PowerPoint to accompany Hole’s Human Anatomy and
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Classification and Dichotomous Keys
... • Most live in extreme environments like the hot springs of Yellowstone because of their tough outer cell wall and protective enzymes. • Archaea have been around at least 3 billion years and scientists believe they are very closely related to some of Earth’s earliest life forms. ...
... • Most live in extreme environments like the hot springs of Yellowstone because of their tough outer cell wall and protective enzymes. • Archaea have been around at least 3 billion years and scientists believe they are very closely related to some of Earth’s earliest life forms. ...
BME205-Tutorial 6 Solutions2015-06-15 15
... 1. At the gene level where proteins (which control cell activity) are synthesized (usually at a much slower rate). 2. At the protein level where enzymatic activity and cell surface receptors enact control over cell activity (usually at a much faster rate). ...
... 1. At the gene level where proteins (which control cell activity) are synthesized (usually at a much slower rate). 2. At the protein level where enzymatic activity and cell surface receptors enact control over cell activity (usually at a much faster rate). ...
Gene Section FUBP1 (far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1)
... the c-myc promoter is lost. This indicates an important role of FUBP1 in maintaining c-myc transcription to prevent its downregulation and differentiation (Avigan et al., 1990). As the KH motifs were first found to be involved in RNA-binding, it is not surprising that FUBP1 also interacts with speci ...
... the c-myc promoter is lost. This indicates an important role of FUBP1 in maintaining c-myc transcription to prevent its downregulation and differentiation (Avigan et al., 1990). As the KH motifs were first found to be involved in RNA-binding, it is not surprising that FUBP1 also interacts with speci ...
Unit # 3 – Cells, Histology, Integumentary system Test Bank
... b. cellulose and protein c. cellulose and lipids d. lipids and protein 5. Which of the following correctly describes the structural arrangement of the cell membrane? a. a solid, rigid layer of phospholipids with loosely bound protein molecules b. a bilayer of phospholipid molecules in which protein ...
... b. cellulose and protein c. cellulose and lipids d. lipids and protein 5. Which of the following correctly describes the structural arrangement of the cell membrane? a. a solid, rigid layer of phospholipids with loosely bound protein molecules b. a bilayer of phospholipid molecules in which protein ...
MEDICAL BIOLOGY AND GENETICS 1 Comenius
... collision of electrons with air molecules and hence the scattering of electrons are avoided. Along the column, at specific intervals magnetic coils are placed. Just as the light is focused by the glass lenses in a light microscope, these magnetic coils in the electron microscope focus the electron b ...
... collision of electrons with air molecules and hence the scattering of electrons are avoided. Along the column, at specific intervals magnetic coils are placed. Just as the light is focused by the glass lenses in a light microscope, these magnetic coils in the electron microscope focus the electron b ...
Cell-Rubric
... Build a 3-dimensional model of a cell that illustrates all of the basic parts of the cell. Your cell model should have the following characteristics: Major organelles named and labeled Show the 3-dimensional nature of cells Be a typical plant or animal cell-your choice Come with definitions ...
... Build a 3-dimensional model of a cell that illustrates all of the basic parts of the cell. Your cell model should have the following characteristics: Major organelles named and labeled Show the 3-dimensional nature of cells Be a typical plant or animal cell-your choice Come with definitions ...
lec1
... phospholipid bilayer and thus has all of the general functions of a cell membrane such as acting as a permeability barrier for most molecules and serving as the location for the transport of molecules into the cell. In addition to these functions, prokaryotic membranes also function in energy conser ...
... phospholipid bilayer and thus has all of the general functions of a cell membrane such as acting as a permeability barrier for most molecules and serving as the location for the transport of molecules into the cell. In addition to these functions, prokaryotic membranes also function in energy conser ...
Unit # 3 – Cells, Histology, Integumentary system Ms
... 3.05 Describe each of the following cellular transport processes and classify them as active or passive (Passive – diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, dialysis and filtration. Active – Phagocytosis, exocytosis, and active transport). 17. Osmosis is: a. movement of a substance across a membran ...
... 3.05 Describe each of the following cellular transport processes and classify them as active or passive (Passive – diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, dialysis and filtration. Active – Phagocytosis, exocytosis, and active transport). 17. Osmosis is: a. movement of a substance across a membran ...
L16v03-growthApop.stamped_doc
... [00:00:53.89] Growth factors are primarily about increasing cell mass. It's not dividing cells, but it's producing protein, producing lipids, producing the molecules that are needed biosynthetically to make a cell larger. [00:01:07.25] And then there are finally things specific as survival factors a ...
