
Schematic Invariants by Reduction to Ground Invariants
... operations. The challenge in this approach is to keep the number of objects as small as possible – to guarantee efficiency and scalability – but not too small, to guarantee correctness and to identify as many and as strong schematic invariants as possible. This idea is, in effect, exploiting the str ...
... operations. The challenge in this approach is to keep the number of objects as small as possible – to guarantee efficiency and scalability – but not too small, to guarantee correctness and to identify as many and as strong schematic invariants as possible. This idea is, in effect, exploiting the str ...
Ms.-Vishakha-R.-Bhadane-el-al
... histogram is to stretch and redistribute the original histogram using the entire range of discrete levels of the image, in a way that an enhancement of image contrast is achieved. The most commonly used histogram normalization technique is histogram equalization where one attempts to change the imag ...
... histogram is to stretch and redistribute the original histogram using the entire range of discrete levels of the image, in a way that an enhancement of image contrast is achieved. The most commonly used histogram normalization technique is histogram equalization where one attempts to change the imag ...
Recognizing solid objects by alignment with an image
... defined by three pairs of non-collinear points. Then we show that an affine transformation of the plane uniquely defines a similarity transformation of space, specifying the orientation of one plane with respect to another, up to a reflection. The results reported by Ullman [1987] and Huttenlocher a ...
... defined by three pairs of non-collinear points. Then we show that an affine transformation of the plane uniquely defines a similarity transformation of space, specifying the orientation of one plane with respect to another, up to a reflection. The results reported by Ullman [1987] and Huttenlocher a ...
Human Facial Expression Recognition using Gabor
... into a number of expressive regions). These regions are combined with terric map. LDA was used as a classifier and performance of the system was about 82.61%. ...
... into a number of expressive regions). These regions are combined with terric map. LDA was used as a classifier and performance of the system was about 82.61%. ...
Learning Low-Rank Representations with Classwise Block
... like background modeling (Cui et al. 2012), saliency detection (Shen and Wu 2012)(Peng et al. 2013), image classification (Zhang et al. 2011). However, the previous work only deals with unsupervised case and does not take advantage of structural information when the label information is available. T ...
... like background modeling (Cui et al. 2012), saliency detection (Shen and Wu 2012)(Peng et al. 2013), image classification (Zhang et al. 2011). However, the previous work only deals with unsupervised case and does not take advantage of structural information when the label information is available. T ...
Selectivity and Tolerance - Penn Arts and Sciences
... lateral to the anterior middle temporal sulcus and spanned #10.5–17.5 mm anterior to the ear canals (Felleman and Van Essen, 1991). A representative V4 chamber was centered 6 mm posterior and 17 mm dorsal to the ear canals. V4 recording sites were confirmed by a combination of receptive field size a ...
... lateral to the anterior middle temporal sulcus and spanned #10.5–17.5 mm anterior to the ear canals (Felleman and Van Essen, 1991). A representative V4 chamber was centered 6 mm posterior and 17 mm dorsal to the ear canals. V4 recording sites were confirmed by a combination of receptive field size a ...
Selectivity and Tolerance - Center for Neural Science
... lateral to the anterior middle temporal sulcus and spanned ⬃10.5–17.5 mm anterior to the ear canals (Felleman and Van Essen, 1991). A representative V4 chamber was centered 6 mm posterior and 17 mm dorsal to the ear canals. V4 recording sites were confirmed by a combination of receptive field size a ...
... lateral to the anterior middle temporal sulcus and spanned ⬃10.5–17.5 mm anterior to the ear canals (Felleman and Van Essen, 1991). A representative V4 chamber was centered 6 mm posterior and 17 mm dorsal to the ear canals. V4 recording sites were confirmed by a combination of receptive field size a ...
Learning Visual Representations for Perception
... space manageable, RLVC interleaves the reinforcement learner with a supervised classification algorithm that seeks to split perceptual states so as to reduce perceptual aliasing. This results in an adaptive discretization of the perceptual space based on the presence or absence of visual features. I ...
