Lecture 5: Universal One-Way Function and Computational Number
... notes on the course website. The lecture notes cover just enough number theory for a student to understand the material in this course. Theorem 2 (Agrawal, Kayal, Saxena) There exists a deterministic polynomial-time algorithm that checks whether a number is prime. See the paper “Primes is in P” for ...
... notes on the course website. The lecture notes cover just enough number theory for a student to understand the material in this course. Theorem 2 (Agrawal, Kayal, Saxena) There exists a deterministic polynomial-time algorithm that checks whether a number is prime. See the paper “Primes is in P” for ...
A1982NR91400001
... right-hand side there is the dependent variable which has been measured. Interpolation is necessary if the experimenter wants to present his or her results in graphic form as a curve in a coordinate system. In this situation, it is natural to compensate for possible errors in the measured quantities ...
... right-hand side there is the dependent variable which has been measured. Interpolation is necessary if the experimenter wants to present his or her results in graphic form as a curve in a coordinate system. In this situation, it is natural to compensate for possible errors in the measured quantities ...
MaxFlow.pdf
... has grown exponentially, it is often prohibitively time-consuming to solve these problems using traditional computing techniques, according to Jonathan Kelner, an associate professor of applied mathematics at MIT and a member of MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). ...
... has grown exponentially, it is often prohibitively time-consuming to solve these problems using traditional computing techniques, according to Jonathan Kelner, an associate professor of applied mathematics at MIT and a member of MIT’s Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL). ...
Document
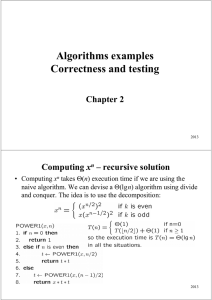
... Chapter 1 Introduction Definition of Algorithm An algorithm is a finite sequence of precise instructions for performing a computation or for solving a problem. Example 1 Describe an algorithm for finding the maximum (largest) value in a finite sequence of integers. Solution ...
... Chapter 1 Introduction Definition of Algorithm An algorithm is a finite sequence of precise instructions for performing a computation or for solving a problem. Example 1 Describe an algorithm for finding the maximum (largest) value in a finite sequence of integers. Solution ...