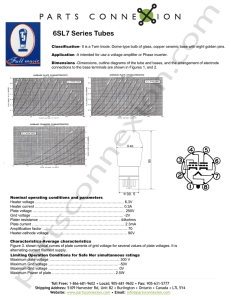
6SL7 Series Tubes
... Classification- It is a Twin triode. Dome-type bulb of glass, copper ceramic base with eight golden pins. Application -It intended for use a voltage amplifier or Phase inuerter. ...
... Classification- It is a Twin triode. Dome-type bulb of glass, copper ceramic base with eight golden pins. Application -It intended for use a voltage amplifier or Phase inuerter. ...
2Pro™ Device Series Specification Status: Released PRODUCT: LVM2P-075R14431
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, users should independently evaluate the suitability of and test each product selected for their own applications. Tyco Electronics Corporation and its affiliates in the TE Connectivity Ltd. group of companies (“TE”) reserves the ...
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, users should independently evaluate the suitability of and test each product selected for their own applications. Tyco Electronics Corporation and its affiliates in the TE Connectivity Ltd. group of companies (“TE”) reserves the ...
Electricity Study Guide
... *If the circuit is parallel in series, first use reciprocals to find the resistance of the “parallel” part, and add it to the overall “series” part. If the circuit is series in parallel, first add to find the “series” resistance, and then find the resistance of the overall “parallel” circuit using t ...
... *If the circuit is parallel in series, first use reciprocals to find the resistance of the “parallel” part, and add it to the overall “series” part. If the circuit is series in parallel, first add to find the “series” resistance, and then find the resistance of the overall “parallel” circuit using t ...
Voltage and Current Quiz Key Equations
... Figure 1: A battery and a lamp form a simple circuit. The arrow indicates the direction of current flow. Use this image to answer question 6. 6. Consider a circuit with a battery and a light bulb. If the current flows clockwise, which side of the battery has the higher voltage (left or right)? ...
... Figure 1: A battery and a lamp form a simple circuit. The arrow indicates the direction of current flow. Use this image to answer question 6. 6. Consider a circuit with a battery and a light bulb. If the current flows clockwise, which side of the battery has the higher voltage (left or right)? ...
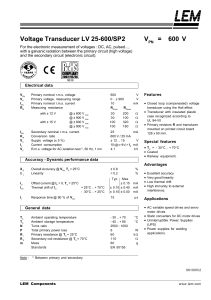
Voltage Transducer LV 25
... Secondary nominal r.m.s. current Conversion ratio Supply voltage (± 5 %) Current consumption R.m.s. voltage for AC isolation test 1), 50 Hz, 1 mn ...
... Secondary nominal r.m.s. current Conversion ratio Supply voltage (± 5 %) Current consumption R.m.s. voltage for AC isolation test 1), 50 Hz, 1 mn ...
Parallel Circuits KEY
... may flow, while a series has one. Each device in the circuit has the same voltage drop as the voltage source and Each device in the circuit may be turned off independently. ...
... may flow, while a series has one. Each device in the circuit has the same voltage drop as the voltage source and Each device in the circuit may be turned off independently. ...
A - Bibb County Schools
... a wire 10 cm in length and 3 cm in diameter a wire 5 cm in length and 3 cm in diameter a wire 10 cm in length and 5 cm in diameter a wire 5 cm in length and 5 cm in diameter ...
... a wire 10 cm in length and 3 cm in diameter a wire 5 cm in length and 3 cm in diameter a wire 10 cm in length and 5 cm in diameter a wire 5 cm in length and 5 cm in diameter ...
Voltage, Current and Ohm`s Law
... WARNING: Do NOT go above 5 volts across any one light bulb or you may burn the bulb out! 1. Using your voltmeter and your ammeter, determine the resistance of each light bulb twice: once when the filament is relatively cool (measure I when V = 1 volt and note brightness of bulb) and again when the f ...
... WARNING: Do NOT go above 5 volts across any one light bulb or you may burn the bulb out! 1. Using your voltmeter and your ammeter, determine the resistance of each light bulb twice: once when the filament is relatively cool (measure I when V = 1 volt and note brightness of bulb) and again when the f ...
Current, Resistance and Power
... material the resistor is made of. If you change material keeping physical geometry the same, the resistance changes ...
... material the resistor is made of. If you change material keeping physical geometry the same, the resistance changes ...
Electricity
... pushing electrons around a circuit or how much energy the current has. Increasing the voltage increases the current. • Voltage can also be called the potential difference. • The symbol for voltage is V. It is measured in a unit called volts. ...
... pushing electrons around a circuit or how much energy the current has. Increasing the voltage increases the current. • Voltage can also be called the potential difference. • The symbol for voltage is V. It is measured in a unit called volts. ...
Power Point
... did so rather quickly. When paper towel was rolled up and placed in the turkey baster it took much longer for the water to flow out. ...
... did so rather quickly. When paper towel was rolled up and placed in the turkey baster it took much longer for the water to flow out. ...
ICSE Guess Paper - 2008
... through a 8 ohm coil. Calculate the emf and the internal resistance of the cell. Solution :- Here, I1 = 0.6 A, R1 = 2 Ω, I2 = 0.3 A, R2 = 8 Ω, r = ? Using, I = E/(R + r), we get 0.6 = E /(2 + r) --- --- --- --- (i) 0.3 = E / (8 + r) --- --- --- --- (ii) from (i) and (ii) we get 0.6(2 + r) = 0.3(8 + ...
... through a 8 ohm coil. Calculate the emf and the internal resistance of the cell. Solution :- Here, I1 = 0.6 A, R1 = 2 Ω, I2 = 0.3 A, R2 = 8 Ω, r = ? Using, I = E/(R + r), we get 0.6 = E /(2 + r) --- --- --- --- (i) 0.3 = E / (8 + r) --- --- --- --- (ii) from (i) and (ii) we get 0.6(2 + r) = 0.3(8 + ...
Supplementary Notes
... currents. Magnetic field due to a moving charge or current element is given by: B = (μ/4π)(qvsinθ/r2) = (μ/4π)(IΔLsinθ/r2) (Biot-Savart Law) If you can choose a closed loop on which B is constant, you can use B║L = μIin (Ampere’s Law) ...
... currents. Magnetic field due to a moving charge or current element is given by: B = (μ/4π)(qvsinθ/r2) = (μ/4π)(IΔLsinθ/r2) (Biot-Savart Law) If you can choose a closed loop on which B is constant, you can use B║L = μIin (Ampere’s Law) ...