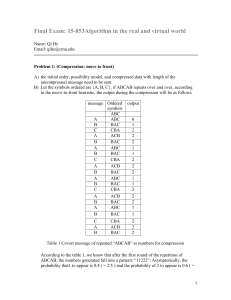
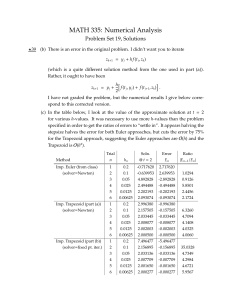
prob_distr_disc_old
... is 1/10. She continues to buy them until she has won 3 times. X = the number of tickets she buys. 2 In Stat 200 last year, students were asked to rate how much they liked various kinds of music on a scale of 1 (don’t like at all) to 6 (like very much). Following is a probability distribution (with o ...
... is 1/10. She continues to buy them until she has won 3 times. X = the number of tickets she buys. 2 In Stat 200 last year, students were asked to rate how much they liked various kinds of music on a scale of 1 (don’t like at all) to 6 (like very much). Following is a probability distribution (with o ...
A Randomized Approximate Nearest Neighbors
... Given a collection of n points x1 , x2 , . . . , xn in Rd and an integer k << n, the task of finding the k nearest neighbors for each xi is known as the “Nearest Neighbors Problem”; it is ubiquitous in a number of areas of Computer Science: Machine Learning, Data Mining, Artificial Intelligence, etc ...
... Given a collection of n points x1 , x2 , . . . , xn in Rd and an integer k << n, the task of finding the k nearest neighbors for each xi is known as the “Nearest Neighbors Problem”; it is ubiquitous in a number of areas of Computer Science: Machine Learning, Data Mining, Artificial Intelligence, etc ...
Tube Feeding and SMA: Recommendations and Practices
... a nissen fundoplication at the same time. • Choose a formula based on tolerance – For infants this may is typically breast milk, standard infant formula – We aim for 45-50% calories from fat during infancy ...
... a nissen fundoplication at the same time. • Choose a formula based on tolerance – For infants this may is typically breast milk, standard infant formula – We aim for 45-50% calories from fat during infancy ...
Combinatorics
... Solution. We can imagine filling in five blanks ___ ___ ___ ___ ___, left to right, to create the (equally likely) outcomes. The total number of these is 5! = 120, by the Product Rule. To count the number of these satisfying the given condition, simply adapt the Product Rule accordingly: Filling in ...
... Solution. We can imagine filling in five blanks ___ ___ ___ ___ ___, left to right, to create the (equally likely) outcomes. The total number of these is 5! = 120, by the Product Rule. To count the number of these satisfying the given condition, simply adapt the Product Rule accordingly: Filling in ...
Discrete Structures - CSIS121
... Dijkstra’s algorithm finds the length of a shortest path between two vertices in a connected simple undirected weighted graph G=(V,E). The time required by Dijkstra's algorithm is O(|V|2). It will be reduced to O(|E|log|V|) if heap is used to keep {vV\Si : L(v) < }, where Si is the set S after ite ...
... Dijkstra’s algorithm finds the length of a shortest path between two vertices in a connected simple undirected weighted graph G=(V,E). The time required by Dijkstra's algorithm is O(|V|2). It will be reduced to O(|E|log|V|) if heap is used to keep {vV\Si : L(v) < }, where Si is the set S after ite ...
Simulated annealing

Simulated annealing (SA) is a generic probabilistic metaheuristic for the global optimization problem of locating a good approximation to the global optimum of a given function in a large search space. It is often used when the search space is discrete (e.g., all tours that visit a given set of cities). For certain problems, simulated annealing may be more efficient than exhaustive enumeration — provided that the goal is merely to find an acceptably good solution in a fixed amount of time, rather than the best possible solution.The name and inspiration come from annealing in metallurgy, a technique involving heating and controlled cooling of a material to increase the size of its crystals and reduce their defects. Both are attributes of the material that depend on its thermodynamic free energy. Heating and cooling the material affects both the temperature and the thermodynamic free energy. While the same amount of cooling brings the same amount of decrease in temperature it will bring a bigger or smaller decrease in the thermodynamic free energy depending on the rate that it occurs, with a slower rate producing a bigger decrease.This notion of slow cooling is implemented in the Simulated Annealing algorithm as a slow decrease in the probability of accepting worse solutions as it explores the solution space. Accepting worse solutions is a fundamental property of metaheuristics because it allows for a more extensive search for the optimal solution.The method was independently described by Scott Kirkpatrick, C. Daniel Gelatt and Mario P. Vecchi in 1983, and by Vlado Černý in 1985. The method is an adaptation of the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm, a Monte Carlo method to generate sample states of a thermodynamic system, invented by M.N. Rosenbluth and published in a paper by N. Metropolis et al. in 1953.