Interesting Facts - Raleigh Charter High School
... life objects from capsules that are scattered underneath their bodies. But unfortunately this method is completely ineffective to protect its self. It has a mutalistic symbiotic relationship with green algae called Zoochlorella. The algae live inside the paramecium in its cytoplasm and provides the ...
... life objects from capsules that are scattered underneath their bodies. But unfortunately this method is completely ineffective to protect its self. It has a mutalistic symbiotic relationship with green algae called Zoochlorella. The algae live inside the paramecium in its cytoplasm and provides the ...
Unit 3 - Madison Public Schools
... natural by-product of cellular metabolism. Enzymes in peroxisomes break hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. Prevalent in cells that are synthesizing and ...
... natural by-product of cellular metabolism. Enzymes in peroxisomes break hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. Prevalent in cells that are synthesizing and ...
02_Classification and functions of simple and complex proteins
... • On the basis of structural shape, proteins can be classified into two major types: fibrous proteins and globular proteins. • А fibrous protein is а protein that has а long, thin, fibrous shape. Such proteins are made up of long rod-shaped or stringlike molecules that can intertwine with one anothe ...
... • On the basis of structural shape, proteins can be classified into two major types: fibrous proteins and globular proteins. • А fibrous protein is а protein that has а long, thin, fibrous shape. Such proteins are made up of long rod-shaped or stringlike molecules that can intertwine with one anothe ...
cell organelles
... and with two tails. The heads like water (hydrophilic) and the tails do not like water (hydrophobic). The tails bump up against each other and the heads are out facing the watery area surrounding the inside or outside of the cell. ...
... and with two tails. The heads like water (hydrophilic) and the tails do not like water (hydrophobic). The tails bump up against each other and the heads are out facing the watery area surrounding the inside or outside of the cell. ...
No. 23
... enter the brain stem by passing through the posterolateral sulcus. This tract conveys the gustatory stimulus and general visceral stimulus to the adjacent nucleus of solitary tract. In fact, the nucleus of solitary tract is shared by ...
... enter the brain stem by passing through the posterolateral sulcus. This tract conveys the gustatory stimulus and general visceral stimulus to the adjacent nucleus of solitary tract. In fact, the nucleus of solitary tract is shared by ...
09. cranial N.nuclei2010-10-01 05:142.8 MB
... Herpes Zoster infection of sensory root of trigeminal N. ….. Leads to severe stabbing pain & eruption of vesicles localised to skin supplied by its branches : ophthalmic , or maxillary or mandibular N….. Trigeminal Neuralgia. Syringo-bulbia ,it is a disease of unknown etiology which affects the clos ...
... Herpes Zoster infection of sensory root of trigeminal N. ….. Leads to severe stabbing pain & eruption of vesicles localised to skin supplied by its branches : ophthalmic , or maxillary or mandibular N….. Trigeminal Neuralgia. Syringo-bulbia ,it is a disease of unknown etiology which affects the clos ...
Virus Powerpoint - Hatboro
... wear face masks to protect themselves from the virus causing SARS. ...
... wear face masks to protect themselves from the virus causing SARS. ...
Ch 8 Cell Reproduction Notes
... Cell Division in Eukaryotes • Cell Cycle – The cell cycle is the repeating set of events in the life of a cell. – The cell cycle consists of cell division and interphase. – Cell division in eukaryotes includes nuclear division, called mitosis, and the division of cytoplasm, called cytokinesis. ...
... Cell Division in Eukaryotes • Cell Cycle – The cell cycle is the repeating set of events in the life of a cell. – The cell cycle consists of cell division and interphase. – Cell division in eukaryotes includes nuclear division, called mitosis, and the division of cytoplasm, called cytokinesis. ...
mb_ch08
... • Describe the events of cell division in prokaryotes. • Name the two parts of the cell that are equally divided during cell division in eukaryotes. • Summarize the events of interphase. • Describe the stages of mitosis. • Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells. • Explai ...
... • Describe the events of cell division in prokaryotes. • Name the two parts of the cell that are equally divided during cell division in eukaryotes. • Summarize the events of interphase. • Describe the stages of mitosis. • Compare cytokinesis in animal cells with cytokinesis in plant cells. • Explai ...