... space manageable, RLVC interleaves the reinforcement learner with a supervised classification algorithm that seeks to split perceptual states so as to reduce perceptual aliasing. This results in an adaptive discretization of the perceptual space based on the presence or absence of visual features. I ...
Comparison of Handwriting characters Accuracy using
... The steps of the proposed comparison algorithms based on DCT, DWT and Gradient are described in Fig. 1. A. Image acquisition An image is acquired to the system as an input. This image should have a specific format, for example, png format. This image can be acquired through the scanner or, digital c ...
... The steps of the proposed comparison algorithms based on DCT, DWT and Gradient are described in Fig. 1. A. Image acquisition An image is acquired to the system as an input. This image should have a specific format, for example, png format. This image can be acquired through the scanner or, digital c ...
Temporal Logic Theorem Proving and its Application to the Feature
... We denote this formula as φ. Formulas (2) and (3) are subformulas of φ representing the particular specification formulas from which we attempt to find a contradiction. We now present an informal proof of φ using the definition of the semantics of LTL given at the end of Sect. 2. We have formalized ...
... We denote this formula as φ. Formulas (2) and (3) are subformulas of φ representing the particular specification formulas from which we attempt to find a contradiction. We now present an informal proof of φ using the definition of the semantics of LTL given at the end of Sect. 2. We have formalized ...
Scalable spatial event representation
... Self-Organizing Map (SOM). An SOM converts complex, nonlinear statistical relationships between high dimensional data items into simple geometric relationships on a lowdimensional display, while preserving the topological layout of the feature space [4]. The output nodes of the SOM are labelled usin ...
... Self-Organizing Map (SOM). An SOM converts complex, nonlinear statistical relationships between high dimensional data items into simple geometric relationships on a lowdimensional display, while preserving the topological layout of the feature space [4]. The output nodes of the SOM are labelled usin ...
Non-CNF QBF Solving with QCIR - Institute for Formal Models and
... However, this tradition of using normal forms limits the information available to the QBF solvers which might negatively impact the solving process. In contrast to SAT, where satisfiability checking problems have to be solved, a QBF solver has to solve validity checking problems (depending on the va ...
... However, this tradition of using normal forms limits the information available to the QBF solvers which might negatively impact the solving process. In contrast to SAT, where satisfiability checking problems have to be solved, a QBF solver has to solve validity checking problems (depending on the va ...
LeCun - NYU Computer Science
... • MKL only gets few % gain over averaging features Features are ...
... • MKL only gets few % gain over averaging features Features are ...
Detecting False Captioning Using Common Sense Reasoning
... the mean, variances and covariance over all color channels. Once a statistical characterization has been achieved for each object of interest, a given ROI can then be classified by making a decision about which of the signature regions it resembles most. Unsupervised classification is a method that ...
... the mean, variances and covariance over all color channels. Once a statistical characterization has been achieved for each object of interest, a given ROI can then be classified by making a decision about which of the signature regions it resembles most. Unsupervised classification is a method that ...
Deep Machine Learning—A New Frontier in Artificial Intelligence
... and finally propagates through an activation function. Some variants of this exist with as few as one map per layer [13] or summations of multiple maps [8]. When the weighting is small, the activation function is nearly linear and the result is a blurring of the image; other weightings can cause the ...
... and finally propagates through an activation function. Some variants of this exist with as few as one map per layer [13] or summations of multiple maps [8]. When the weighting is small, the activation function is nearly linear and the result is a blurring of the image; other weightings can cause the ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... For preparation of the training and the test sets of samples, a database of 5,000 bangla character samples is formed. 50 Bangla characters are collected from 100 peoples of different age groups. A training set of 3500 samples and a test set of 1500 samples are then formed through random selection of ...
... For preparation of the training and the test sets of samples, a database of 5,000 bangla character samples is formed. 50 Bangla characters are collected from 100 peoples of different age groups. A training set of 3500 samples and a test set of 1500 samples are then formed through random selection of ...
Paper []
... with respect to a map of its environment. This allows it to plan actions and predict their results, using its map. We define place recognition as identifying the current position and orientation, a task sometimes called “global localization” (Thrun et al. 2001). However, not every location in the en ...
