Chapter 12
... • The sequential events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system, which is similar to a clock • The cell cycle control system is regulated by both internal and external controls • The clock has specific checkpoints where the cell cycle stops until a go-ahead signal is ...
... • The sequential events of the cell cycle are directed by a distinct cell cycle control system, which is similar to a clock • The cell cycle control system is regulated by both internal and external controls • The clock has specific checkpoints where the cell cycle stops until a go-ahead signal is ...
Biology 11 - Burnaby Online
... assessment is for the student to learn how to correctly research information on the internet, find some science websites to use for research on future assignments, and learn about the main concepts within the Biology 12 course. The words, listed after the main topic, may be used to search for inform ...
... assessment is for the student to learn how to correctly research information on the internet, find some science websites to use for research on future assignments, and learn about the main concepts within the Biology 12 course. The words, listed after the main topic, may be used to search for inform ...
The Microscope: Window on an Invisible Realm
... Preparation of Specimens for Light Microscopy Fresh Specimens Wet mounts – done in saline, water or broth True size, shape motility and arrangement can be seen Poor contrast Short term – cells dry out Preparing Smears For Staining Developed by Robert Koch – more permanent Staining – colo ...
... Preparation of Specimens for Light Microscopy Fresh Specimens Wet mounts – done in saline, water or broth True size, shape motility and arrangement can be seen Poor contrast Short term – cells dry out Preparing Smears For Staining Developed by Robert Koch – more permanent Staining – colo ...
worm notes
... 2. Worms have bilateral symmetry 2. Worms have 3 cell layers (not 2) 3. inner cells, middle cells, outer cells 2. Worms have Organs (structures with different cells for a common purpose) ...
... 2. Worms have bilateral symmetry 2. Worms have 3 cell layers (not 2) 3. inner cells, middle cells, outer cells 2. Worms have Organs (structures with different cells for a common purpose) ...
Chapter-23
... • Peptide in venom interferes with ability to feel pain • Prevents prey from damaging the snail • Ziconotide injectable pain killing drug is a synthetic version of the peptide • No additive unlike morphine ...
... • Peptide in venom interferes with ability to feel pain • Prevents prey from damaging the snail • Ziconotide injectable pain killing drug is a synthetic version of the peptide • No additive unlike morphine ...
Integumentary
... • Scale-like modification of the epidermis • Made of thin, dead, scaly cells, packed together • Protect the ends of the fingers and toes • Produced by the nail root: an area of rapid mitosis ...
... • Scale-like modification of the epidermis • Made of thin, dead, scaly cells, packed together • Protect the ends of the fingers and toes • Produced by the nail root: an area of rapid mitosis ...
The Respiratory System Larynx (Voice Box) - Course
... • Introduce oxygen into the blood stream which delivers oxygen to organs and tissues that need it. • Not let food system go anywhere butthe thebrain digestive •It works with the nervous because sendstract signals to the lungs to breathe. ...
... • Introduce oxygen into the blood stream which delivers oxygen to organs and tissues that need it. • Not let food system go anywhere butthe thebrain digestive •It works with the nervous because sendstract signals to the lungs to breathe. ...
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHAPTER3
... A small cube, 1 mm tall, has a volume of 1 mm3 (height ⫻ width ⫻ depth is 1 mm3). The surface area is 6 mm2. (Each side has a surface area of 1 mm2, and 6 ⫻ 1 mm2 is 6 mm2). Therefore, the ratio of surface area to volume is 6:1 because the surface area is 6 mm2 and the volume is 1 mm3. Contrast this ...
... A small cube, 1 mm tall, has a volume of 1 mm3 (height ⫻ width ⫻ depth is 1 mm3). The surface area is 6 mm2. (Each side has a surface area of 1 mm2, and 6 ⫻ 1 mm2 is 6 mm2). Therefore, the ratio of surface area to volume is 6:1 because the surface area is 6 mm2 and the volume is 1 mm3. Contrast this ...