... [00:00:53.89] Growth factors are primarily about increasing cell mass. It's not dividing cells, but it's producing protein, producing lipids, producing the molecules that are needed biosynthetically to make a cell larger. [00:01:07.25] And then there are finally things specific as survival factors a ...
Outer Envelope Study Guide.psd
... Hormones are carried from the glands where they are produced to cells in other body regions, signaling them into action. But how do these target cells recognize the appropriate hormone? Cells that are targets for hormones carry special proteins on their plasma membrane, proteins that fit the hormone ...
... Hormones are carried from the glands where they are produced to cells in other body regions, signaling them into action. But how do these target cells recognize the appropriate hormone? Cells that are targets for hormones carry special proteins on their plasma membrane, proteins that fit the hormone ...
Ch 13 Notes
... • Presence of envelope around some viruses viral genome must be separated from its protein coat • Eukaryotic nature of animal cells • Lack of cell wall in animal cells attach to plasma membrane Attachment of Animal Viruses • Chemical attraction • Animal viruses do not have tails or tail fibers • Hav ...
... • Presence of envelope around some viruses viral genome must be separated from its protein coat • Eukaryotic nature of animal cells • Lack of cell wall in animal cells attach to plasma membrane Attachment of Animal Viruses • Chemical attraction • Animal viruses do not have tails or tail fibers • Hav ...
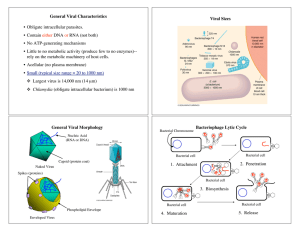
General Viral Characteristics • Obligate intracellular parasites
... Viral mRNAs are transcribed in the nucleus (using host enzymes) and are transported into the cytoplasm. Capsid proteins are translated using host tRNAs and ribosomes. ...
... Viral mRNAs are transcribed in the nucleus (using host enzymes) and are transported into the cytoplasm. Capsid proteins are translated using host tRNAs and ribosomes. ...
Cells
... histone protein Contains the DNA – the genome of the eukaryotic species Site of Replication and Transcription nuclear pores ...
... histone protein Contains the DNA – the genome of the eukaryotic species Site of Replication and Transcription nuclear pores ...
July 28, 1914
... Who said the following statement: “but before I can live with other folks I’ve got to live with myself. The one thing that doesn’t abide by majority rule is a person’s conscience.” ...
... Who said the following statement: “but before I can live with other folks I’ve got to live with myself. The one thing that doesn’t abide by majority rule is a person’s conscience.” ...
PAP Cell Transport PPT
... •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do not dehydrate. •Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by removing excess salt and water. ...
... •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do not dehydrate. •Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by removing excess salt and water. ...
The Cell Cycle Control System
... MPF (maturation-promoting factor) is a cyclin-Cdk complex that triggers a cell’s passage past the G2 checkpoint into the M phase Stop and Go Signs: Internal and External Signals at the Checkpoints ...
... MPF (maturation-promoting factor) is a cyclin-Cdk complex that triggers a cell’s passage past the G2 checkpoint into the M phase Stop and Go Signs: Internal and External Signals at the Checkpoints ...
protein translocation.
... • The "default" for a protein released from "free" ribosomes is to remain in the cytosol. • To be targeted to a specific location requires an appropriate signal, typically a sequence motif that causes it to be assembled into a macromolecular structure or recognized by a ...
... • The "default" for a protein released from "free" ribosomes is to remain in the cytosol. • To be targeted to a specific location requires an appropriate signal, typically a sequence motif that causes it to be assembled into a macromolecular structure or recognized by a ...
Regents Biology
... to run daily life & growth, the cell must… read genes (DNA) build proteins structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors ...
... to run daily life & growth, the cell must… read genes (DNA) build proteins structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors ...
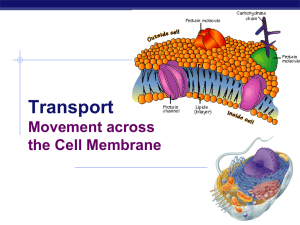
Chapter 8. Movement across the Membrane
... Membrane Carbohydrates Play a key role in cell-cell recognition ability of a cell to distinguish neighboring cells from another important in organ & tissue development basis for rejection of foreign cells by immune system ...
... Membrane Carbohydrates Play a key role in cell-cell recognition ability of a cell to distinguish neighboring cells from another important in organ & tissue development basis for rejection of foreign cells by immune system ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.