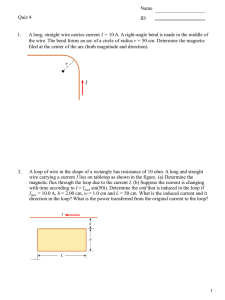
Title: Electricity Problem: How are voltage, current, and resistance
... Electrically charged particles exert forces on each other. There are two types of charges: negative and positive. Atoms are made up of particles that carry these different types of charges. Within an atom, electrons are negatively charged, and protons are positively charged. Other particles called n ...
... Electrically charged particles exert forces on each other. There are two types of charges: negative and positive. Atoms are made up of particles that carry these different types of charges. Within an atom, electrons are negatively charged, and protons are positively charged. Other particles called n ...
File - TAG Internship Portfolio
... Ohm’s Law describes how electrical currents, voltage, and resistance are all related. The equation can be algebraically manipulated to solve for any of the missing variables. Evidence of Learning What students should know: electric current - flow of charge through a conductor - unit is amperes (A) ...
... Ohm’s Law describes how electrical currents, voltage, and resistance are all related. The equation can be algebraically manipulated to solve for any of the missing variables. Evidence of Learning What students should know: electric current - flow of charge through a conductor - unit is amperes (A) ...
abc - Southern Methodist University
... A series AC circuit contains the following components: a 150 Ω resistor, and inductor of 250 mH, a capacitor of 2.00 μF, and source with ΔVmax = 160 V operating at 60.0 Hz. Calculate the (a) inductive reactance, (b) capacitive reactance, (c ) impedance, (d) maximum current (e) phase angle between th ...
... A series AC circuit contains the following components: a 150 Ω resistor, and inductor of 250 mH, a capacitor of 2.00 μF, and source with ΔVmax = 160 V operating at 60.0 Hz. Calculate the (a) inductive reactance, (b) capacitive reactance, (c ) impedance, (d) maximum current (e) phase angle between th ...
Power points II
... constant, it could be a tensor or it could be a function of E. • Resistivity—the inverse of conductivity • Resistance—the ability of a material to resist the flow of electric charge • Ohm—the unit of resistance. 1 = 1 V/A ...
... constant, it could be a tensor or it could be a function of E. • Resistivity—the inverse of conductivity • Resistance—the ability of a material to resist the flow of electric charge • Ohm—the unit of resistance. 1 = 1 V/A ...
Module 4, Lecture 4: Electric Current and Resistance Electric
... Module 4, Lecture 4: Electric Current and Resistance Current – any motion of ___________ from one region to another. ...
... Module 4, Lecture 4: Electric Current and Resistance Current – any motion of ___________ from one region to another. ...
Science 9 electricity powerpoint Topic 2
... • Electrical charge is measured in Coulombs • This is named after Charles A. Coulomb • 1 coloumb = 6.25 billion billion electrons ...
... • Electrical charge is measured in Coulombs • This is named after Charles A. Coulomb • 1 coloumb = 6.25 billion billion electrons ...
CR circuit - schoolphysics
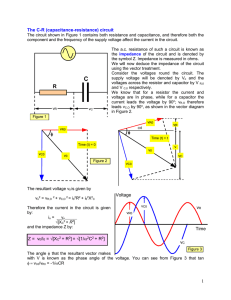
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
ET120 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... electrical circuits including the interrelations of voltage, current, impedance and power. The student will demonstrate analytical skills and insights that will be applied to more advanced circuits encountered in later courses. The student will use a mathematical and problem solving approach for int ...
... electrical circuits including the interrelations of voltage, current, impedance and power. The student will demonstrate analytical skills and insights that will be applied to more advanced circuits encountered in later courses. The student will use a mathematical and problem solving approach for int ...
PHYSICS (Electricity) Class-X Q.1 What is represented by joule
... (i) Refrigerator of rating 400W for ten hours each day. (ii) Two electric fans of rating 80W each for twelve hours each day. (iii) Six electric tubes of rating 18W each for 6 hours each day. Calculate the electricity bill of the household for the month of June if the cost per unit of electric energy ...
