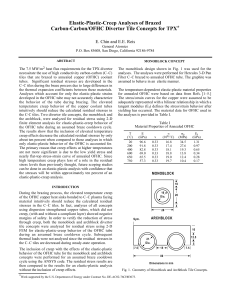
Influence of the cutting regime on the residual stresses generated by
... geometric distortions of a component/structure, especially those subjected to alternating service loads and/or corrosive environments. It arises from the elastic response of material to inhomogeneous distribution of non-elastic strains, e.g., precipitation, phase transformation, thermal expansion, e ...
... geometric distortions of a component/structure, especially those subjected to alternating service loads and/or corrosive environments. It arises from the elastic response of material to inhomogeneous distribution of non-elastic strains, e.g., precipitation, phase transformation, thermal expansion, e ...
Elastic-Plastic-Creep Analyses of Brazed Carbon
... are not more significant is that the total strains developed in the OFHC tube are about the same whether achieved by an elastic-plastic path or a combined elastic- plastic-creep path. This is due to the low yield stress and nearly flat-top stressstrain curve of annealed OFHC. It is theorized that it ...
... are not more significant is that the total strains developed in the OFHC tube are about the same whether achieved by an elastic-plastic path or a combined elastic- plastic-creep path. This is due to the low yield stress and nearly flat-top stressstrain curve of annealed OFHC. It is theorized that it ...
Mechanical Engineering: Module 8
... If I think of a surface element, and if I talk about the stress vector on this particular setter, or the stress vector on this side exerting a force on that side, the unit outward normal would be in this direction. Visa-versa, if I wanted the force for the fluid on this side, being exerted on the fl ...
... If I think of a surface element, and if I talk about the stress vector on this particular setter, or the stress vector on this side exerting a force on that side, the unit outward normal would be in this direction. Visa-versa, if I wanted the force for the fluid on this side, being exerted on the fl ...
3.6 Yield Phenomena 3.6.1 Introduction
... Another observed phenomenon, closely related to the yield-point phenomena associated with interstitial atoms, is that of temperature-dependent serrated curves. Serrated stress/strain curves are similar to those observed in twinned specimens, but their origin is different, as mentioned. In Fig. 3.18, ...
... Another observed phenomenon, closely related to the yield-point phenomena associated with interstitial atoms, is that of temperature-dependent serrated curves. Serrated stress/strain curves are similar to those observed in twinned specimens, but their origin is different, as mentioned. In Fig. 3.18, ...
measuring the yield stress of waxy crude oils considering its
... becomes a function of the experimental protocol, the accuracy of the rheometer at low shear rates and the patience of the experimentalist. These time dependent materials are sensitive to the time scale over which the gel is subjected to a given shear stress. Therefore, another source of different be ...
... becomes a function of the experimental protocol, the accuracy of the rheometer at low shear rates and the patience of the experimentalist. These time dependent materials are sensitive to the time scale over which the gel is subjected to a given shear stress. Therefore, another source of different be ...
4 Constitutive Equations
... For homogenous and isotropic elastic materials we commonly require the strain energy function to be a convex potential. However, non-convex energy functions are encountered in many applications such as phase transitions in shape memory alloys [Bha03, RC05], in phase field theory (see Section ??) and ...
... For homogenous and isotropic elastic materials we commonly require the strain energy function to be a convex potential. However, non-convex energy functions are encountered in many applications such as phase transitions in shape memory alloys [Bha03, RC05], in phase field theory (see Section ??) and ...
Probabilistic multiscale models and measurements of self
... al., 1989; Krapez et al., 1999; La Rosa and Risitano, 2000; Lehr, 1926; Luong, 1995; Mabru and Chrysochoos, 2001; Moore and Kommers, 1921; Stärk, 1980; Stromeyer, 1915; Welter, 1937; Yang et al., 2005). Various experimental procedures were proposed involving the use of thermocouples (Doudard et al., ...
... al., 1989; Krapez et al., 1999; La Rosa and Risitano, 2000; Lehr, 1926; Luong, 1995; Mabru and Chrysochoos, 2001; Moore and Kommers, 1921; Stärk, 1980; Stromeyer, 1915; Welter, 1937; Yang et al., 2005). Various experimental procedures were proposed involving the use of thermocouples (Doudard et al., ...
damage model for brittle elastic solids with unequal tensile
... Griffith cracks (Rice [14]), free energy at the current state is equal to the work done in transforming the body from its initial to current state along an imagined reversible and isothermal path. This path can be recreated by a sequence of two steps. First, new microcrack ...
