SNS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING Kurumbapalayam(Po
... The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit called voltage. The unit of voltage is the volt. Voltage represented by V or v. 5. Define electric potential. (May2004 ) Capacity of charged body to do work is electric potential. Electric potential = Work done / Charge = W/Q When on ...
... The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit called voltage. The unit of voltage is the volt. Voltage represented by V or v. 5. Define electric potential. (May2004 ) Capacity of charged body to do work is electric potential. Electric potential = Work done / Charge = W/Q When on ...
PRG-702: TYRISTOR POWER REGULATOR, SINGLE PHASE
... Theta’s PRG 702 POWER REGULATORS are suitable for controlling power of load from 1KW to 10KW. The load can be resistive like heaters, or inductive like transformers. The input connection is from 230 VAC supply. It includes various following features. The controllers have an optional current limiting ...
... Theta’s PRG 702 POWER REGULATORS are suitable for controlling power of load from 1KW to 10KW. The load can be resistive like heaters, or inductive like transformers. The input connection is from 230 VAC supply. It includes various following features. The controllers have an optional current limiting ...
Transformers - Port Hope High School
... A current of 1 Ampere is flowing when 1 Coulomb of charge flows past a point in a circuit in 1 second. Charge = current x time (C) (A) (s) If a current of 5 A is flowing then 5 C of charge pass a point in 1 second. In general, if a steady current I (amperes) flows for time t (seconds) the charge Q ( ...
... A current of 1 Ampere is flowing when 1 Coulomb of charge flows past a point in a circuit in 1 second. Charge = current x time (C) (A) (s) If a current of 5 A is flowing then 5 C of charge pass a point in 1 second. In general, if a steady current I (amperes) flows for time t (seconds) the charge Q ( ...
ELECTRICITY JSUNIL TUTORIAL, SAMASTIPUR 10 PHYSICS TEST PAPERS
... (b) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its: (I) area of cross-section? (II) Diameter? (c) What will be the resistance of a metal wire of length 2 meters and area of cross of section 1.55 x 10-6 m2, if the resistivity of the metal be 2.8 x 10-8 m? ...
... (b) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its: (I) area of cross-section? (II) Diameter? (c) What will be the resistance of a metal wire of length 2 meters and area of cross of section 1.55 x 10-6 m2, if the resistivity of the metal be 2.8 x 10-8 m? ...
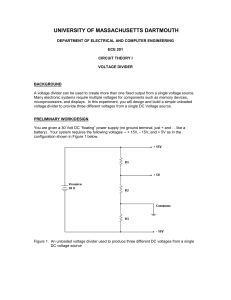
Voltage Divider
... A voltage divider can be used to create more than one fixed output from a single voltage source. Many electronic systems require multiple voltages for components such as memory devices, microprocessors, and displays. In this experiment, you will design and build a simple unloaded voltage divider to ...
... A voltage divider can be used to create more than one fixed output from a single voltage source. Many electronic systems require multiple voltages for components such as memory devices, microprocessors, and displays. In this experiment, you will design and build a simple unloaded voltage divider to ...
Kirchhoff`s Laws oBJEctiVE BaSic principlES
... current to flow are considered to be positive, whereas if the currents flow in the opposite direction they are considered to be negative, along with the voltages driving them. These rules can, for example, be applied to circuits featuring resistors in series or in parallel. ...
... current to flow are considered to be positive, whereas if the currents flow in the opposite direction they are considered to be negative, along with the voltages driving them. These rules can, for example, be applied to circuits featuring resistors in series or in parallel. ...
Electric Circuits - Greater Philadelphia Sea Perch Challenge
... This is measured in Joules per Coulomb, which is known as a Volt. In a circuit, as opposed to an electric field in general, the potential difference is often referred to as the voltage (V) of a circuit. The voltage drives electrons around the circuit, or the voltage does work moving the charges. How ...
... This is measured in Joules per Coulomb, which is known as a Volt. In a circuit, as opposed to an electric field in general, the potential difference is often referred to as the voltage (V) of a circuit. The voltage drives electrons around the circuit, or the voltage does work moving the charges. How ...
Real Contents
... Potential difference and electric potential Potential differences in a uniform electric field Electric potential and potential energy due to point charges Electric potential due to continuous charge distributions ...
... Potential difference and electric potential Potential differences in a uniform electric field Electric potential and potential energy due to point charges Electric potential due to continuous charge distributions ...