... (i) Refrigerator of rating 400W for ten hours each day. (ii) Two electric fans of rating 80W each for twelve hours each day. (iii) Six electric tubes of rating 18W each for 6 hours each day. Calculate the electricity bill of the household for the month of June if the cost per unit of electric energy ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide
... Examples of good conductor of electric current: transition metals like silver and copper Examples of poor conductors: glass, wood, plastic, rubber Insulators have a higher resistance to electric current than conductors. Circuits Circuits have 3 major parts: The wires in a circuit represent the “path ...
... Examples of good conductor of electric current: transition metals like silver and copper Examples of poor conductors: glass, wood, plastic, rubber Insulators have a higher resistance to electric current than conductors. Circuits Circuits have 3 major parts: The wires in a circuit represent the “path ...
Electric current 2
... - Resistance also varies with temperature - Resistors that follows Ohm’s law will have a current vs. voltage graph that is linear - Voltage vs. Current is nonlinear for a diode Electromotive Force and Circuits - If a circuit is not complete, a positive net charge will build at the end of the conduct ...
... - Resistance also varies with temperature - Resistors that follows Ohm’s law will have a current vs. voltage graph that is linear - Voltage vs. Current is nonlinear for a diode Electromotive Force and Circuits - If a circuit is not complete, a positive net charge will build at the end of the conduct ...
Voltage, Current, and Resistance
... The text defines current as the flow of electrons, which is typically the definition used in disciplines such as Physics. I will use the time rate of change of positive charges during this semester, which means either that the direction of positive current in my examples will be the opposite directi ...
... The text defines current as the flow of electrons, which is typically the definition used in disciplines such as Physics. I will use the time rate of change of positive charges during this semester, which means either that the direction of positive current in my examples will be the opposite directi ...
leds and resistor values
... Standard Values Resistors are only made in certain values. They are based on the ‘E12 series of preferred values’. These are ...
... Standard Values Resistors are only made in certain values. They are based on the ‘E12 series of preferred values’. These are ...
In the circuit shown below, the switch closes at t = 0. a) Find iL(t → ∞).
... The switch bypasses the current source and resistor. If we consider a voltage loop around the outside, we have only R2. Thus, the voltage drop across R2 must be zero. It follows from Ohm's law that the current in R2 must be zero. Since the current in R2 is the same as the current in L, we must have ...
... The switch bypasses the current source and resistor. If we consider a voltage loop around the outside, we have only R2. Thus, the voltage drop across R2 must be zero. It follows from Ohm's law that the current in R2 must be zero. Since the current in R2 is the same as the current in L, we must have ...
Chapter 2,3, & 4
... distances from the nucleus. Orbits are grouped onto energy bands known as shells. Electrons with the highest energy exist in the outermost shell, known as the valence shell, and its’ electrons are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are relatively loosely bound to the atom. If a valence elec ...
... distances from the nucleus. Orbits are grouped onto energy bands known as shells. Electrons with the highest energy exist in the outermost shell, known as the valence shell, and its’ electrons are called valence electrons. Valence electrons are relatively loosely bound to the atom. If a valence elec ...
Current Electricity
... Electric Current - number of charges that are moving in a circuit; measured in Amperes (A) Potential Difference (Voltage) - amount of energy that the charges will lose as they move around the circuit; measured in Volts (V) Resistance - ability of an object to slow down the charges as they move aroun ...
... Electric Current - number of charges that are moving in a circuit; measured in Amperes (A) Potential Difference (Voltage) - amount of energy that the charges will lose as they move around the circuit; measured in Volts (V) Resistance - ability of an object to slow down the charges as they move aroun ...
Science 9 Current Electricity Notes 2012
... electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. ...
... electrical energy each charged particle carries. The higher the energy of each charged particle, the greater the potential energy. ...
Document
... voltage sources, constant current sources, and resistors. In this case, the circuit voltages and currents are constant, independent of time. • Direct current is produced by sources such as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and others. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but c ...
... voltage sources, constant current sources, and resistors. In this case, the circuit voltages and currents are constant, independent of time. • Direct current is produced by sources such as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and others. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but c ...