PDF
... Converging on convergent extension regulators Convergent extension (CE) is a morphogenetic process during which cells within a layer intercalate (converge), making the layer longer and thinner (extended) as a result. CE is important for diverse morphogenetic events, from gastrulation to organogenesi ...
... Converging on convergent extension regulators Convergent extension (CE) is a morphogenetic process during which cells within a layer intercalate (converge), making the layer longer and thinner (extended) as a result. CE is important for diverse morphogenetic events, from gastrulation to organogenesi ...
Honors Biology - WordPress.com
... Have an outer layer of cells and an inner layer of cells separated by a jellylike layer. 1. Epithelium: Animal tissue consisting of one or more layers of cells that have only one free surface, because the other surface adheres to a member or other substance. 2. Mesoglea: The jellylike substance that ...
... Have an outer layer of cells and an inner layer of cells separated by a jellylike layer. 1. Epithelium: Animal tissue consisting of one or more layers of cells that have only one free surface, because the other surface adheres to a member or other substance. 2. Mesoglea: The jellylike substance that ...
Types of Organisms
... 6. Which statement best compares a multicellular organism to a unicellular organism? (1) A multicellular organism has organ systems that interact to carry out life functions, while a singlecelled organism carries out life functions without using organ systems. (2) A single-celled organism carries o ...
... 6. Which statement best compares a multicellular organism to a unicellular organism? (1) A multicellular organism has organ systems that interact to carry out life functions, while a singlecelled organism carries out life functions without using organ systems. (2) A single-celled organism carries o ...
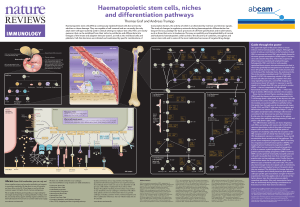
Haematopoietic stem cells, niches and differentiation
... attrition or tissue damage. They are capable of self-renewal and are currently the only adult stem-cell type routinely used in clinical settings to replace lost cells. HSCs are mostly quiescent but can be mobilized from their niche to proliferate and differentiate into lineages of the innate and ada ...
... attrition or tissue damage. They are capable of self-renewal and are currently the only adult stem-cell type routinely used in clinical settings to replace lost cells. HSCs are mostly quiescent but can be mobilized from their niche to proliferate and differentiate into lineages of the innate and ada ...
THE GENERATION OF NEURONS FROM EMBRYONIC STEM
... transplantation in culture, it is fundamental for us to understand how these cells are generated during our development, and how they operate at the molecular level, both in health and in disease. Without this comprehensive picture of their behaviour, any attempted drug treatment, transplantation or ...
... transplantation in culture, it is fundamental for us to understand how these cells are generated during our development, and how they operate at the molecular level, both in health and in disease. Without this comprehensive picture of their behaviour, any attempted drug treatment, transplantation or ...
cells alive web quest - Mr. Jenkins` Classroom
... Lymphocyte Red Blood Cells Baker’s Yeast E. Coli Staphylococcus Ebola Virus Rhinovirus Question #1: Where you surprised at how small some of the items were? Why or why not? Remember to use complete sentences. ...
... Lymphocyte Red Blood Cells Baker’s Yeast E. Coli Staphylococcus Ebola Virus Rhinovirus Question #1: Where you surprised at how small some of the items were? Why or why not? Remember to use complete sentences. ...
Document
... NGSS HS-LS1-2 Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for how carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules.[Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence from models and simulati ...
... NGSS HS-LS1-2 Construct and revise an explanation based on evidence for how carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen from sugar molecules may combine with other elements to form amino acids and/or other large carbon-based molecules.[Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on using evidence from models and simulati ...
Multiple Choice
... Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Many marine organisms have body surfaces that are permeable to water but not to salt. Osmosis can change the pressure of their body fluids. Fortunately, the ocean is very stable in its salt content. Wh ...
... Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Many marine organisms have body surfaces that are permeable to water but not to salt. Osmosis can change the pressure of their body fluids. Fortunately, the ocean is very stable in its salt content. Wh ...
RP101 improves the efficacy of chemotherapy in pancreas
... RP101 [(E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine (BVDU)], which supports apoptosis and prevents the acquisition of chemoresistance, was tested in cultured human ancreatic tumor cells. RP101 downregulated uridine phosphorylase, a marker of poor prognosis, and APEX1, which is involved in DNA repair, and re ...
