Cell Structure
... cell is basic unit of all life; structural and functional c. nucleus d. organelles and internal structures ...
... cell is basic unit of all life; structural and functional c. nucleus d. organelles and internal structures ...
Vacuoles
... plants,protist and some primitive animals. Vacuole is the cavity of a cell,surrounded by single membrane and contains fluid,food and or metabolic wastes. ...
... plants,protist and some primitive animals. Vacuole is the cavity of a cell,surrounded by single membrane and contains fluid,food and or metabolic wastes. ...
Human Body Test 12/16 [1388442]
... D. Humans have many systems that perform the same function. 11. Which best describes a single-celled organism? A. an organism with one cell that uses other cells to survive B. an organism with many cells that work together to survive C. an organism with many cells that battle each other to survive D ...
... D. Humans have many systems that perform the same function. 11. Which best describes a single-celled organism? A. an organism with one cell that uses other cells to survive B. an organism with many cells that work together to survive C. an organism with many cells that battle each other to survive D ...
NC-3000™ Cell Cycle Assays
... In a given population, cells will be distributed among three major phases of the cell cycle: G1 /G0 phase (one set of paired chromosomes per cell), S phase (DNA synthesis with variable amount of DNA), and G2/M phase (two sets of paired chromosomes per cell, prior to cell division). The NucleoCounter ...
... In a given population, cells will be distributed among three major phases of the cell cycle: G1 /G0 phase (one set of paired chromosomes per cell), S phase (DNA synthesis with variable amount of DNA), and G2/M phase (two sets of paired chromosomes per cell, prior to cell division). The NucleoCounter ...
17.0 Analyze the Relationships Within Living Systems
... Life processes take place on a cellular level Everything in the production process of plants and animals must be understood at cellular level to make improvements ...
... Life processes take place on a cellular level Everything in the production process of plants and animals must be understood at cellular level to make improvements ...
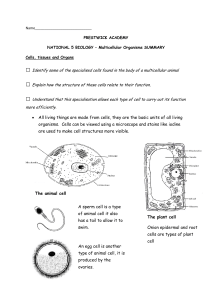
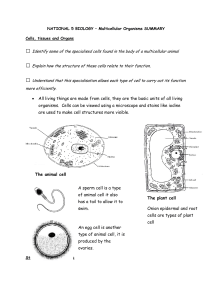
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... PRESTWICK ACADEMY NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
... PRESTWICK ACADEMY NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
Organization of the Cell
... MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The plasma membrane separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings and regulates what goes in and out. ...
... MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The plasma membrane separates the living cell from its nonliving surroundings and regulates what goes in and out. ...
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
... NATIONAL 5 BIOLOGY – Multicellular Organisms SUMMARY Cells, tissues and Organs ...
Cell Processes Notes
... METABOLISM – the sum total of all chemical changes that take place in living organisms. It includes cell activities such as absorption of food, releasing energy from food, growth and repair of cells, making protein, getting rid of waste, maintaining homeostasis, and carrying out cell division. All t ...
... METABOLISM – the sum total of all chemical changes that take place in living organisms. It includes cell activities such as absorption of food, releasing energy from food, growth and repair of cells, making protein, getting rid of waste, maintaining homeostasis, and carrying out cell division. All t ...
Sex and the Simpleton: Evolution of Sex and the Rise of the
... Prokaryotes have a single “chromosome”, contained within a “nucleoid region” rather than a distinct membrane-bound nucleus ...
... Prokaryotes have a single “chromosome”, contained within a “nucleoid region” rather than a distinct membrane-bound nucleus ...
Unit B: Cells and Systems - St. John Paul II Collegiate
... particles through a membrane without a cost of energy from the cell. *About 70% of a cell’s content is water. Osmosis: Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Water moves from a high concentration to a low concentration. Fluid Movement in Plants All the water in a plant is conne ...
... particles through a membrane without a cost of energy from the cell. *About 70% of a cell’s content is water. Osmosis: Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Water moves from a high concentration to a low concentration. Fluid Movement in Plants All the water in a plant is conne ...
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT
... method called meiosis. Meiosis is a complex process by which gametes form; involves duplication and division of reproductive cells and their chromosomes. The number of chromosomes in cells divide into two’s, and each set of cell will receive 1 from each sets of chromosomes makes up 23 sets. ...
... method called meiosis. Meiosis is a complex process by which gametes form; involves duplication and division of reproductive cells and their chromosomes. The number of chromosomes in cells divide into two’s, and each set of cell will receive 1 from each sets of chromosomes makes up 23 sets. ...