... Griffith cracks (Rice [14]), free energy at the current state is equal to the work done in transforming the body from its initial to current state along an imagined reversible and isothermal path. This path can be recreated by a sequence of two steps. First, new microcrack ...
Stress and Strain
... measure of the intensity of internal forces acting parallel or tangent to a plane of cut. To get a sense of shear stresses, hold a stack of paper with both hands such that one hand is under the stack while the other hand is above it. First, press the stack of papers together. Then, slowly slide one ...
... measure of the intensity of internal forces acting parallel or tangent to a plane of cut. To get a sense of shear stresses, hold a stack of paper with both hands such that one hand is under the stack while the other hand is above it. First, press the stack of papers together. Then, slowly slide one ...
Relationship between Yield stress and yield Strength on Various
... Abstract: Stress is ability of materials to resist failure. The relationship between yield strength and yield stress of various grade of steel being hot rolled is necessary to predetermine the failure of engineering materials.The Torsional tests obtained by previous researchers for temperature range ...
... Abstract: Stress is ability of materials to resist failure. The relationship between yield strength and yield stress of various grade of steel being hot rolled is necessary to predetermine the failure of engineering materials.The Torsional tests obtained by previous researchers for temperature range ...
Strength of materials
... Three other elastic moduli are Poisson's ratio, Lamé's first parameter, and P-wave modulus. Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of an elastic material and is a quantity used to characterize materials. It is defined as the ratio of the uniaxial stress over the uniaxial strain in the range o ...
... Three other elastic moduli are Poisson's ratio, Lamé's first parameter, and P-wave modulus. Young's modulus is a measure of the stiffness of an elastic material and is a quantity used to characterize materials. It is defined as the ratio of the uniaxial stress over the uniaxial strain in the range o ...
464_lec.pdf
... elastic part of the deformation is assumed to be linear and to display isotropic material behavior. This implies that the stress rate is, at any moment in time, related to the elastic strain rate by the generalized Hooke's law: ...
... elastic part of the deformation is assumed to be linear and to display isotropic material behavior. This implies that the stress rate is, at any moment in time, related to the elastic strain rate by the generalized Hooke's law: ...
A Novel 3D Finite Element Simulation Model for
... 3D Finite-Element shot peening models known from literature do not take into account component thickness as a geometric parameter influencing the residual stress state after shot peening. Hence classic approaches and a new approach of model constraints were investigated for their capability to contr ...
... 3D Finite-Element shot peening models known from literature do not take into account component thickness as a geometric parameter influencing the residual stress state after shot peening. Hence classic approaches and a new approach of model constraints were investigated for their capability to contr ...
on plastic void growth in strong ductile materials
... The plots in Fig. 3 reveal a relatively mild effect of elastic compressibility on the value of σcr . For the considered material properties, an increase of Poisson’s ratio from 1/3 to 1/2 increases the critical stress by about 5%. The value of the yield stress Y was selected to facilitate the compar ...
... The plots in Fig. 3 reveal a relatively mild effect of elastic compressibility on the value of σcr . For the considered material properties, an increase of Poisson’s ratio from 1/3 to 1/2 increases the critical stress by about 5%. The value of the yield stress Y was selected to facilitate the compar ...
12.3 - De Anza
... When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed. § The curve is no longer a straight line. With additional stress, the material ultimately breaks. ...
... When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed. § The curve is no longer a straight line. With additional stress, the material ultimately breaks. ...
Chapter 12
... When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed. The curve is no longer a straight line. With additional stress, the material ultimately breaks. ...
... When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed. The curve is no longer a straight line. With additional stress, the material ultimately breaks. ...
Use of Copper-Base Shape Memory Alloys in Seismic Energy
... suitable for low-rise structures is base isolation [1]. Another approach, appropriate for medium and highrise structures, lies in taking advantage of the energy dissipation potential of specific devices [2]. Examples of passive supplementary dampers include devices based on metal yielding, friction, ...
... suitable for low-rise structures is base isolation [1]. Another approach, appropriate for medium and highrise structures, lies in taking advantage of the energy dissipation potential of specific devices [2]. Examples of passive supplementary dampers include devices based on metal yielding, friction, ...
Finite Element Analysis of Thermal Stresses in a Pad-Disc Brake System (a Review)
... the circumference of the rubbing path, so called buckling mode of the disc. The temperature and the stresses due to the mechanical and the thermal loads were calculated. At the first stage an effect of the mechanical load, resulting from the pressure and the friction force on the stresses in the pad ...