... with respect to a map of its environment. This allows it to plan actions and predict their results, using its map. We define place recognition as identifying the current position and orientation, a task sometimes called “global localization” (Thrun et al. 2001). However, not every location in the en ...
An Application of Ant Colony Optimization to Image Clustering
... with unsupervised learning, commonly known as clustering, is to partition a given data set into groups (clusters) such that the data points in a cluster are more similar to each other than points in different clusters [1]. The clustering of images to semantic meaningful classes involves many image a ...
... with unsupervised learning, commonly known as clustering, is to partition a given data set into groups (clusters) such that the data points in a cluster are more similar to each other than points in different clusters [1]. The clustering of images to semantic meaningful classes involves many image a ...
Propositional Fragments for Knowledge
... restrictions are put on the prefix of the input: if no alternations of quantifiers occur, the problem reduces to the satisfiability problem or to the validity problem, and both of them are in P for OBDD< formulae; if the prefix is of the form ∀S1 ∃S2 , the problem is Πp1 -complete (= coNP-complete); ...
... restrictions are put on the prefix of the input: if no alternations of quantifiers occur, the problem reduces to the satisfiability problem or to the validity problem, and both of them are in P for OBDD< formulae; if the prefix is of the form ∀S1 ∃S2 , the problem is Πp1 -complete (= coNP-complete); ...
Geometric Hashing
... the coordinates of any 3-D point can be computed in this coordinate frame. • During recognition, we vote for all the bins lying on a given line in the 3D hash-table. ...
... the coordinates of any 3-D point can be computed in this coordinate frame. • During recognition, we vote for all the bins lying on a given line in the 3D hash-table. ...
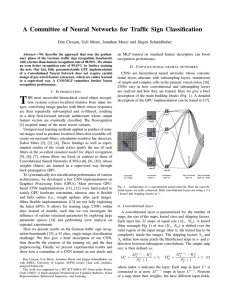
A Committee of Neural Networks for Traffic Sign Classification
... HE most successful hierarchical visual object recognition systems extract localized features from input images, convolving image patches with filters whose responses are then repeatedly sub-sampled and re-filtered, resulting in a deep feed-forward network architecture whose output feature vectors ar ...
... HE most successful hierarchical visual object recognition systems extract localized features from input images, convolving image patches with filters whose responses are then repeatedly sub-sampled and re-filtered, resulting in a deep feed-forward network architecture whose output feature vectors ar ...
SOILIE: A Computational Model of 2D Visual Imagination
... SOILIE has very low context sensitivity when the query has strongly correlated words from different contexts, such as homonyms. One such example is the word “mouse,” which can refer to both computer mouse and the animal. The engine currently has no way of differentiating these two contexts and if tw ...
... SOILIE has very low context sensitivity when the query has strongly correlated words from different contexts, such as homonyms. One such example is the word “mouse,” which can refer to both computer mouse and the animal. The engine currently has no way of differentiating these two contexts and if tw ...
[slides] Kernels and clustering
... [These slides were adapted from the ones created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley, available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] ...
... [These slides were adapted from the ones created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley, available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] ...
Optical Illusion - CS 229: Machine Learning
... of this effect might be misjudgment of the value of the angle between horizontal and diagonal lines, which could be explained by lateral inhibition between V1 neurons. The steps of our experiment are: 1- Learn bases from natural images 2- Observe bases activation for illusory images 3- Study bases a ...
... of this effect might be misjudgment of the value of the angle between horizontal and diagonal lines, which could be explained by lateral inhibition between V1 neurons. The steps of our experiment are: 1- Learn bases from natural images 2- Observe bases activation for illusory images 3- Study bases a ...














![Paper []](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003017995_1-046254b1ae1b27a2341a00c9aa796ada-300x300.png)




![[slides] Kernels and clustering](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004208335_1-990c8ce2efe99730694ed35e841f416e-300x300.png)