John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka for the discovery
... mature intestinal cell. This modified egg cell developed into a normal tadpole. The DNA of the mature cell still had all the information needed to develop all cells in the frog. Shinya Yamanaka discovered more than 40 years later, in 2006, how intact mature cells in mice could be reprogrammed to bec ...
... mature intestinal cell. This modified egg cell developed into a normal tadpole. The DNA of the mature cell still had all the information needed to develop all cells in the frog. Shinya Yamanaka discovered more than 40 years later, in 2006, how intact mature cells in mice could be reprogrammed to bec ...
Learning objectives
... CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Learning objectives: How We Study Cells 1. Distinguish between magnification and resolution. 2. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractiona ...
... CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Learning objectives: How We Study Cells 1. Distinguish between magnification and resolution. 2. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractiona ...
Protists - the Kyrene home page
... 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of all organisms. 3. All cells come from other cells all ready in existence. ...
... 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of all organisms. 3. All cells come from other cells all ready in existence. ...
monitoring_growth
... • A visible growth of bacteria on an agar plate containing many millions of cells. • A method of inoculating an agar plate with bacteria so that the bacteria are gradually diluted. • A layer of bacteria growing on the surface of an agar plate. ...
... • A visible growth of bacteria on an agar plate containing many millions of cells. • A method of inoculating an agar plate with bacteria so that the bacteria are gradually diluted. • A layer of bacteria growing on the surface of an agar plate. ...
Chapter 17 - Protists
... Plasmodium – single mass of cytoplasm undivided by membranes & containing many nuclei Extend pseudopodia to engulf bacteria & organic matter. Cytoplasmic streaming to distribute nutrients and oxygen throughout the organism. ...
... Plasmodium – single mass of cytoplasm undivided by membranes & containing many nuclei Extend pseudopodia to engulf bacteria & organic matter. Cytoplasmic streaming to distribute nutrients and oxygen throughout the organism. ...
Chapter 6 learning objectives
... CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Learning objectives: How We Study Cells 1. Distinguish between magnification and resolution. 2. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractiona ...
... CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Learning objectives: How We Study Cells 1. Distinguish between magnification and resolution. 2. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractiona ...
Chapter Six
... CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Learning objectives: How We Study Cells 1. Distinguish between magnification and resolution. 2. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractiona ...
... CHAPTER 6 A TOUR OF THE CELL Learning objectives: How We Study Cells 1. Distinguish between magnification and resolution. 2. Describe the principles, advantages, and limitations of the light microscope, transmission electron microscope, and scanning electron microscope. 3. Explain why cell fractiona ...
Anatomy and Physiology notes - Introduction, Cell
... What are emergent properties? give some individual organism examples. organ system organ tissue cell cell organelle molecule What is a very important emergent atom property at the cell level? ...
... What are emergent properties? give some individual organism examples. organ system organ tissue cell cell organelle molecule What is a very important emergent atom property at the cell level? ...
Liooacelldiv13 (1)
... 1. Examine the cells row by row, and count the cells that are in interphase. There should be 57 cells that can be identified as being in interphase. 2. Examine the cells row by row four ...
... 1. Examine the cells row by row, and count the cells that are in interphase. There should be 57 cells that can be identified as being in interphase. 2. Examine the cells row by row four ...
Mrs. Kaplan`s Science Page!
... Name the three organelles that could be seen through the microscope in a cheek cell or onion cell. Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus ...
... Name the three organelles that could be seen through the microscope in a cheek cell or onion cell. Cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus ...
Relationships between cellular activity and culturability
... Further image analysis of the succinate-enhanced tetrazolium reactions used in these studies revealed the additional features that are demonstrated in Fig. 1. Three subpopulations, defined by the ratio between their optical weight (OW) (amount of formazan per cell) and cell area (CA), were apparent ...
... Further image analysis of the succinate-enhanced tetrazolium reactions used in these studies revealed the additional features that are demonstrated in Fig. 1. Three subpopulations, defined by the ratio between their optical weight (OW) (amount of formazan per cell) and cell area (CA), were apparent ...
document
... ___________________ c. absence of visible striations & single, centrallylocated nuclei number of nuclei 5. What is the name of the structure that attaches skeletal muscles to bones? 6. Bundles of skeletal muscle cells are called ________________. 7. The connective tissue which immediately surrounds ...
... ___________________ c. absence of visible striations & single, centrallylocated nuclei number of nuclei 5. What is the name of the structure that attaches skeletal muscles to bones? 6. Bundles of skeletal muscle cells are called ________________. 7. The connective tissue which immediately surrounds ...

![Human Body Test 12/16 [1388442]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020444861_1-5f310fa9844f0b2fa5e006a0adbe59b7-300x300.png)