Lab 25 Electrical Resistance - Series
... An electric current is a flow of charge (electrons). For Direct Current (DC) charge always flows in the same direction. In Alternating Current (AC) the charge changes direction by moving back and forth at a frequency (cycles per second) of the electrical system. Nearly all substances fall into one o ...
... An electric current is a flow of charge (electrons). For Direct Current (DC) charge always flows in the same direction. In Alternating Current (AC) the charge changes direction by moving back and forth at a frequency (cycles per second) of the electrical system. Nearly all substances fall into one o ...
275DAY1BASICCONCEPTS Lecture Notes Page
... wire. Very fine wire (for example, 30 gauge) required more passes through the drawing dies than did 0 gauge wire. The AWG tables are for a single, solid, round conductor. The AWG of a stranded wire is determined by the total cross-sectional area of the conductor, which determines its current-carryin ...
... wire. Very fine wire (for example, 30 gauge) required more passes through the drawing dies than did 0 gauge wire. The AWG tables are for a single, solid, round conductor. The AWG of a stranded wire is determined by the total cross-sectional area of the conductor, which determines its current-carryin ...
Chapter 25 – Current, Resistance and Electromotive Force
... - No steady motion of charge in incomplete circuit. Electromotive Force (emf) - In an electric circuit there should be a device that acts like the water pump in a fountain = source of emf. - In this device, the charge travels “uphill” from lower to higher V (opposite to normal conductor) due to the ...
... - No steady motion of charge in incomplete circuit. Electromotive Force (emf) - In an electric circuit there should be a device that acts like the water pump in a fountain = source of emf. - In this device, the charge travels “uphill” from lower to higher V (opposite to normal conductor) due to the ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... 14. Alternating current, vector diagrams, LRC series in AC circuits 15. Maxwell’s equations, production of electromagnetic waves 16. Energy of EM waves, the Poynting vector, radiation pressure Laboratory experiments 1. Plane capacitor and dielectric constant of different materials 2. Ohm’s law in DC ...
... 14. Alternating current, vector diagrams, LRC series in AC circuits 15. Maxwell’s equations, production of electromagnetic waves 16. Energy of EM waves, the Poynting vector, radiation pressure Laboratory experiments 1. Plane capacitor and dielectric constant of different materials 2. Ohm’s law in DC ...
Ohmic devices - marineabudhabi
... 3rd CALL: Call for the teacher before using the ohmmeter. E8. With the ohmmeter, measure the resistance of resistors 1 and 2. R1 = ………….. R2 = ………….. Q9. Compare your measurements with the characteristics obtained at question I.2.b. What do you notice? Q10. Write a general relation that links the re ...
... 3rd CALL: Call for the teacher before using the ohmmeter. E8. With the ohmmeter, measure the resistance of resistors 1 and 2. R1 = ………….. R2 = ………….. Q9. Compare your measurements with the characteristics obtained at question I.2.b. What do you notice? Q10. Write a general relation that links the re ...
Source Conversions Proof
... For any realistic voltage source comprised of an ideal voltage source with series internal resistance there exists an equivalent current source consisting of an ideal current source with parallel internal resistance. The converse is also true. By equivalent we mean that both sources will produce the ...
... For any realistic voltage source comprised of an ideal voltage source with series internal resistance there exists an equivalent current source consisting of an ideal current source with parallel internal resistance. The converse is also true. By equivalent we mean that both sources will produce the ...
CTFinal
... A ray of light is sent into an optic fiber at an angle such that the angle with the normal to the pipe is . The fiber has an inner core with index ni and an outer cladding with index no. If no/ni is not large enough there will be no internal reflection. What is the minimum value of no/ni required f ...
... A ray of light is sent into an optic fiber at an angle such that the angle with the normal to the pipe is . The fiber has an inner core with index ni and an outer cladding with index no. If no/ni is not large enough there will be no internal reflection. What is the minimum value of no/ni required f ...
Unit 2 Section 2 - Belfast Royal Academy
... V across 10 = IR = 0.5 x 10 = 5V V across 20 = (10 – 5) = 5 V Current through 20 = V/R = 5/20 = 0.25 A (c) V across 20 = 5 V; V across 10 = 5 V (see above) ...
... V across 10 = IR = 0.5 x 10 = 5V V across 20 = (10 – 5) = 5 V Current through 20 = V/R = 5/20 = 0.25 A (c) V across 20 = 5 V; V across 10 = 5 V (see above) ...