WorldWarIISummary
... Germany halted its air efforts in May 1941. Meanwhile, British forces in North Africa were fighting to repel the invading Italians. Britain managed to keep Italy out of Egypt and pushed them back to Libya. In the beginning of 1941, the Afrika Korps, led by General Erwin Rommel, was sent to help the ...
... Germany halted its air efforts in May 1941. Meanwhile, British forces in North Africa were fighting to repel the invading Italians. Britain managed to keep Italy out of Egypt and pushed them back to Libya. In the beginning of 1941, the Afrika Korps, led by General Erwin Rommel, was sent to help the ...
Ch. 13: WWII - Mrs. Rostas
... in northern Africa against German General Erwin Rommel (known as “The Desert Fox”) in 1942 Eisenhower's army lost to Rommel in February 1943, but by May 1943 Rommel's army surrendered to the Allies – they now had a base to attack southern Europe ...
... in northern Africa against German General Erwin Rommel (known as “The Desert Fox”) in 1942 Eisenhower's army lost to Rommel in February 1943, but by May 1943 Rommel's army surrendered to the Allies – they now had a base to attack southern Europe ...
Unit 3 Terms
... On July 28 Stalin issued his most famous order of the war, “Not a step back!” While threatening severe punishment for defeatists, he called on the troops to fight a “patriotic” war for Russia.. The German advances to Stalingrad and into the Caucasus had added about 1100 km to their line. On the morn ...
... On July 28 Stalin issued his most famous order of the war, “Not a step back!” While threatening severe punishment for defeatists, he called on the troops to fight a “patriotic” war for Russia.. The German advances to Stalingrad and into the Caucasus had added about 1100 km to their line. On the morn ...
The Road to Revolution – Ch
... racial purity of the Aryan “master race” (North European whites); some ethnic groups/races were considered “not worth living” or “impure,” such as Jews, Roma (Gypsies), Slavs, Serbs, Polish, disabled, etc.; Nazis especially blamed Jews for bringing about the downfall of Germany during WWI and leadin ...
... racial purity of the Aryan “master race” (North European whites); some ethnic groups/races were considered “not worth living” or “impure,” such as Jews, Roma (Gypsies), Slavs, Serbs, Polish, disabled, etc.; Nazis especially blamed Jews for bringing about the downfall of Germany during WWI and leadin ...
File
... • By April German defenses crumbled and American forces close within 70 miles of Berlin. ...
... • By April German defenses crumbled and American forces close within 70 miles of Berlin. ...
World War II
... By September 1944 the Allies had crossed the German border. As they paused to bring in supplies and regroup, Germans launched their final counterattack. – In heavy snow they drove against the Allies in northern France: pushed westward to create dangerous bulge in the Allied lines. Became known as Ba ...
... By September 1944 the Allies had crossed the German border. As they paused to bring in supplies and regroup, Germans launched their final counterattack. – In heavy snow they drove against the Allies in northern France: pushed westward to create dangerous bulge in the Allied lines. Became known as Ba ...
File - Ms. halty`s class
... • Japan – Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki – All lands conquered returned to pre-war status – Slowly recover thanks to Western democratic aid ...
... • Japan – Atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki – All lands conquered returned to pre-war status – Slowly recover thanks to Western democratic aid ...
World War II Many economic and political causes led toward World
... - Weaknesses of the League of Nations. It had no real power and could only weakly protest against acts of aggression. - Appeasement. Appeasement is granting concessions to maintain peace. - Tendencies toward isolationism and pacifism in Europe and the US. Pacifism is opposition to war under any circ ...
... - Weaknesses of the League of Nations. It had no real power and could only weakly protest against acts of aggression. - Appeasement. Appeasement is granting concessions to maintain peace. - Tendencies toward isolationism and pacifism in Europe and the US. Pacifism is opposition to war under any circ ...
Major Fronts of the war
... WHO WAS INVOLVED? AMERICAN LEADER: DWIGHT D. EISENHOWER GERMAN LEADER: ROMMEL SOLDIERS AMERICAN CANADIAN BRITISH GERMAN ...
... WHO WAS INVOLVED? AMERICAN LEADER: DWIGHT D. EISENHOWER GERMAN LEADER: ROMMEL SOLDIERS AMERICAN CANADIAN BRITISH GERMAN ...
Chapter 16: World War II
... By the end of May 1940, the Germans had trapped the Allied forces around the northern French city of Lille. Outnumbered, outgunned, and pounded from the air, the Allies retreated to the beaches of Dunkirk near the ...
... By the end of May 1940, the Germans had trapped the Allied forces around the northern French city of Lille. Outnumbered, outgunned, and pounded from the air, the Allies retreated to the beaches of Dunkirk near the ...
