... • In this last stage of the cell cycle, the cytoplasm and other organelles are distributed to the two ends of the cell. • In an animal cell the cell membrane pinches in called the cleavage furrow. • This separates the dividing cell into 2 new daughter cells. • Each daughter cell has a nucleus with a ...
... • In this last stage of the cell cycle, the cytoplasm and other organelles are distributed to the two ends of the cell. • In an animal cell the cell membrane pinches in called the cleavage furrow. • This separates the dividing cell into 2 new daughter cells. • Each daughter cell has a nucleus with a ...
File
... 4. What are the main differences between plant and animal cells? a. Animal cells are eukaryotes and plant cells are not. b. Plant cells are eukaryotes and animal cells are not. c. Animal cells have cell walls and chloroplasts; plant cells do not. d. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts; anim ...
... 4. What are the main differences between plant and animal cells? a. Animal cells are eukaryotes and plant cells are not. b. Plant cells are eukaryotes and animal cells are not. c. Animal cells have cell walls and chloroplasts; plant cells do not. d. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts; anim ...
Chapter 4: Cellular Structure
... Ribosomes consist of 1 large and 1 small subunit. • both subunits are made of rRNA & ribosomal proteins • smaller, somewhat different from eukaryotic ribosomes • specifically targeted by some antibiotics ...
... Ribosomes consist of 1 large and 1 small subunit. • both subunits are made of rRNA & ribosomal proteins • smaller, somewhat different from eukaryotic ribosomes • specifically targeted by some antibiotics ...
How is life synthesized from non
... This theory proposes that eukaryotic cells arose from symbiosis among several prokaryotic cells. What evidence is there to support this idea? ...
... This theory proposes that eukaryotic cells arose from symbiosis among several prokaryotic cells. What evidence is there to support this idea? ...
Cells Organisms are composed of one to many microscopic cells
... Eukaryotic flagella typically contain a pair of single microtubules, surrounded by a cylinder of nine paired microtubules (9 + 2 arrangement). ...
... Eukaryotic flagella typically contain a pair of single microtubules, surrounded by a cylinder of nine paired microtubules (9 + 2 arrangement). ...
The Anatomy of a Cell
... Even though your body cells have different jobs to do, certain aspects of their internal anatomies (structures) are similar. While doing this project, you will learn the internal anatomy of a generalized cell. Animal cells and plants have many similarities and many differences. Look at the two diffe ...
... Even though your body cells have different jobs to do, certain aspects of their internal anatomies (structures) are similar. While doing this project, you will learn the internal anatomy of a generalized cell. Animal cells and plants have many similarities and many differences. Look at the two diffe ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.