3.1 Cell Theory - Perry Local Schools
... Centrioles are tubes found in the centrosomes. – Centrioles help divide DNA. – Centrioles form cilia and flagella. Cilia & flagella assist in movement and feeding – Cilia – short, numerous hair-like extensions – Flagella – longer, move with a whip-like motion – cell usually only has 1 or 2 ...
... Centrioles are tubes found in the centrosomes. – Centrioles help divide DNA. – Centrioles form cilia and flagella. Cilia & flagella assist in movement and feeding – Cilia – short, numerous hair-like extensions – Flagella – longer, move with a whip-like motion – cell usually only has 1 or 2 ...
Chapter 6 Question 2 Activity: Prokaryotic Cell
... They are the sites of reactions that convert chemical energy to ATP. They contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Their matrix contains enzymes that function in cellular respiration. Their inner membrane has infoldings called cristae. ...
... They are the sites of reactions that convert chemical energy to ATP. They contain the green pigment chlorophyll. Their matrix contains enzymes that function in cellular respiration. Their inner membrane has infoldings called cristae. ...
class 9 biology chapter- 1 fundamental unit of life introductory
... Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following: (i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C. (ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment? (iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D. Ans. (i) Water ...
... Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following: (i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C. (ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment? (iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D. Ans. (i) Water ...
CELL STRUCTURE_2012_crossing the
... – Much larger: 10100mm in diameter – More complex structure – compartments called organelles – Animals, plants, fungi and protists ...
... – Much larger: 10100mm in diameter – More complex structure – compartments called organelles – Animals, plants, fungi and protists ...
10.2 Process of Cell Division
... Chromosomes The genetic information that is passed on from one generation of cells to the next is carried by chromosomes. Every cell must copy its genetic information before cell division begins. Each daughter cell gets its own copy of that genetic information. Cells of every organism have a specifi ...
... Chromosomes The genetic information that is passed on from one generation of cells to the next is carried by chromosomes. Every cell must copy its genetic information before cell division begins. Each daughter cell gets its own copy of that genetic information. Cells of every organism have a specifi ...
Lecture 9
... Cells synthesise a large number of different macromolecules. The Golgi apparatus is integral in modifying, sorting, and packaging these macromolecules for cell secretion (exocytosis) or use within the cell. It primarily modifies proteins delivered from the rough endoplasmic reticulum but is also inv ...
... Cells synthesise a large number of different macromolecules. The Golgi apparatus is integral in modifying, sorting, and packaging these macromolecules for cell secretion (exocytosis) or use within the cell. It primarily modifies proteins delivered from the rough endoplasmic reticulum but is also inv ...
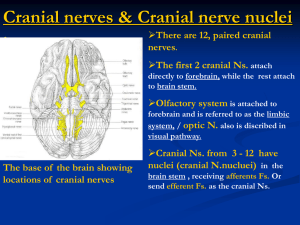
The Cranial Nerves
... mucous membranes of nasal and palatine mucosa Special Sensory - taste on anterior 2/3’s of tongue Damage produces sagging facial muscles and disturbed sense of taste (no sweet and salty) ...
... mucous membranes of nasal and palatine mucosa Special Sensory - taste on anterior 2/3’s of tongue Damage produces sagging facial muscles and disturbed sense of taste (no sweet and salty) ...
Amino Acid Uptake for the Synthesis of Secretory Protein by the
... With the adveDt of radlotracen, studies with "C· and "H·labelled amino acids provided ovenmelming evidence that mlJk proteins are of matIlID!lJ'y gland origin. Of the lactoproteins 8)1J1thesi.zed, casein IC't'OIInts for 80 per ceat or the total proteins. Mammary secretory cells synthesize e.>selltia ...
... With the adveDt of radlotracen, studies with "C· and "H·labelled amino acids provided ovenmelming evidence that mlJk proteins are of matIlID!lJ'y gland origin. Of the lactoproteins 8)1J1thesi.zed, casein IC't'OIInts for 80 per ceat or the total proteins. Mammary secretory cells synthesize e.>selltia ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.