Discuss the major American military operations
... United States. Until that time, the United States had largely maintained neutrality, although it had, since March that same year, supplied the Allies with war materiel (Baer, 1996). During the war over 16 million Americans served in the United States military. Many others served with the Merchant Ma ...
... United States. Until that time, the United States had largely maintained neutrality, although it had, since March that same year, supplied the Allies with war materiel (Baer, 1996). During the war over 16 million Americans served in the United States military. Many others served with the Merchant Ma ...
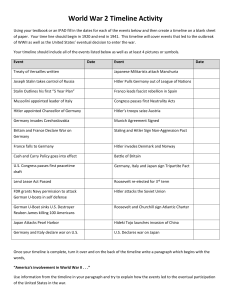
1920-1941 Timeline
... of WWII as well as the United States’ eventual decision to enter the war. Your timeline should include all of the events listed below as well as at least 4 pictures or symbols. Event ...
... of WWII as well as the United States’ eventual decision to enter the war. Your timeline should include all of the events listed below as well as at least 4 pictures or symbols. Event ...
World War II Outcomes - Revere Local Schools
... • Close to 50-60 million dead and over 34 million wounded. U.S.—over one million dead or wounded. • Many displaced persons • The ground war destroyed much of the countryside and cities • Some people lived in partially destroyed homes with no water, electricity, and little food. Others wandered Europ ...
... • Close to 50-60 million dead and over 34 million wounded. U.S.—over one million dead or wounded. • Many displaced persons • The ground war destroyed much of the countryside and cities • Some people lived in partially destroyed homes with no water, electricity, and little food. Others wandered Europ ...
World War II
... impact on the economy of the United States since World War II. The arms race started as a result of America’s exclusive control of the atom bomb. This race to develop new and better bombs and ways to deliver them to the target have resulted in extensive government spending which has both stimulated ...
... impact on the economy of the United States since World War II. The arms race started as a result of America’s exclusive control of the atom bomb. This race to develop new and better bombs and ways to deliver them to the target have resulted in extensive government spending which has both stimulated ...
World War II
... Italians invaded from the South. German troops marched into Paris on June 14th. The French government asked for an armistice, under which Germany occupied northern France, including Paris, and the coast. In the south, a government was established at Vichy (VEE-shee) that was very cooperativ ...
... Italians invaded from the South. German troops marched into Paris on June 14th. The French government asked for an armistice, under which Germany occupied northern France, including Paris, and the coast. In the south, a government was established at Vichy (VEE-shee) that was very cooperativ ...
Mini-Quiz/ Exam Prep Unit 2 (1900-1945), Chapters 25
... What was the name of the secret US military program to develop an atomic weapon during the war? _________________________________________________________ ...
... What was the name of the secret US military program to develop an atomic weapon during the war? _________________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 16 Sec.4
... civilians endured extreme hardships. Except for a few of its territories, such as Hawaii, the U.S did not suffer invasion or bombing. Nonetheless, Americans at home made a crucial contribution to the Allied war effort. Americans produced the weapons and equipment that helped win the war. ...
... civilians endured extreme hardships. Except for a few of its territories, such as Hawaii, the U.S did not suffer invasion or bombing. Nonetheless, Americans at home made a crucial contribution to the Allied war effort. Americans produced the weapons and equipment that helped win the war. ...
Chapter 16 Take Home Quiz Use your text/note book
... B. Poland. C. Germany. D. Great Britain. ____ 2. Great Britain and France entered World War II because of the invasion of A. Poland. B. Finland. C. Denmark and Norway. D. the Baltic States. ____ 3. The Germans first successfully used the blitzkrieg in an attack on A. France. B. Poland. C. Finland. D ...
... B. Poland. C. Germany. D. Great Britain. ____ 2. Great Britain and France entered World War II because of the invasion of A. Poland. B. Finland. C. Denmark and Norway. D. the Baltic States. ____ 3. The Germans first successfully used the blitzkrieg in an attack on A. France. B. Poland. C. Finland. D ...
The Interwar Period
... Aggressive actions by Italy, Germany, and Japan show the ineffectiveness of the League of Nations League of Nations attempts appeasement to prevent war Hitler’s invasion of Poland Britain and France declare war on Germany ...
... Aggressive actions by Italy, Germany, and Japan show the ineffectiveness of the League of Nations League of Nations attempts appeasement to prevent war Hitler’s invasion of Poland Britain and France declare war on Germany ...
Foreign relations of the Axis powers

Foreign relations of the Axis powers includes states which were not officially members of the Axis but had relations with one or more Axis members.