Standard 3
... A class observes an unknown plant and discovers that the plant’s seeds have only one cotyledon. When the class examines the leaves and the stem, what will they MOST LIKELY find? A parallel veins and a ring of vascular bundles B parallel veins and scattered vascular bundles C a netted arrangement of ...
... A class observes an unknown plant and discovers that the plant’s seeds have only one cotyledon. When the class examines the leaves and the stem, what will they MOST LIKELY find? A parallel veins and a ring of vascular bundles B parallel veins and scattered vascular bundles C a netted arrangement of ...
Root and Leaf Structure
... the stomata, the bene ts of regulating the opening and closing of the stomata are greater than the energy expenditure of moving ions into and out of the guard cells. Plants actively regulate the movement of these ions and can respond rapidly to changes in the amount of sunlight, relative humidity an ...
... the stomata, the bene ts of regulating the opening and closing of the stomata are greater than the energy expenditure of moving ions into and out of the guard cells. Plants actively regulate the movement of these ions and can respond rapidly to changes in the amount of sunlight, relative humidity an ...
20.1 Origins of Plant Life
... 20.1 Origins of Plant Life • A vascular system allows resources to move to different parts of the plant. – specialized tissues – brings water and mineral nutrients up from roots – disperses sugars from the leaves – allows plants to grow higher off the ground ...
... 20.1 Origins of Plant Life • A vascular system allows resources to move to different parts of the plant. – specialized tissues – brings water and mineral nutrients up from roots – disperses sugars from the leaves – allows plants to grow higher off the ground ...
botany-vascular and non-vascular plants
... The cambium is a meristem, which is a site of cell division and active growth. It is located between the xylem and phloem inside the bark of a stem and is the tissue responsible for a stem’s increase in girth, as it produces both the xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem cells are dead at maturity and con ...
... The cambium is a meristem, which is a site of cell division and active growth. It is located between the xylem and phloem inside the bark of a stem and is the tissue responsible for a stem’s increase in girth, as it produces both the xylem and phloem tissues. Xylem cells are dead at maturity and con ...
Rain Snow Evaporation Groundwater Clouds
... combination of what the instructions say and what’s going on in our surroundings. A plant’s genetic code can “tell” the plant to grow. Plants usually grow in ways that help them get the resources they need. Their roots grow to find nutrients (plant food) and water, while their stems and leaves grow ...
... combination of what the instructions say and what’s going on in our surroundings. A plant’s genetic code can “tell” the plant to grow. Plants usually grow in ways that help them get the resources they need. Their roots grow to find nutrients (plant food) and water, while their stems and leaves grow ...
Common Rush
... through August with fruit production during summer and fall. Senescense can take up to 260 days, dependant on temperature. Growth is increased if planted near running water (6). Seedlings are sensitive to shading (3). Propagation: Reproduces from rhizomes or seeds. Water disperses the heavy seed, al ...
... through August with fruit production during summer and fall. Senescense can take up to 260 days, dependant on temperature. Growth is increased if planted near running water (6). Seedlings are sensitive to shading (3). Propagation: Reproduces from rhizomes or seeds. Water disperses the heavy seed, al ...
Echinoderms are invertebrates that have pentaradial
... The madreporite is a lightcolored, calcerous opening used to filter water into the water vascular system of echinoderms. Acting as a pressureequalizing valve, it is visible as a small red or yellow buttonlike structure (similar to a small wart) on the aboral surface of the central disk of a sea s ...
... The madreporite is a lightcolored, calcerous opening used to filter water into the water vascular system of echinoderms. Acting as a pressureequalizing valve, it is visible as a small red or yellow buttonlike structure (similar to a small wart) on the aboral surface of the central disk of a sea s ...
Anatomy - Helping Material for Botany
... phloem is found outside the secondary xylem lycopsid trees apparently did not produce secondary phloem (Taylor, Taylor, and Krings, 2009, pp. 286-287). The core of water conducting woody tissue (xylem ring) was only centimeters in diameter. This relatively small xylem ring was encased in a wide are ...
... phloem is found outside the secondary xylem lycopsid trees apparently did not produce secondary phloem (Taylor, Taylor, and Krings, 2009, pp. 286-287). The core of water conducting woody tissue (xylem ring) was only centimeters in diameter. This relatively small xylem ring was encased in a wide are ...
The Plant Kingdom - Junta de Andalucía
... 9. Read the text and answer the questions. Plant reactions There are two types of plant reaction: permanent – related to growth and temporary – caused by stimuli in the habitat. For example, if you place a plant horizontally, the stem will grow and curve towards the light and the roots will grow dow ...
... 9. Read the text and answer the questions. Plant reactions There are two types of plant reaction: permanent – related to growth and temporary – caused by stimuli in the habitat. For example, if you place a plant horizontally, the stem will grow and curve towards the light and the roots will grow dow ...
Plants and the Colorization of Land
... Chapter 30: Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants ...
... Chapter 30: Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants ...
Cambridge Communications Inc
... • Place the Amaryllis in a cooler, dark room, where it can focus on developing roots. • After about 2 weeks or when some growth appears, move the plant to a warmer location with some sunlight. • Water the plant more frequently now, moist but not wet, is good. • To prevent the stem from tiltin ...
... • Place the Amaryllis in a cooler, dark room, where it can focus on developing roots. • After about 2 weeks or when some growth appears, move the plant to a warmer location with some sunlight. • Water the plant more frequently now, moist but not wet, is good. • To prevent the stem from tiltin ...
Chapter 2: Plant Structures and Functions
... house or classroom. What do all of these plants have in common? They are all vascular plants. Vascular plants have specialized cells and tissues that form vessels. These vessels work together to transport water, food, and waste to and from all parts of the plant. The main parts of vascular plants ar ...