... RP101 [(E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine (BVDU)], which supports apoptosis and prevents the acquisition of chemoresistance, was tested in cultured human ancreatic tumor cells. RP101 downregulated uridine phosphorylase, a marker of poor prognosis, and APEX1, which is involved in DNA repair, and re ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum -located next to the nucleus -a passageway for ribosomes and other structures to move throughout the cell *smooth ER does not have ribosomes *rough ER contains ribosomes ...
... 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum -located next to the nucleus -a passageway for ribosomes and other structures to move throughout the cell *smooth ER does not have ribosomes *rough ER contains ribosomes ...
Tissues
... How do cells stick together? Tight Junctions rows of proteins that seal cells together Prevents molecules from getting stuck in between cells Important in epithelial cells of the intestines Adhering Junctions Mass of proteins (called desmosomes) that spot weld the cell together at a very specifi ...
... How do cells stick together? Tight Junctions rows of proteins that seal cells together Prevents molecules from getting stuck in between cells Important in epithelial cells of the intestines Adhering Junctions Mass of proteins (called desmosomes) that spot weld the cell together at a very specifi ...
Review 2 - Allen ISD
... 17. Study the diagram and the statement above. Michelle is observing cell division in an onion cell, but this type of cell division also occurs in the human body. Which statement is not true about this type of cell division in humans? a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as wel ...
... 17. Study the diagram and the statement above. Michelle is observing cell division in an onion cell, but this type of cell division also occurs in the human body. Which statement is not true about this type of cell division in humans? a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as wel ...
Wipe Out
... 17. Study the diagram and the statement above. Michelle is observing cell division in an onion cell, but this type of cell division also occurs in the human body. Which statement is not true about this type of cell division in humans? a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as wel ...
... 17. Study the diagram and the statement above. Michelle is observing cell division in an onion cell, but this type of cell division also occurs in the human body. Which statement is not true about this type of cell division in humans? a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as wel ...
Wipe Out
... 17. Study the diagram and the statement above. Michelle is observing cell division in an onion cell, but this type of cell division also occurs in the human body. Which statement is not true about this type of cell division in humans? a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as wel ...
... 17. Study the diagram and the statement above. Michelle is observing cell division in an onion cell, but this type of cell division also occurs in the human body. Which statement is not true about this type of cell division in humans? a. This type of cell division is humans produces sex cells as wel ...
Journey Inside the Cell - CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION UNIT
... The nucleus is the cell structure that directs all the cells activities! It is found near the center of the cell. This is where the CHROMATIN (DNA) is found! The nucleus is made up of three important parts: –The nuclear envelope which protects the nucleus. This is often called the nuclear membrane - ...
... The nucleus is the cell structure that directs all the cells activities! It is found near the center of the cell. This is where the CHROMATIN (DNA) is found! The nucleus is made up of three important parts: –The nuclear envelope which protects the nucleus. This is often called the nuclear membrane - ...
Lecture Guide-InnateImmune (CH14)_7e
... virulent pathogens have evolved mechanisms to evade the process of phagocytosis…can you think of some ways in which an organism could evade phagocytosis? We’ll talk more about this when we discuss pathogenesis. Cells of the immune system need to be connected and communicating with each other to coor ...
... virulent pathogens have evolved mechanisms to evade the process of phagocytosis…can you think of some ways in which an organism could evade phagocytosis? We’ll talk more about this when we discuss pathogenesis. Cells of the immune system need to be connected and communicating with each other to coor ...
Tonicity
... In animal cells, being in a hypertonic environment results in crenation, where the shape of the cell becomes distorted and wrinkled as water leaves the cell. Some organisms have evolved methods of circumventing Hypertonicity; for example, saltwater is hypertonic to the fish that live in it. Since th ...
... In animal cells, being in a hypertonic environment results in crenation, where the shape of the cell becomes distorted and wrinkled as water leaves the cell. Some organisms have evolved methods of circumventing Hypertonicity; for example, saltwater is hypertonic to the fish that live in it. Since th ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 3 – The Origin and
... -A young fossil will have a high ratio of 14C compared to 12C -An old fossil will have lost much of its 14C through radioactive decay, so it will have a low ratio of 14C compared to 12C After 50,000 years, the 14C radioactivity is so low it cannot be used to measure age accurately. (Thus, carbon 1 ...