What do you see now? - Parkway C-2
... following questions in your lab book using complete sentences. • 1. Are all cells the same size? • 2. Do all cells have the same stuff? • 3. Which type of cell can be found in your body? Explain. • 4. Give a rational for why eukaryotic cells not only need but have many more internal structures than ...
... following questions in your lab book using complete sentences. • 1. Are all cells the same size? • 2. Do all cells have the same stuff? • 3. Which type of cell can be found in your body? Explain. • 4. Give a rational for why eukaryotic cells not only need but have many more internal structures than ...
Active transport - Teachit Science
... 6. The absorption of mineral ions is done by active transport. The energy for active transport comes from respiration which uses glucose and oxygen to produce energy. If there is insufficient oxygen the active transport of mineral ions can not take place. 7. The size of the concentration gradient; t ...
... 6. The absorption of mineral ions is done by active transport. The energy for active transport comes from respiration which uses glucose and oxygen to produce energy. If there is insufficient oxygen the active transport of mineral ions can not take place. 7. The size of the concentration gradient; t ...
The Bacterial Cytoskeleton
... organisation of FtsZ is vastly different to that of tubulin, which probably reflects the fact that the two proteins have evolved to perform very different functions. Functions of the Z Ring Being the first event in the bacterial cell division process, the formation of the Z ring establishes both whe ...
... organisation of FtsZ is vastly different to that of tubulin, which probably reflects the fact that the two proteins have evolved to perform very different functions. Functions of the Z Ring Being the first event in the bacterial cell division process, the formation of the Z ring establishes both whe ...
circulatory system notes
... Each heart beat pushes about 90 milliliters of oxygenated blood from the heart into the aorta, the body's largest blood vessel. • From there, the blood flows to smaller arteries and then capillaries. • Eventually, it transfers its oxygen to body cells and returns back to the heart through the veins. ...
... Each heart beat pushes about 90 milliliters of oxygenated blood from the heart into the aorta, the body's largest blood vessel. • From there, the blood flows to smaller arteries and then capillaries. • Eventually, it transfers its oxygen to body cells and returns back to the heart through the veins. ...
07 PPT
... separates the living cell from its surroundings •It exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others ...
... separates the living cell from its surroundings •It exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others ...
The munc13-4–rab27 complex is specifically
... were obtained. For analysis of size distribution, the average of 3D volumes was used. Positioning and relative position to the nucleus were evaluated manually on a single slice. To find overlap between structures identified in 2 independent channels, the 3D volumes were analyzed for overlap. For col ...
... were obtained. For analysis of size distribution, the average of 3D volumes was used. Positioning and relative position to the nucleus were evaluated manually on a single slice. To find overlap between structures identified in 2 independent channels, the 3D volumes were analyzed for overlap. For col ...
AP Biology Summer Assignment 2016-17
... c) Living organisms can only tolerate small changes of pH in their environment because they must maintain homeostasis. 4. Explain the structure and function of carbohydrates in living things. a) The function of carbohydrates is to provide cells (and organisms) with energy. b) Carbohydrates are macro ...
... c) Living organisms can only tolerate small changes of pH in their environment because they must maintain homeostasis. 4. Explain the structure and function of carbohydrates in living things. a) The function of carbohydrates is to provide cells (and organisms) with energy. b) Carbohydrates are macro ...
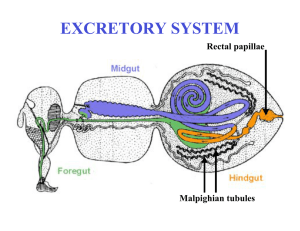
Excretory system - Faculty Support Site
... Diuretic hormones generally act on the Malpighian tubules to stimulate urine production Antidiuretic hormones generally increase fluid reabsorption by act on the hindgut Malpighian tubules are not innervated, thus they must be regulated by hormones released in the blood Muscles of the tubules can be ...
... Diuretic hormones generally act on the Malpighian tubules to stimulate urine production Antidiuretic hormones generally increase fluid reabsorption by act on the hindgut Malpighian tubules are not innervated, thus they must be regulated by hormones released in the blood Muscles of the tubules can be ...