... house or classroom. What do all of these plants have in common? They are all vascular plants. Vascular plants have specialized cells and tissues that form vessels. These vessels work together to transport water, food, and waste to and from all parts of the plant. The main parts of vascular plants ar ...
anatomy of flowering plants
... Sclerenchyma: Sclerenchyma consists of long, narrow cells with thick and lignified cell walls having a few or numerous pits. They are usually dead and without protoplasts. On the basis of variation in form, structure, origin and development, sclerenchyma may be either fibres or sclereids. The fibres ...
... Sclerenchyma: Sclerenchyma consists of long, narrow cells with thick and lignified cell walls having a few or numerous pits. They are usually dead and without protoplasts. On the basis of variation in form, structure, origin and development, sclerenchyma may be either fibres or sclereids. The fibres ...
Plants final review key - Hicksville Public Schools
... (2) Seeds are produced from the flower of the plant. (3) Underground stems from a plant grow into new plants. (4) A leaf falls to the soil, develops roots, and grows. ...
... (2) Seeds are produced from the flower of the plant. (3) Underground stems from a plant grow into new plants. (4) A leaf falls to the soil, develops roots, and grows. ...
(1) A - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... (2) Seeds are produced from the flower of the plant. (3) Underground stems from a plant grow into new plants. (4) A leaf falls to the soil, develops roots, and grows. ...
... (2) Seeds are produced from the flower of the plant. (3) Underground stems from a plant grow into new plants. (4) A leaf falls to the soil, develops roots, and grows. ...
exam 4 practice questions
... 11. Non-vascular plants have a dominant ____________ stage of their life cycle where photosynthesis can be carried out: a. Gametophyte (n) b. Gametophyte (2n) c. Sporophyte (n) d. Sporophyte (2n) 12. All bryophytes have stomata. a. True b. False 13. In non-vascular sexual reproduction, the “seta” ac ...
... 11. Non-vascular plants have a dominant ____________ stage of their life cycle where photosynthesis can be carried out: a. Gametophyte (n) b. Gametophyte (2n) c. Sporophyte (n) d. Sporophyte (2n) 12. All bryophytes have stomata. a. True b. False 13. In non-vascular sexual reproduction, the “seta” ac ...
Chapter 1 Plants and How They Grow complete
... Explain how a leaf helps a plant control its water amount. A leaf lets out water through its tiny holes if there is too much water in the plant. In dry places, leaves have fuzzy or waxy coatings that help keep water in. 6. What might happen to a plant if you taped the bottom of its leaves? The plant ...
... Explain how a leaf helps a plant control its water amount. A leaf lets out water through its tiny holes if there is too much water in the plant. In dry places, leaves have fuzzy or waxy coatings that help keep water in. 6. What might happen to a plant if you taped the bottom of its leaves? The plant ...
Chapter 35
... The tip of the roots in both monocots and dicots is covered with root hairs. Root hairs are extension of the epidermal cells and increase the absorbing area of the root. Some plants have roots arising above ground from stems or leaves. These roots are said to be ...
... The tip of the roots in both monocots and dicots is covered with root hairs. Root hairs are extension of the epidermal cells and increase the absorbing area of the root. Some plants have roots arising above ground from stems or leaves. These roots are said to be ...
Plant Diversity
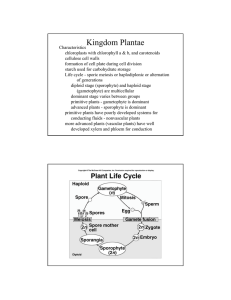
... Sporophyte - a multicellular diploid organism that produces spores by meiosis - spores germinate and grow into gametophytes Gametophyte - a multicellular haploid organism that produces gametes by mitosis can be either male or female, females produce eggs, males produce sperms, fusion of gametes prod ...
... Sporophyte - a multicellular diploid organism that produces spores by meiosis - spores germinate and grow into gametophytes Gametophyte - a multicellular haploid organism that produces gametes by mitosis can be either male or female, females produce eggs, males produce sperms, fusion of gametes prod ...
Document
... Figure 5 Diversity of water-conducting cells (tracheids) in early land plants (median longitudinal sectionthrough cells, basal and proximal end wa. lls not shown; cells are 20–40 m diameter). a, Top,bryophyte hydroid; bottom, details of hydroid wall showing distribution of plasmodesmata-derivedmicr ...
... Figure 5 Diversity of water-conducting cells (tracheids) in early land plants (median longitudinal sectionthrough cells, basal and proximal end wa. lls not shown; cells are 20–40 m diameter). a, Top,bryophyte hydroid; bottom, details of hydroid wall showing distribution of plasmodesmata-derivedmicr ...
Seed Plants
... pollen grains which allow fertilization to occur even in the absence of available water. Transported via: Wind or Animals ...
... pollen grains which allow fertilization to occur even in the absence of available water. Transported via: Wind or Animals ...
PROPAGATION OF NATIVE PLANTS - austplants
... Place the box in a glasshouse, bush house, igloo, cold frame or a morning sun position on a veranda. Without heat or misting the system is maintained over the whole year and apart from the rooting time slowing up in June, July and August, no ill effects from temperatures down to 9°C have been notice ...
... Place the box in a glasshouse, bush house, igloo, cold frame or a morning sun position on a veranda. Without heat or misting the system is maintained over the whole year and apart from the rooting time slowing up in June, July and August, no ill effects from temperatures down to 9°C have been notice ...
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants, phloem being the other. The word xylem is derived from the Greek word ξύλον (xylon), meaning ""wood""; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant.The basic function of xylem is to transport water, but it also transports some nutrients.