RHEOLOGY
... All the previous models wored under the assuption that the relationship between the strain rate and the stress was linear ( ė α σ ), but at elevated tempuratures experiments have shown that the relationship is not linear. A physical model for rocks using nonlinear behaviour is a blocg and spring in ...
... All the previous models wored under the assuption that the relationship between the strain rate and the stress was linear ( ė α σ ), but at elevated tempuratures experiments have shown that the relationship is not linear. A physical model for rocks using nonlinear behaviour is a blocg and spring in ...
Articular Cartilage Notes - Biomechanics and Biol+
... short time properties An assumption is cartilage behaves elastically when subjected to fast load application o Ideally this is only true after a short time period of load application before the fluid in the cartilage has had time to flow or at equilibrium when movement of interstitial fluid ceases o ...
... short time properties An assumption is cartilage behaves elastically when subjected to fast load application o Ideally this is only true after a short time period of load application before the fluid in the cartilage has had time to flow or at equilibrium when movement of interstitial fluid ceases o ...
Slides for lecture #23
... Small time dependent effects can be observed also for elastic deformation - e.g. related to reversible diffusion of C in a steel under stress. If a sample is vibrated close to resonance, the deviation from perfect elasticity, i.e. the existence of dissipative processes, results in a change of the re ...
... Small time dependent effects can be observed also for elastic deformation - e.g. related to reversible diffusion of C in a steel under stress. If a sample is vibrated close to resonance, the deviation from perfect elasticity, i.e. the existence of dissipative processes, results in a change of the re ...
Project_FEA.doc
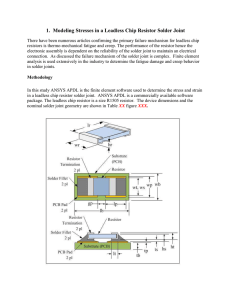
... In ANSYS there are various models available to simulate visco-plasticity. The Anand model was originally developed for metal forming applications. It is however applicable to applications that involve strain and temperature effect including solder joints and high temperature creep [ANSYS]. The Anand ...
... In ANSYS there are various models available to simulate visco-plasticity. The Anand model was originally developed for metal forming applications. It is however applicable to applications that involve strain and temperature effect including solder joints and high temperature creep [ANSYS]. The Anand ...
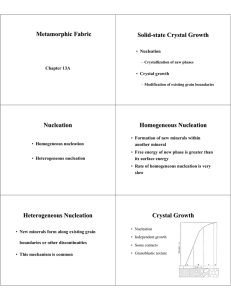
Metamorphic Fabric Solid-state Crystal Growth Nucleation
... • Defined as a uniform stress on a point regardless of direction • Hydrostatic pressure increases with depth in the earth • Its value equals ρgz ...
... • Defined as a uniform stress on a point regardless of direction • Hydrostatic pressure increases with depth in the earth • Its value equals ρgz ...
Classes of materials
... In order to select the correct material of construction, the process environment to which the material will be exposed must be clearly defined. In addition to the main corrosive chemicals present, the following factors must be considered: 1. Temperature—affects corrosion rate and mechanical properti ...
... In order to select the correct material of construction, the process environment to which the material will be exposed must be clearly defined. In addition to the main corrosive chemicals present, the following factors must be considered: 1. Temperature—affects corrosion rate and mechanical properti ...
Syllabus High Temperature Structural Materials
... oxidation and/or corrosion at high temperature in aerospace, energy related field, and material processing etc. In the introduction, typical strengthening mechanism of alloys for high temperature materials is introduced. At high temperature, materials deform gradually when they are exposed even unde ...
... oxidation and/or corrosion at high temperature in aerospace, energy related field, and material processing etc. In the introduction, typical strengthening mechanism of alloys for high temperature materials is introduced. At high temperature, materials deform gradually when they are exposed even unde ...
properties of materials
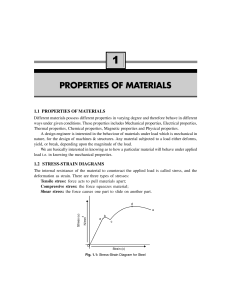
... The stress-strain diagram for steel is shown in Fig. 1.1(a). The salient points are: Point a: Limit of proportionality. 0-a is a straight line and stress is proportional to strain. The slope of the line gives the value of Young’s Modulus of Elasticity; E. Point b gives the yield point of the materia ...
... The stress-strain diagram for steel is shown in Fig. 1.1(a). The salient points are: Point a: Limit of proportionality. 0-a is a straight line and stress is proportional to strain. The slope of the line gives the value of Young’s Modulus of Elasticity; E. Point b gives the yield point of the materia ...
