Cardiac physiology
... Cardiac cycle 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the pressure i ...
... Cardiac cycle 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the pressure i ...
An Investigation of Cardiac Dynamics and Substrate Metabolism in
... • Allows for measurement of myocardial function and metabolism under defined loading conditions • Ex Vivo - Independent of neurohormonal influence • Desirable – easy genetic modification, rapid reproductive cycle, similarity to human physiology ...
... • Allows for measurement of myocardial function and metabolism under defined loading conditions • Ex Vivo - Independent of neurohormonal influence • Desirable – easy genetic modification, rapid reproductive cycle, similarity to human physiology ...
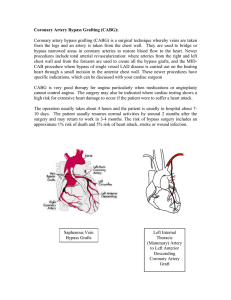
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
... Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a surgical technique whereby veins are taken from the legs and an artery is taken from the chest wall. They are used to bridge or bypass narrowed areas in coronary arteries to restore blood flow to the heart. Newer procedures include total arterial revascula ...
... Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a surgical technique whereby veins are taken from the legs and an artery is taken from the chest wall. They are used to bridge or bypass narrowed areas in coronary arteries to restore blood flow to the heart. Newer procedures include total arterial revascula ...
Definition and Classification of Shock
... Organ perfusion compromised by an overall decrease or maldistribution in cardiac output Worsened by abnormalities of distribution of blood flow within the organs. ...
... Organ perfusion compromised by an overall decrease or maldistribution in cardiac output Worsened by abnormalities of distribution of blood flow within the organs. ...
Definition and Classification of Shock
... Organ perfusion compromised by an overall decrease or maldistribution in cardiac output Worsened by abnormalities of distribution of blood flow within the organs. ...
... Organ perfusion compromised by an overall decrease or maldistribution in cardiac output Worsened by abnormalities of distribution of blood flow within the organs. ...
chapter-5-hf-lecture
... left atrial and pulmonary venous pressures. Causes: acute ischemia, chronic hypertension or severe aortic stenosis. Presentation: HF, acute pulmonary edema. Treatment: treatment of underlying cause * Beta blockers & calcium blockers => ↓HR => ↑ filling time * ACE inhibitors =>↓ hypertension & improv ...
... left atrial and pulmonary venous pressures. Causes: acute ischemia, chronic hypertension or severe aortic stenosis. Presentation: HF, acute pulmonary edema. Treatment: treatment of underlying cause * Beta blockers & calcium blockers => ↓HR => ↑ filling time * ACE inhibitors =>↓ hypertension & improv ...
Preanaesthetic Assessment - Neurological Society of India
... disease, cardiac arrhythmia, or diabetic >40 years of age ...
... disease, cardiac arrhythmia, or diabetic >40 years of age ...
Preload
... Factors determining the preload (LVEDP) 1) Period of the ventricle diastole (filling) – heart rate 2) Speed of the venous return (difference between the venous pressure and atrial pressure) Importance of the heterometeric regulation • In general, heterometric regulation plays only a short-time role ...
... Factors determining the preload (LVEDP) 1) Period of the ventricle diastole (filling) – heart rate 2) Speed of the venous return (difference between the venous pressure and atrial pressure) Importance of the heterometeric regulation • In general, heterometric regulation plays only a short-time role ...
General Medical Officer (GMO) Manual: Clinical Section
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
Pressors
... Approximately 200,000 fatalities Unfortunately, even with optimal treatment, the mortality rate from severe sepsis or septic shock is approximately 40% . ...
... Approximately 200,000 fatalities Unfortunately, even with optimal treatment, the mortality rate from severe sepsis or septic shock is approximately 40% . ...
Arrhythmias - The Brookside Associates
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
... Holter monitor (24-hour rhythm strip) is helpful in relating symptoms to cardiac rhythm. In patients with less frequent symptoms, an event recorder or loop monitor can be provided and carried by the patient on a month by month basis. The signal-averaged electrocardiogram (ECG) is a new technique dev ...
CV Assessment
... SNS & HR (to help pump all the blood returned to it) 2. Remember “Starling’s Law” ...
... SNS & HR (to help pump all the blood returned to it) 2. Remember “Starling’s Law” ...
ESC review 2011
... Kaplan-Meier time-to-event plot for admission to hospital for acute myocardial infarction in patients with baseline heart rate of ≥70 bpm ...
