War has started!!!!
... • Instead of taking a stand against Fascist aggression in the 1930s, Britain and France repeatedly made concessions, hoping to keep peace. • Both nations were dealing with serious economic problems as a result of the Great Depression. In addition, the horrors of World War I had created a deep desire ...
... • Instead of taking a stand against Fascist aggression in the 1930s, Britain and France repeatedly made concessions, hoping to keep peace. • Both nations were dealing with serious economic problems as a result of the Great Depression. In addition, the horrors of World War I had created a deep desire ...
Essential Question/s Was WW II the “Good war”? Do “Extreme times
... surrender, Americans dropped A-bombs onto Hiroshima (on August 6, 1945), killing 180,000 and Nagasaki (on August 9, 1945), killing 80,000. 4. On August 8, 1945, the Soviets declared war on Japan, just as promised, and two days later, on August 10, Japan sued for peace on one condition: that the Empe ...
... surrender, Americans dropped A-bombs onto Hiroshima (on August 6, 1945), killing 180,000 and Nagasaki (on August 9, 1945), killing 80,000. 4. On August 8, 1945, the Soviets declared war on Japan, just as promised, and two days later, on August 10, Japan sued for peace on one condition: that the Empe ...
World War II (1939 – 1945) Prior Wars Complete the table below
... 30. What role did geography play in the German victory over France? Explain. 31. In what other wars have we seen geography play a role in one side’s victory? Explain. 32. Why do you think the British withdrew from France and left the French on their own against the Germans? 33. Would you have done t ...
... 30. What role did geography play in the German victory over France? Explain. 31. In what other wars have we seen geography play a role in one side’s victory? Explain. 32. Why do you think the British withdrew from France and left the French on their own against the Germans? 33. Would you have done t ...
World War II
... – Mussolini was hated by his people. – As the Allies began taking over, Mussolini was arrested an put into prison. • But… • Hitler sent more Germany troops to fight in Italy and free Mussolini. • It took almost another year to take Italy. ...
... – Mussolini was hated by his people. – As the Allies began taking over, Mussolini was arrested an put into prison. • But… • Hitler sent more Germany troops to fight in Italy and free Mussolini. • It took almost another year to take Italy. ...
The Attack on Pearl Harbor
... already been hit by torpedoes and are beginning to sink. The lines in the water show the torpedo’s path. The smoke in the background is from another ship that has been hit. ...
... already been hit by torpedoes and are beginning to sink. The lines in the water show the torpedo’s path. The smoke in the background is from another ship that has been hit. ...
Allies Win the War
... Sea and to invade Italy ► Allies won North Africa in may 1943 ► 1944 Allies captured Rome ► June 6, 1944 largest water-to-land invasion in history (Allied forces) ...
... Sea and to invade Italy ► Allies won North Africa in may 1943 ► 1944 Allies captured Rome ► June 6, 1944 largest water-to-land invasion in history (Allied forces) ...
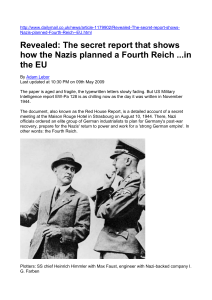
Nazi Fourth Reich - Friends of the Sabbath
... and Nazi bankers and officials reintegrated. In 1957, John J. McCloy, the American High Commissioner for Germany, issued an amnesty for industrialists convicted of war crimes. The two most powerful Nazi industrialists, Alfried Krupp of Krupp Industries and Friedrich Flick, whose Flick Group eventual ...
... and Nazi bankers and officials reintegrated. In 1957, John J. McCloy, the American High Commissioner for Germany, issued an amnesty for industrialists convicted of war crimes. The two most powerful Nazi industrialists, Alfried Krupp of Krupp Industries and Friedrich Flick, whose Flick Group eventual ...
M / C Review Chapter 27
... Inter-service rivalry effectively kept the military intelligence services from sharing and coordinating the information they had collected which could have allowed them to anticipate the Pearl Harbor attack. At the time of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, she United States found itself A Partial ...
... Inter-service rivalry effectively kept the military intelligence services from sharing and coordinating the information they had collected which could have allowed them to anticipate the Pearl Harbor attack. At the time of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, she United States found itself A Partial ...
NB#2: The Failure of Appeasement and Beginning of World War II
... but fails to assist either Libya or Ethiopia ...
... but fails to assist either Libya or Ethiopia ...
WWII Timeline
... 23- Jews must wear star of David for identification 1940------------------------------------------------------------------------------------FEB 12- Deportation of Jews began APR 9- Germany invades Denmark and Norway MAY 10- Germany invades Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg - Winston Churchill bec ...
... 23- Jews must wear star of David for identification 1940------------------------------------------------------------------------------------FEB 12- Deportation of Jews began APR 9- Germany invades Denmark and Norway MAY 10- Germany invades Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg - Winston Churchill bec ...
CH. 19 WORLD WAR II
... boats braved the bombs and strafing runs of the Luftwaffe to rescue 200,000 British and 140,000 French troops. Some boats made three or more journeys on their own amid dive bombing and strafing by the Luftwaffe. Unlit and unable to comprehend, or respond to naval signals by night, they risked being ...
... boats braved the bombs and strafing runs of the Luftwaffe to rescue 200,000 British and 140,000 French troops. Some boats made three or more journeys on their own amid dive bombing and strafing by the Luftwaffe. Unlit and unable to comprehend, or respond to naval signals by night, they risked being ...
World War II People
... Called the “organizer of victory” by Churchill for leading the US Military during World War II as FDR’s military advisor. ...
