Processes - UC Davis Computer Science
... • The act of switching the CPU from one process to another is called a context switch systems may do 100s or 1000s of switches/sec. takes a few microseconds on today’s hardware ...
... • The act of switching the CPU from one process to another is called a context switch systems may do 100s or 1000s of switches/sec. takes a few microseconds on today’s hardware ...
Linux+ Guide to Linux Certification
... • Linux and UNIX share similar design goals: – Develop an operating system that would support software development • Included utilities in OS for which programmers typically need to write code • Each utility designed for simplicity • Each utility designed to be used in combination with each other ...
... • Linux and UNIX share similar design goals: – Develop an operating system that would support software development • Included utilities in OS for which programmers typically need to write code • Each utility designed for simplicity • Each utility designed to be used in combination with each other ...
The Architecture of Virtual Machines
... VIRTUAL MACHINES The concept of virtualization can be applied not only to subsystems such as disks but to an entire machine. To implement a virtual machine, developers add a software layer to a real machine to support the desired architecture. By doing so, a VM can circumvent real machine compatibil ...
... VIRTUAL MACHINES The concept of virtualization can be applied not only to subsystems such as disks but to an entire machine. To implement a virtual machine, developers add a software layer to a real machine to support the desired architecture. By doing so, a VM can circumvent real machine compatibil ...
Operating System Tutorial
... An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives ...
... An Operating System (OS) is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. An operating system is a software which performs all the basic tasks like file management, memory management, process management, handling input and output, and controlling peripheral devices such as disk drives ...
Message passing
... – Program order within a process. – Blocking send and receive can provide point to point synchronization between processes. – Mutual exclusion inherent. ...
... – Program order within a process. – Blocking send and receive can provide point to point synchronization between processes. – Mutual exclusion inherent. ...
WORD
... ◦ Resource allocator: decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use ◦ Control program: controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of computer Kernel: the one program running at all times on the computer Bootstrap program: loaded at power-up or reboot ...
... ◦ Resource allocator: decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use ◦ Control program: controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of computer Kernel: the one program running at all times on the computer Bootstrap program: loaded at power-up or reboot ...
Study Guide to Accompany Operating Systems Concepts 9 Ed by
... ◦ Resource allocator: decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use ◦ Control program: controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of computer Kernel: the one program running at all times on the computer Bootstrap program: loaded at power-up or reboot ...
... ◦ Resource allocator: decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use ◦ Control program: controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of computer Kernel: the one program running at all times on the computer Bootstrap program: loaded at power-up or reboot ...
6up-pdf - ETH Systems Group
... 1. fork(): creates “child” copy of calling process 2. exec(): replaces text of calling process with a new program ...
... 1. fork(): creates “child” copy of calling process 2. exec(): replaces text of calling process with a new program ...
EECC756 - Shaaban
... Historically, parallel architectures tied to programming models • Divergent architectures, with no predictable pattern of growth. ...
... Historically, parallel architectures tied to programming models • Divergent architectures, with no predictable pattern of growth. ...
doc
... ◦ Resource allocator: decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use ◦ Control program: controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of computer Kernel: the one program running at all times on the computer Bootstrap program: loaded at power-up or reboot ...
... ◦ Resource allocator: decides between conflicting requests for efficient and fair resource use ◦ Control program: controls execution of programs to prevent errors and improper use of computer Kernel: the one program running at all times on the computer Bootstrap program: loaded at power-up or reboot ...
Document
... Related work Current main methods in tackling the software bugs in WSNs Simulation: different from real execution (Li & Regehr, 2010; Sasnauskas et al., 2010) Testbeds: designed for network performance evaluation rather than for software bug detection Large-scale real deployment: expensive ...
... Related work Current main methods in tackling the software bugs in WSNs Simulation: different from real execution (Li & Regehr, 2010; Sasnauskas et al., 2010) Testbeds: designed for network performance evaluation rather than for software bug detection Large-scale real deployment: expensive ...
A real-time operating system
... at the same time. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources to multiple users. ...
... at the same time. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources to multiple users. ...
Computer-System Architecture
... n Requires a cache management policy. n Caching introduces another level in storage hierarchy. This requires data that is simultaneously stored in more than one level to be consistent. ...
... n Requires a cache management policy. n Caching introduces another level in storage hierarchy. This requires data that is simultaneously stored in more than one level to be consistent. ...
What is an Operating System?
... In 1998 this was the essence of a suit filed by the United State Department of Justice against Microsoft ...
... In 1998 this was the essence of a suit filed by the United State Department of Justice against Microsoft ...
What is an Operating System?
... price make it useful for individuals (and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator) ...
... price make it useful for individuals (and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator) ...
sample unformatted document
... Mac OS by Apple Computer became the first widespread OS to feature a graphical user interface. Many of its features such as windows and icons would later become commonplace in GUIs. The first microcomputers did not have the capacity or need for the elaborate operating systems that had been developed ...
... Mac OS by Apple Computer became the first widespread OS to feature a graphical user interface. Many of its features such as windows and icons would later become commonplace in GUIs. The first microcomputers did not have the capacity or need for the elaborate operating systems that had been developed ...
A Study of Real-time Memory Management: Evaluating Operating
... It must be noticed that virtual memory does not come cheap. Special hardware and software is required to implement translation from logical to physical memory addresses, protected-mode operating systems must perform mode switches whenever they allocate or release pages, and memory is allocated in bl ...
... It must be noticed that virtual memory does not come cheap. Special hardware and software is required to implement translation from logical to physical memory addresses, protected-mode operating systems must perform mode switches whenever they allocate or release pages, and memory is allocated in bl ...
PPTX - Duke Computer Science
... conventions for use of the registers by executable code. • Each processor core has at least one register set for use by a code stream running on that core. – Multi-threaded cores (“SMT”) have multiple register sets and can run multiple streams of instructions simultaneously. ...
... conventions for use of the registers by executable code. • Each processor core has at least one register set for use by a code stream running on that core. – Multi-threaded cores (“SMT”) have multiple register sets and can run multiple streams of instructions simultaneously. ...
What is an Operating System?
... Computer-System Operation I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently. Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type. Each device controller has a local buffer. CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers I/O is from the device to local buffer of contro ...
... Computer-System Operation I/O devices and the CPU can execute concurrently. Each device controller is in charge of a particular device type. Each device controller has a local buffer. CPU moves data from/to main memory to/from local buffers I/O is from the device to local buffer of contro ...
Distributed operating system
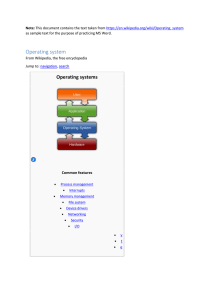
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.