Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
... Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
Physics_A2_37_GeneratingElectricity
... Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
... Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical Power = Energy transferred per s from source ...
SNC1P Electricity Review
... 6. Draw a closed series circuit with the following features: a cell, connecting wires, two light bulbs, a switch, a fuse, and a resistor. Show how you would properly connect and ammeter anywhere in the circuit, and show how you would properly connect a voltmeter to read the potential difference acr ...
... 6. Draw a closed series circuit with the following features: a cell, connecting wires, two light bulbs, a switch, a fuse, and a resistor. Show how you would properly connect and ammeter anywhere in the circuit, and show how you would properly connect a voltmeter to read the potential difference acr ...
Circuit Breaker Types.ppt
... In this chapter we have discussed the calculation of symmetrical subtransient fault current in a network. However the instantaneous current following a fault will also contain the dc component. In a high power circuit breaker selection, the subtransient current is multiplied by a factor of 1.6 to de ...
... In this chapter we have discussed the calculation of symmetrical subtransient fault current in a network. However the instantaneous current following a fault will also contain the dc component. In a high power circuit breaker selection, the subtransient current is multiplied by a factor of 1.6 to de ...
Relay contact protection • Noise reduction on controllers
... 220 ohms or a .5 mF + 330 ohms range. If you need a higher capacitance than 1.0 mF, you may be better off with a Zener or a varistor in terms of cost and space. For most relays and triacs .1 mF + 100 ohms provides a satisfactory suppression. When protecting contacts in AC circuits, the same general ...
... 220 ohms or a .5 mF + 330 ohms range. If you need a higher capacitance than 1.0 mF, you may be better off with a Zener or a varistor in terms of cost and space. For most relays and triacs .1 mF + 100 ohms provides a satisfactory suppression. When protecting contacts in AC circuits, the same general ...
BasicElectronicWorksheet
... Replace the capacitors with exact voltage rating. If impossible the voltage rating must be greater If a lower rating is used the circuit will result in damage. _______________ the flow of current (I) Can be used as a ____________ in a circuit R are ____________ polarity sensitive Measured in _______ ...
... Replace the capacitors with exact voltage rating. If impossible the voltage rating must be greater If a lower rating is used the circuit will result in damage. _______________ the flow of current (I) Can be used as a ____________ in a circuit R are ____________ polarity sensitive Measured in _______ ...
Ohm`s Law - EdRenzi.com
... The law which governs most simple and many complex electrical phenomena is known as Ohm’s Law. It is the most important law in electricity. In 1827, a German locksmith and mathematician named Georg Simon Ohm, introduced the law which bears his name. His many years of experimenting with electricity b ...
... The law which governs most simple and many complex electrical phenomena is known as Ohm’s Law. It is the most important law in electricity. In 1827, a German locksmith and mathematician named Georg Simon Ohm, introduced the law which bears his name. His many years of experimenting with electricity b ...
Learning Objectives
... • Current produced in a simple dynamo can flow in two ways, if it flows in the same direction and is called direct current (DC). • If it flows and keeps changing direction it is called alternating current(AC). ...
... • Current produced in a simple dynamo can flow in two ways, if it flows in the same direction and is called direct current (DC). • If it flows and keeps changing direction it is called alternating current(AC). ...
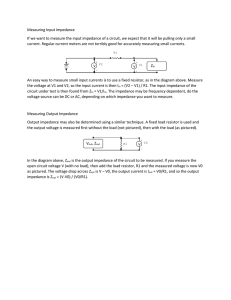
Measuring Input Impedance If we want to measure the input
... In the diagram above, Zout is the output impedance of the circuit to be measured. If you measure the open circuit voltage V (with no load), then add the load resistor, R1 and the measured voltage is now V0 as pictured. The voltage drop across Zout is V – V0, the output current is Iout = V0/R1, and s ...
... In the diagram above, Zout is the output impedance of the circuit to be measured. If you measure the open circuit voltage V (with no load), then add the load resistor, R1 and the measured voltage is now V0 as pictured. The voltage drop across Zout is V – V0, the output current is Iout = V0/R1, and s ...
Input Components
... colours, shapes, sizes and brightness. The more common colours being red, green and yellow. They are also available in bi and tri - colour versions Round ones come in 3, 5 and 8mm sizes. There are also rectangular, square and bar types. Flashing types are available and seven segment displays are mad ...
... colours, shapes, sizes and brightness. The more common colours being red, green and yellow. They are also available in bi and tri - colour versions Round ones come in 3, 5 and 8mm sizes. There are also rectangular, square and bar types. Flashing types are available and seven segment displays are mad ...
Name MEASURING AND USING ELECTRICITY from the series
... MEASURING AND USING ELECTRICITY from the series Electricity and Magnetism ...
... MEASURING AND USING ELECTRICITY from the series Electricity and Magnetism ...
Electronics Technology Fundamentals
... the circuits, you had 2 resistors connected as shown to the right (with different values) and a meter set on Ohms measuring them. Are the resistors in series? ...
... the circuits, you had 2 resistors connected as shown to the right (with different values) and a meter set on Ohms measuring them. Are the resistors in series? ...
Unijunction Transistor(UJT) - Corporate Group of Institutes
... As long as IB = 0, the circuit of behaves as a voltage divider. Assume now that vE is gradually increased from zero using an emitter supply VEE . The diode remains reverse biased till vE voltage is less than ƞVBB and no emitter current flows except leakage current. The emitter diode will be revers ...
... As long as IB = 0, the circuit of behaves as a voltage divider. Assume now that vE is gradually increased from zero using an emitter supply VEE . The diode remains reverse biased till vE voltage is less than ƞVBB and no emitter current flows except leakage current. The emitter diode will be revers ...
in an Electrical ckts.
... The voltage between the ends of an ideal conductor is zero regardless of the current flowing through the conductor. When two points in a ckt are connected together by an ideal conductor, we say that the points are shorted together. Another term for an ideal conductor is short ckt. All points in a ck ...
... The voltage between the ends of an ideal conductor is zero regardless of the current flowing through the conductor. When two points in a ckt are connected together by an ideal conductor, we say that the points are shorted together. Another term for an ideal conductor is short ckt. All points in a ck ...
Ohm Zone: Series Circuit I
... Below is the menu from OhmZone. Click on the “popups” button that is the question mark. This will give you a description of each of the components as your mouse moves over them. You will find this very useful. ...
... Below is the menu from OhmZone. Click on the “popups” button that is the question mark. This will give you a description of each of the components as your mouse moves over them. You will find this very useful. ...
Review from 1/19
... current in schematics and books is capital ‘I’. An amp is the basic unit of current, and the notation for the amp is the capital ‘A’. An amp is a very large amount of current, we will typically work with mAmps (1/1000 A). The quantity of electrons used in determining an ampere is called "coulomb;” o ...
... current in schematics and books is capital ‘I’. An amp is the basic unit of current, and the notation for the amp is the capital ‘A’. An amp is a very large amount of current, we will typically work with mAmps (1/1000 A). The quantity of electrons used in determining an ampere is called "coulomb;” o ...
Electrical Principles Wk 1B
... Current (I) flows through a circuit when a source of power is connected to a device ...
... Current (I) flows through a circuit when a source of power is connected to a device ...