... the circumference of the rubbing path, so called buckling mode of the disc. The temperature and the stresses due to the mechanical and the thermal loads were calculated. At the first stage an effect of the mechanical load, resulting from the pressure and the friction force on the stresses in the pad ...
a new frontier for deposit stress measurement
... Spiral Contractometer with calibration weights, support stand and spiral test pieces. Container 4” diameter and 10” height for nickel strike anode basket and ...
... Spiral Contractometer with calibration weights, support stand and spiral test pieces. Container 4” diameter and 10” height for nickel strike anode basket and ...
738_1.pdf
... uniaxial or biaxial stress, alters the crystal symmetry and thus lifts certain phonon mode degeneracies (splittings). Because strain in a semiconductor microstructure presents as second rank tensor £ /y , the determination of all strain components can be very complicated. This not only requires meas ...
... uniaxial or biaxial stress, alters the crystal symmetry and thus lifts certain phonon mode degeneracies (splittings). Because strain in a semiconductor microstructure presents as second rank tensor £ /y , the determination of all strain components can be very complicated. This not only requires meas ...
RHEOLOGY
... describe the general behaviour of rheology by introducing strain rate and what the creep curve is. From this we introduce equations that represent the behaviour of different materials that we can calculate the motion and deformation of a body of rock. The relationships regarding such behaviour inclu ...
... describe the general behaviour of rheology by introducing strain rate and what the creep curve is. From this we introduce equations that represent the behaviour of different materials that we can calculate the motion and deformation of a body of rock. The relationships regarding such behaviour inclu ...
Engineering Mechanics
... Models are generally used in science and engineering to reduce a complex reality for detailed investigations. The prediction of a future state of a system is the main goal, which has to be achieved. Due to the hypothetical nature of this approach, it is irrelevant whether the assumed state will be a ...
... Models are generally used in science and engineering to reduce a complex reality for detailed investigations. The prediction of a future state of a system is the main goal, which has to be achieved. Due to the hypothetical nature of this approach, it is irrelevant whether the assumed state will be a ...
Chapter 3 Fracture
... Most ductile metals other than steel do not have a well-defined yield point. For these materials the yield strength is typically determined by the "offset yield method", by which a line is drawn parallel to the linear elastic portion of the curve and intersecting the abscissa at some arbitrary value ...
... Most ductile metals other than steel do not have a well-defined yield point. For these materials the yield strength is typically determined by the "offset yield method", by which a line is drawn parallel to the linear elastic portion of the curve and intersecting the abscissa at some arbitrary value ...
Stress (mechanics)

In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that expresses the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting a weight, each particle in the bar pushes on the particles immediately below it. When a liquid is in a closed container under pressure, each particle gets pushed against by all the surrounding particles. The container walls and the pressure-inducing surface (such as a piston) push against them in (Newtonian) reaction. These macroscopic forces are actually the average of a very large number of intermolecular forces and collisions between the particles in those molecules.Strain inside a material may arise by various mechanisms, such as stress as applied by external forces to the bulk material (like gravity) or to its surface (like contact forces, external pressure, or friction). Any strain (deformation) of a solid material generates an internal elastic stress, analogous to the reaction force of a spring, that tends to restore the material to its original non-deformed state. In liquids and gases, only deformations that change the volume generate persistent elastic stress. However, if the deformation is gradually changing with time, even in fluids there will usually be some viscous stress, opposing that change. Elastic and viscous stresses are usually combined under the name mechanical stress.Significant stress may exist even when deformation is negligible or non-existent (a common assumption when modeling the flow of water). Stress may exist in the absence of external forces; such built-in stress is important, for example, in prestressed concrete and tempered glass. Stress may also be imposed on a material without the application of net forces, for example by changes in temperature or chemical composition, or by external electromagnetic fields (as in piezoelectric and magnetostrictive materials).The relation between mechanical stress, deformation, and the rate of change of deformation can be quite complicated, although a linear approximation may be adequate in practice if the quantities are small enough. Stress that exceeds certain strength limits of the material will result in permanent deformation (such as plastic flow, fracture, cavitation) or even change its crystal structure and chemical composition.In some branches of engineering, the term stress is occasionally used in a looser sense as a synonym of ""internal force"". For example, in the analysis of trusses, it may refer to the total traction or compression force acting on a beam, rather than the force divided by the area of its cross-section.