... -A young fossil will have a high ratio of 14C compared to 12C -An old fossil will have lost much of its 14C through radioactive decay, so it will have a low ratio of 14C compared to 12C After 50,000 years, the 14C radioactivity is so low it cannot be used to measure age accurately. (Thus, carbon 1 ...
A Framework for Function
... the cell's material together on the inside. In eukaryotic cells, it is found between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Organelles move about freely in the cytoplasm, and other cell activity occurs here. In prokaryotic cells, all cellular activities occur in the cytoplasm. This gellike material is h ...
... the cell's material together on the inside. In eukaryotic cells, it is found between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Organelles move about freely in the cytoplasm, and other cell activity occurs here. In prokaryotic cells, all cellular activities occur in the cytoplasm. This gellike material is h ...
Protocols for C
... fluorescence and light scatter gates. Enrichment cell sorting used a fluorescence threshold trigger (FLTT) instead of the standard light scatter threshold trigger (LSTT)3. This technique helps reduce the analysis of small particles and negative cells and allows for higher throughput of cell suspensi ...
... fluorescence and light scatter gates. Enrichment cell sorting used a fluorescence threshold trigger (FLTT) instead of the standard light scatter threshold trigger (LSTT)3. This technique helps reduce the analysis of small particles and negative cells and allows for higher throughput of cell suspensi ...
Unit 3 (part 1) Study Guide (ANSWERS) Objectives: Can you
... Theodore Schwann - zoologist who observed that the tissues of animals had cells (1839) Matthias Schleiden - botonist, observed that the tissues of plants contained cells (1845) Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He also predicted that ce ...
... Theodore Schwann - zoologist who observed that the tissues of animals had cells (1839) Matthias Schleiden - botonist, observed that the tissues of plants contained cells (1845) Rudolf Virchow - also reported that every living thing is made of up vital units, known as cells. He also predicted that ce ...
All a virus does is reproduce!
... The body protects itself against viruses by taking a leaf out of the virus’ own book. Just as the virus attacks by getting an exact fit on the target cell, special cells, called b-lymphocytes, produce specific ‘antibody’ cells that exactly fit the intruders. This attachment either incapacitates the ...
... The body protects itself against viruses by taking a leaf out of the virus’ own book. Just as the virus attacks by getting an exact fit on the target cell, special cells, called b-lymphocytes, produce specific ‘antibody’ cells that exactly fit the intruders. This attachment either incapacitates the ...
Biology 1406 Chapter 7 Lecture Notes
... Every cell is surrounded by a cell or plasma membrane. Think of this membrane as a gatekeeper, allowing only specific substances to enter and leave the cell Functions of the Cell Membrane To isolate the cells contents from the external environment To regulate the exchange of substances entering and ...
... Every cell is surrounded by a cell or plasma membrane. Think of this membrane as a gatekeeper, allowing only specific substances to enter and leave the cell Functions of the Cell Membrane To isolate the cells contents from the external environment To regulate the exchange of substances entering and ...
CHAPTER 12 THE CELL CYCLE Section C: Regulation of the Cell
... 3. Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls • Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body’s control mechanisms. • Cancer cells do not stop dividing when growth factors are depleted either because they manufacture their own, have an abnormalit ...
... 3. Cancer cells have escaped from cell cycle controls • Cancer cells divide excessively and invade other tissues because they are free of the body’s control mechanisms. • Cancer cells do not stop dividing when growth factors are depleted either because they manufacture their own, have an abnormalit ...
Holiday Packet 2
... a. They are both wastes resulting from protein synthesis. b. They are both building blocks of starch. c. They are both needed for the synthesis of larger molecules. d. They are both stored as fat molecules in the liver. In a cell, information that controls the production of proteins must pass from t ...
... a. They are both wastes resulting from protein synthesis. b. They are both building blocks of starch. c. They are both needed for the synthesis of larger molecules. d. They are both stored as fat molecules in the liver. In a cell, information that controls the production of proteins must pass from t ...