From skin to the treatment of diseases the possibilities of iPS cell
... further passaging (p16) these differences seemed to be eliminated and the matched cells become very similar to each other (40). For therapeutic purposes of the iPSC technology, the chosen cell types have to be easily accessible in the patient. Skin cells like dermal fibroblasts, keratinocytes, derma ...
... further passaging (p16) these differences seemed to be eliminated and the matched cells become very similar to each other (40). For therapeutic purposes of the iPSC technology, the chosen cell types have to be easily accessible in the patient. Skin cells like dermal fibroblasts, keratinocytes, derma ...
Frog lab questions:
... 1. What are some characteristics that enable the frog to live on land? 2. What are the parts of the circulatory system? 3. How many lobes does the liver have? 4. What organs make up the digestive system? 5. What are the parts of the excretory system? 6. What are the parts of the nervous system? 7. W ...
... 1. What are some characteristics that enable the frog to live on land? 2. What are the parts of the circulatory system? 3. How many lobes does the liver have? 4. What organs make up the digestive system? 5. What are the parts of the excretory system? 6. What are the parts of the nervous system? 7. W ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... A “resting” neuron typically has a membrane potential of about -70 mV. When ions move into or out of a neuron, its membrane potential changes. Such changes transmit information through the nervous system. 12.3: Electrochemical gradients: which way will ions go? Each ion’s direction of movement ...
... A “resting” neuron typically has a membrane potential of about -70 mV. When ions move into or out of a neuron, its membrane potential changes. Such changes transmit information through the nervous system. 12.3: Electrochemical gradients: which way will ions go? Each ion’s direction of movement ...
10.2 Process of Cell Division
... Every cell must copy its genetic information before cell division begins. Each daughter cell gets its own copy of that genetic information. Cells of every organism have a specific number of chromosomes. ...
... Every cell must copy its genetic information before cell division begins. Each daughter cell gets its own copy of that genetic information. Cells of every organism have a specific number of chromosomes. ...
proofs oofs proofs proof
... small soluble molecules are filtered from the blood and pass into the nephron. Red blood cells and large molFIGURE 4.2 Gross anatomy of kidney showing the ecules do not cross from the blood into the capsule. renal artery that supplies the kidney with about one The average rate of filtration (known a ...
... small soluble molecules are filtered from the blood and pass into the nephron. Red blood cells and large molFIGURE 4.2 Gross anatomy of kidney showing the ecules do not cross from the blood into the capsule. renal artery that supplies the kidney with about one The average rate of filtration (known a ...
Cardiovascular System
... Carry O2 to all tissues from lungs Carry CO2 from tissues to lungs Hemoglobin – bright red when combined with O2 RBC’s live approximately 120 days ...
... Carry O2 to all tissues from lungs Carry CO2 from tissues to lungs Hemoglobin – bright red when combined with O2 RBC’s live approximately 120 days ...
DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF A DENSITOMETRIC HPTLC METHOD FOR
... activity. It is highly stable in the presence of β-lactamase enzymes. As a result, many organisms, which produce β-lactamase and are therefore resistant to penicillin and some cephalosporins, may be susceptible to cefpodoxime. Cefpodoxime is indicated for the treatment of patients infected with susc ...
... activity. It is highly stable in the presence of β-lactamase enzymes. As a result, many organisms, which produce β-lactamase and are therefore resistant to penicillin and some cephalosporins, may be susceptible to cefpodoxime. Cefpodoxime is indicated for the treatment of patients infected with susc ...
Higher Human Biology Chapter 11 Questions
... The probability of a particular outcome is always the same regardless of the result that came before. If there are three yellow marbles in a box and I white marble, there is a 1 in 4 chance that a white marble will be picked each time regardless of whether a white one was picked before or not. Lack ...
... The probability of a particular outcome is always the same regardless of the result that came before. If there are three yellow marbles in a box and I white marble, there is a 1 in 4 chance that a white marble will be picked each time regardless of whether a white one was picked before or not. Lack ...