... Called the “organizer of victory” by Churchill for leading the US Military during World War II as FDR’s military advisor. ...
What were the primary causes of WWII?
... France, Soviet Union, United States, and China • The Soviet Union joined the allies in 1941 after Hitler broke the NonAggression pact ...
... France, Soviet Union, United States, and China • The Soviet Union joined the allies in 1941 after Hitler broke the NonAggression pact ...
Preview Sheet World War II
... In the 1930’s, changes were occurring in Europe while many Americans remained focused on the Great Depression. Totalitarian governments were in power in Germany, Italy, and Japan. Each of these nations threatened world peace through their aggressive actions. It wasn’t until 1939 when Europe reacted ...
... In the 1930’s, changes were occurring in Europe while many Americans remained focused on the Great Depression. Totalitarian governments were in power in Germany, Italy, and Japan. Each of these nations threatened world peace through their aggressive actions. It wasn’t until 1939 when Europe reacted ...
AMERICA IN WWII
... Invasion of Italy commanded by George Patton – July 10, 1943 – British & US forces land on Sicily; ...
... Invasion of Italy commanded by George Patton – July 10, 1943 – British & US forces land on Sicily; ...
File wwii-
... 3. Battle of El Alamein—signaled end of German presence in North Africa -- Pushed Rommel all the way to Tunisia; massive German casualties. C. Europe 1. Invasion of Italy (commanded by George C. Patton) a. July 1943, British and U.S. forces land on Sicily; victorious within 1 month b. Mussolini forc ...
... 3. Battle of El Alamein—signaled end of German presence in North Africa -- Pushed Rommel all the way to Tunisia; massive German casualties. C. Europe 1. Invasion of Italy (commanded by George C. Patton) a. July 1943, British and U.S. forces land on Sicily; victorious within 1 month b. Mussolini forc ...
US History I - Mr. Bolanos
... for the war. FDR and Churchill determined what the outcomes would be after the war as well. The basis for the United Nations would come out of this meeting. Among their goals were collective security, disarmament, self-determination, economic cooperation and freedom of the seas 29. How did the U.S. ...
... for the war. FDR and Churchill determined what the outcomes would be after the war as well. The basis for the United Nations would come out of this meeting. Among their goals were collective security, disarmament, self-determination, economic cooperation and freedom of the seas 29. How did the U.S. ...
chapter assessment
... How can the United States use its resources to achieve victory? Write a newspaper article in which you describe the ways in which the United States used its resources during World War II. Include information about rationing and about the various offices that the federal government established to mon ...
... How can the United States use its resources to achieve victory? Write a newspaper article in which you describe the ways in which the United States used its resources during World War II. Include information about rationing and about the various offices that the federal government established to mon ...
Folie 1 - University of Hong Kong
... ‘Blitzkrieg’ on Poland • G campaign in PL: 1-28 Sep 39 = Begin of World War II • GB + F: declaration-of-war on G, 3 Sep 39 • SU: Invasion of PL from East, 17 Sep 39 = PL military defeat + division: Western PL → Annexation by G + creation of ‘Government General for the Occupied Polish Territories’ ...
... ‘Blitzkrieg’ on Poland • G campaign in PL: 1-28 Sep 39 = Begin of World War II • GB + F: declaration-of-war on G, 3 Sep 39 • SU: Invasion of PL from East, 17 Sep 39 = PL military defeat + division: Western PL → Annexation by G + creation of ‘Government General for the Occupied Polish Territories’ ...
World War II
... • Often times, the Jews dug their own graves before they were executed. • As many as one million Jews were killed through this fashion, but was soon perceived as inadequate. • Nazis opted for the systematic annihilation of Jews in specially built death camps. ...
... • Often times, the Jews dug their own graves before they were executed. • As many as one million Jews were killed through this fashion, but was soon perceived as inadequate. • Nazis opted for the systematic annihilation of Jews in specially built death camps. ...
America in World War II 1941-1945
... Many Americans, including President Roosevelt, wanted to begin a diversionary invasion of France in 1942 or 1943. They feared that the Soviets, unable to hold out forever against Germany, might make a separate peace as they had in 1918 and leave the Western Allies to face Germany alone. British mili ...
... Many Americans, including President Roosevelt, wanted to begin a diversionary invasion of France in 1942 or 1943. They feared that the Soviets, unable to hold out forever against Germany, might make a separate peace as they had in 1918 and leave the Western Allies to face Germany alone. British mili ...
Chapter 21 Sections 2 through 4 Overview
... 3. Within a month after D-Day, a million Allied troops were in France. 4. In August 1944, Allied forces liberated Paris. E. Rapid Soviet Advance From the East 1. In January 1944, the Red Army freed Leningrad from an 890-day German siege. 2. By the spring of 1944, the Soviet troops had entered Ukrain ...
... 3. Within a month after D-Day, a million Allied troops were in France. 4. In August 1944, Allied forces liberated Paris. E. Rapid Soviet Advance From the East 1. In January 1944, the Red Army freed Leningrad from an 890-day German siege. 2. By the spring of 1944, the Soviet troops had entered Ukrain ...
... After learning that the Japanese had attacked Pearl Harbor, thus ensuring that the United States would enter World War II, Prime Minister Winston Churchill breathed a sigh of relief. "Hitler's fate was sealed," he would later recall. "Mussolini's fate was sealed. As for the Japanese, they would be g ...
Foreign relations of the Axis powers

Foreign relations of the Axis powers includes states which were not officially members of the Axis but had relations with one or more Axis members.