... Kaplan-Meier time-to-event plot for admission to hospital for acute myocardial infarction in patients with baseline heart rate of ≥70 bpm ...
treatment delivered in less than a minute lifevest system overview no
... condition is changing and permanent SCA risk has not been established. This allows a patient’s physician time to assess the patient’s long-term arrhythmic risk and make appropriate plans. ...
... condition is changing and permanent SCA risk has not been established. This allows a patient’s physician time to assess the patient’s long-term arrhythmic risk and make appropriate plans. ...
Heart Failure Whistle Stop Talks
... pressure, pulmonary crackles, and displaced apex beat) resulting from an abnormality of cardiac structure or function. 3.ACCF/AHA ‘The cardinal manifestations of HF are dyspnoea and fatigue, which may limit exercise tolerance, and fluid retention, which may lead to pulmonary and/or splanchnic conges ...
... pressure, pulmonary crackles, and displaced apex beat) resulting from an abnormality of cardiac structure or function. 3.ACCF/AHA ‘The cardinal manifestations of HF are dyspnoea and fatigue, which may limit exercise tolerance, and fluid retention, which may lead to pulmonary and/or splanchnic conges ...
Cardiac Tamponade - Jefferson EM Ultrasound
... Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade.” Journal of Emergencies, Trauma, and Shock 5.1 (2012): 72–75. PMC. Web. 10 Dec. 2016. ...
... Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade.” Journal of Emergencies, Trauma, and Shock 5.1 (2012): 72–75. PMC. Web. 10 Dec. 2016. ...
Heart Intro SJW
... The amount of blood pumped can be calculated: Heart Rate x Stroke Volume = Cardiac Output. Heart rate: The number of heart beats per minute. Stroke volume: The volume of blood pumped from heart with each beat. Cardiac output: The amount of blood pumped by heart in one minute. ...
... The amount of blood pumped can be calculated: Heart Rate x Stroke Volume = Cardiac Output. Heart rate: The number of heart beats per minute. Stroke volume: The volume of blood pumped from heart with each beat. Cardiac output: The amount of blood pumped by heart in one minute. ...
The cardiac cycle
... Introduction It is important that the chambers of the heart contract in a coordinated fashion. The sequence of events involved in one heartbeat is called the cardiac cycle. ...
... Introduction It is important that the chambers of the heart contract in a coordinated fashion. The sequence of events involved in one heartbeat is called the cardiac cycle. ...
Regulation of Heart Rate
... nearly impossible in humans. dP/dt is not an accurate measure because this increases with increasing preload and afterload. (dP/dt)/P ventricle is better. P ventricle is instantaneous ventricular pressure. Excess K+ decreases contractility. Excess Ca++ causes spastic contraction, and low Ca++ causes ...
... nearly impossible in humans. dP/dt is not an accurate measure because this increases with increasing preload and afterload. (dP/dt)/P ventricle is better. P ventricle is instantaneous ventricular pressure. Excess K+ decreases contractility. Excess Ca++ causes spastic contraction, and low Ca++ causes ...
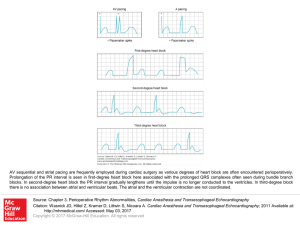
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
... AV sequential and atrial pacing are frequently employed during cardiac surgery as various degrees of heart block are often encountered perioperatively. Prolongation of the PR interval is seen in first-degree heart block here associated with the prolonged QRS complexes often seen during bundle branch ...
High grade B-cell lymphoma causing severe right heart failure
... are a challenge to manage during cardiac surgery since the etiology often guides therapy. We present a case of a patient with a history of lymphoma in severe right heart failure with a preoperative low quality transthoracic echo (TTE) suggestive of an intracardiac thrombus. However, an intraoperativ ...
... are a challenge to manage during cardiac surgery since the etiology often guides therapy. We present a case of a patient with a history of lymphoma in severe right heart failure with a preoperative low quality transthoracic echo (TTE) suggestive of an intracardiac thrombus. However, an intraoperativ ...
HEART DISEASE IN PREGNANCY
... Prognosis depending on the functional status v In general, women in NYHA classes I and II lesions usually do well during pregnancy and have a favorable prognosis with a mortality rate of <1%. v Patients in NYHA classes III and IV may have a mortality rate of 5% to 15%. These patients should be advi ...
... Prognosis depending on the functional status v In general, women in NYHA classes I and II lesions usually do well during pregnancy and have a favorable prognosis with a mortality rate of <1%. v Patients in NYHA classes III and IV may have a mortality rate of 5% to 15%. These patients should be advi ...