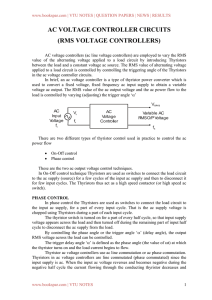
MAX6715–MAX6729 Dual/Triple Ultra-Low-Voltage SOT23 µP Supervisory Circuits General Description
... The MAX6715–MAX6729 are ultra-low-voltage microprocessor (µP) supervisory circuits designed to monitor two or three system power-supply voltages. These devices assert a system reset if any monitored supply falls below its factorytrimmed or adjustable threshold and maintain reset for a minimum timeou ...
... The MAX6715–MAX6729 are ultra-low-voltage microprocessor (µP) supervisory circuits designed to monitor two or three system power-supply voltages. These devices assert a system reset if any monitored supply falls below its factorytrimmed or adjustable threshold and maintain reset for a minimum timeou ...
Proceedings Template
... resulting in increased delay. Hence, this technique can only be used for paths that are non-critical. If the Vth of the sleep transistor is high, extra leakage saving is possible. The circuit topology is known as MTCMOS (Figure 4b) [15]. In fact, only one type (i.e. either PMOS or NMOS) of high Vth ...
... resulting in increased delay. Hence, this technique can only be used for paths that are non-critical. If the Vth of the sleep transistor is high, extra leakage saving is possible. The circuit topology is known as MTCMOS (Figure 4b) [15]. In fact, only one type (i.e. either PMOS or NMOS) of high Vth ...
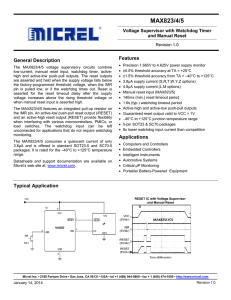
MAX823/4/5 Features General Description Voltage Supervisor with Watchdog Timer
... The MAX823/4/5 voltage supervisory circuits combine low-current, manual reset input, watchdog timer, activehigh and active-low push-pull outputs. The reset outputs are asserted and held when the supply voltage falls below the factory-programmed threshold voltage, when the /MR pin is pulled low, or i ...
... The MAX823/4/5 voltage supervisory circuits combine low-current, manual reset input, watchdog timer, activehigh and active-low push-pull outputs. The reset outputs are asserted and held when the supply voltage falls below the factory-programmed threshold voltage, when the /MR pin is pulled low, or i ...
UPC ENERGY PROCESSING BY MEANS OF POWER GYRATORS
... Experimental response of a boost converter-based R-semigyrator in sliding-mode to a pulsating load Simulated response of a PWM boost-shunt converter-based R-semigyrator to a pulsating input current. Simulated response of a PWM boost-shunt converter-based R-semigyrator to a pulsating load. Parallel c ...
... Experimental response of a boost converter-based R-semigyrator in sliding-mode to a pulsating load Simulated response of a PWM boost-shunt converter-based R-semigyrator to a pulsating input current. Simulated response of a PWM boost-shunt converter-based R-semigyrator to a pulsating load. Parallel c ...
Sepam™ Series 40 Protective Relays
... This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment ge ...
... This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment ge ...
Live Tank Circuit Breakers Application Guide
... SF6 gas circuit breakers are superior to these earlier technologies as they require substantially less maintenance. Furthermore, the numbers of breaking units are reduced. Up to 300 kV one interrupter per phase is used, and at 550 kV only two interrupters are required. All ABB SF6 live tank circuit ...
... SF6 gas circuit breakers are superior to these earlier technologies as they require substantially less maintenance. Furthermore, the numbers of breaking units are reduced. Up to 300 kV one interrupter per phase is used, and at 550 kV only two interrupters are required. All ABB SF6 live tank circuit ...
Temperature Measurement Using RTDs
... provide the greatest voltage sensitivity. The RTD signal is generally measured one of two ways: either by connecting the RTD element in one leg of a Wheatstone bridge excited by a constant reference voltage, or by running it in series with a precision current reference and measuring the correspondin ...
... provide the greatest voltage sensitivity. The RTD signal is generally measured one of two ways: either by connecting the RTD element in one leg of a Wheatstone bridge excited by a constant reference voltage, or by running it in series with a precision current reference and measuring the correspondin ...
TRANSCONDUCTANCE BASED CMOS CIRCUITS
... circuits based on the transconductance of a MOST, they are not the only ones. Linear circuits with an electronically variable I-V transfer characteristic, voltage amplification or current amplification have also been proposed [13]. In this thesis the collective noun "transactors" will be used for ci ...
... circuits based on the transconductance of a MOST, they are not the only ones. Linear circuits with an electronically variable I-V transfer characteristic, voltage amplification or current amplification have also been proposed [13]. In this thesis the collective noun "transactors" will be used for ci ...
CURSO DE ELECTRONICA IV Alfonso Pérez García.
... the impedance across the capacitors can be estimated from a formula I won't lay on you here because it includes beta, hie, as well as XC1 and XC2. Suffice to say it can be shown that the input impedance is a negative resistor in series with C1 and C2. And the frequency is in accordance with: ...
... the impedance across the capacitors can be estimated from a formula I won't lay on you here because it includes beta, hie, as well as XC1 and XC2. Suffice to say it can be shown that the input impedance is a negative resistor in series with C1 and C2. And the frequency is in accordance with: ...
Design, Fabrication, and Performance of Infrared and Visible Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Lasers
... grow nonlattice-matched DBR’s, and then wafer bond them to the optical cavity. For example, DBR mirrors consisting of GaAs–AlAs layers have been grown separately and then wafer bonded to phosphide-based alloys for operation at 1.3 and 1.55 m [12]. An important issue associated with current injection ...
... grow nonlattice-matched DBR’s, and then wafer bond them to the optical cavity. For example, DBR mirrors consisting of GaAs–AlAs layers have been grown separately and then wafer bonded to phosphide-based alloys for operation at 1.3 and 1.55 m [12]. An important issue associated with current injection ...
care and feeding of power grid tubes - F1FRV
... without driving the tube into the positive grid region. The difference between a tube with a µ of 5 and one with a µ of 160 can be seen by comparing Figure 1 to Figure 2. Observe how much more anode current at a given anode voltage can be obtained from the 3CX3000A1 (Figure 1) without driving the gr ...
... without driving the tube into the positive grid region. The difference between a tube with a µ of 5 and one with a µ of 160 can be seen by comparing Figure 1 to Figure 2. Observe how much more anode current at a given anode voltage can be obtained from the 3CX3000A1 (Figure 1) without driving the gr ...
MAX6736–MAX6745 Low-Power Dual-/Triple-Voltage SC70 µP Supervisory Circuits General Description
... MR, RSTIN, PFI to GND............................-0.3V to (VCC1 + 0.3V) Input/Output Current, All Pins .............................................20mA Continuous Power Dissipation (TA = +70°C) 5-Pin SC70 (derate 3.1mW/°C above +70°C) ..............247mW ...
... MR, RSTIN, PFI to GND............................-0.3V to (VCC1 + 0.3V) Input/Output Current, All Pins .............................................20mA Continuous Power Dissipation (TA = +70°C) 5-Pin SC70 (derate 3.1mW/°C above +70°C) ..............247mW ...