A - Free-lancers.net
... impurities. So experimental data about radiation changes of scintillation crystals can be quite different even for ‘good’ samples depending on a dislocation density and seed pore concentration. This circumstance complicates the research of mechanisms of crystal radiation damages. The study of these ...
... impurities. So experimental data about radiation changes of scintillation crystals can be quite different even for ‘good’ samples depending on a dislocation density and seed pore concentration. This circumstance complicates the research of mechanisms of crystal radiation damages. The study of these ...
Elastic-Plastic-Creep Analyses of Brazed Carbon
... These results show that the inclusion of elevated temperature creep effects decrease the calculated residual stresses by only about ten percent when compared to those analyses in which only elastic-plastic behavior of the OFHC is accounted for. The primary reason that creep effects at higher tempera ...
... These results show that the inclusion of elevated temperature creep effects decrease the calculated residual stresses by only about ten percent when compared to those analyses in which only elastic-plastic behavior of the OFHC is accounted for. The primary reason that creep effects at higher tempera ...
lecture 10-12 mechanical failure
... involving the diffusion of vacancies or interstitials. Occurs for 10-4 < s/G < 10-2. • Diffusion creep involves the flow of vacancies and interstitials through a crystal under the influence of applied stress. Occurs for s/G < 10-4. This category includes Nabarro -Herring and Coble creep (discussed ...
... involving the diffusion of vacancies or interstitials. Occurs for 10-4 < s/G < 10-2. • Diffusion creep involves the flow of vacancies and interstitials through a crystal under the influence of applied stress. Occurs for s/G < 10-4. This category includes Nabarro -Herring and Coble creep (discussed ...
Lecture #19 Creep in Metals: - References:
... are below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods, and near the melting point. Creep always increases with temperature. The rate of this deformation is a function of the material properties, exposure time, exposure temperatur ...
... are below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods, and near the melting point. Creep always increases with temperature. The rate of this deformation is a function of the material properties, exposure time, exposure temperatur ...
Chap 8 Learn Obj
... 11. Briefly state why sharp corners should be avoided in designing structures that are subjected to stresses. ...
... 11. Briefly state why sharp corners should be avoided in designing structures that are subjected to stresses. ...
Word file
... distributions of MX carbonitrides were observed after tempering heat treatment but that extensive coarsening of the nano-size MX carbonitrides took place during creep, as observed to be 60 nm in size or more after creep for 1.5x103 h at 923 K. The extensive coarsening of MX carbonitrides caused a d ...
... distributions of MX carbonitrides were observed after tempering heat treatment but that extensive coarsening of the nano-size MX carbonitrides took place during creep, as observed to be 60 nm in size or more after creep for 1.5x103 h at 923 K. The extensive coarsening of MX carbonitrides caused a d ...
Creep (deformation)
In materials science, creep (sometimes called cold flow) is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of mechanical stresses. It can occur as a result of long-term exposure to high levels of stress that are still below the yield strength of the material. Creep is more severe in materials that are subjected to heat for long periods, and generally increases as they near their melting point.The rate of deformation is a function of the material properties, exposure time, exposure temperature and the applied structural load. Depending on the magnitude of the applied stress and its duration, the deformation may become so large that a component can no longer perform its function — for example creep of a turbine blade will cause the blade to contact the casing, resulting in the failure of the blade. Creep is usually of concern to engineers and metallurgists when evaluating components that operate under high stresses or high temperatures. Creep is a deformation mechanism that may or may not constitute a failure mode. For example, moderate creep in concrete is sometimes welcomed because it relieves tensile stresses that might otherwise lead to cracking.Unlike brittle fracture, creep deformation does not occur suddenly upon the application of stress. Instead, strain accumulates as a result of long-term stress. Therefore, creep is a ""time-dependent"" deformation.The temperature range in which creep deformation may occur differs in various materials. For example, tungsten requires a temperature in the thousands of degrees before creep deformation can occur, while ice will creep at temperatures near 0 °C (32 °F). As a general guideline, the effects of creep deformation generally become noticeable at approximately 30% of the melting point (as measured on a thermodynamic temperature scale such as Kelvin or Rankine) for metals, and at 40–50% of melting point for ceramics. Virtually any material will creep upon approaching its melting temperature. Since the creep minimum temperature is related to the melting point, creep can be seen at relatively low temperatures for some materials. Plastics and low-melting-temperature metals, including many solders, can begin to creep at room temperature, as can be seen markedly in old lead hot-water pipes. Glacier flow is an example of creep processes in ice.