BeowulfSysMgmt4 - Computer Science at SUNY Potsdam
... The cost of switching to other microprocessor architectures or operating systems is high, especially in production environments or organizations with low to average skill levels Deep Computing customers have application workloads that include various properties that are both problem and implemen ...
... The cost of switching to other microprocessor architectures or operating systems is high, especially in production environments or organizations with low to average skill levels Deep Computing customers have application workloads that include various properties that are both problem and implemen ...
lecture 14
... The main disadvantage of the semaphore discussed in the previous section is that they all require busy waiting. While a process is in its critical section, any other process that tries to enter its critical section must loop continuously in the entry code. This continual looping is clearly a problem ...
... The main disadvantage of the semaphore discussed in the previous section is that they all require busy waiting. While a process is in its critical section, any other process that tries to enter its critical section must loop continuously in the entry code. This continual looping is clearly a problem ...
chubby and paxos
... P2c- For any v and n, if a proposal with value v and number n is issued, then there is a set S consisting of a majority of acceptors such that either (a) no acceptor in S has accepted any proposal numbered less than n, or (b) v is the value of the highest-numbered proposal among all proposals number ...
... P2c- For any v and n, if a proposal with value v and number n is issued, then there is a set S consisting of a majority of acceptors such that either (a) no acceptor in S has accepted any proposal numbered less than n, or (b) v is the value of the highest-numbered proposal among all proposals number ...
Figure 5.01 - College of the Holy Cross
... Threads allow a program to continue running even if part is ...
... Threads allow a program to continue running even if part is ...
Middleware issues for ad hoc networks
... systems They use a Distributed Hash Function (DHT) to map physical addresses to a logical address space ...
... systems They use a Distributed Hash Function (DHT) to map physical addresses to a logical address space ...
Slide 1
... Traps and exception handling • Kernel implements a trap handler which deals with hardware interrupts and processor exceptions • The trap handler disables interrupts, determines the cause of the interrupt, saves processor state, re-enables interrupts and dispatches code to deal with type of interrup ...
... Traps and exception handling • Kernel implements a trap handler which deals with hardware interrupts and processor exceptions • The trap handler disables interrupts, determines the cause of the interrupt, saves processor state, re-enables interrupts and dispatches code to deal with type of interrup ...
What is real time and why do I need it?
... hard real-time environments where failure to perform activities in a timely manner can result in harm to persons or property. But an RTOS can be just as useful for applications that must meet QoS guarantees, particularly when failure to do so could result in financial penalty. This covers obvious se ...
... hard real-time environments where failure to perform activities in a timely manner can result in harm to persons or property. But an RTOS can be just as useful for applications that must meet QoS guarantees, particularly when failure to do so could result in financial penalty. This covers obvious se ...
Chapter 3: Processes
... This PCB contains all necessary info for a process pid t_pid; /* process identifier */ long state; /* state of the process */ unsigned int time_slice /* scheduling information */ struct task_struct *parent; /* this process’s parent */ struct list_head children; /* this process’s children */ struct f ...
... This PCB contains all necessary info for a process pid t_pid; /* process identifier */ long state; /* state of the process */ unsigned int time_slice /* scheduling information */ struct task_struct *parent; /* this process’s parent */ struct list_head children; /* this process’s children */ struct f ...
tr-2002-70
... 3 SmartMoveX Active Badge and Network Data Logger The hardware for our active badge system is called SmartMoveX and was invented at Microsoft Research in Cambridge, UK. SmartMoveX consists of a small radio transmitter that transmits 433 MHz FM to multiple receivers as shown in Figure 1. Each transmi ...
... 3 SmartMoveX Active Badge and Network Data Logger The hardware for our active badge system is called SmartMoveX and was invented at Microsoft Research in Cambridge, UK. SmartMoveX consists of a small radio transmitter that transmits 433 MHz FM to multiple receivers as shown in Figure 1. Each transmi ...
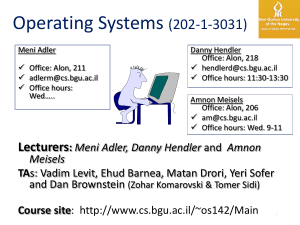
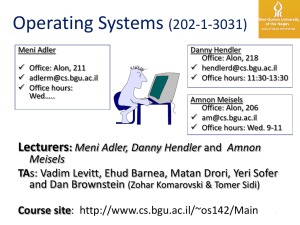
Operating Systems, 082
... Processes - a key concept Resource container for “program in execution” Timesharing, process suspension/preemption Process Table Process Groups Signals ...
... Processes - a key concept Resource container for “program in execution” Timesharing, process suspension/preemption Process Table Process Groups Signals ...
ccr-9501-mcquilln - Computer Communication Review
... procedure over a period of about six months. We then began an extensive series of tests on the ARPANET, at off-peak hours but under actual network conditions [5]. Our tests involved a great deal more than simply turning the new routing algorithm on to see whether it would run. The tests were specifi ...
... procedure over a period of about six months. We then began an extensive series of tests on the ARPANET, at off-peak hours but under actual network conditions [5]. Our tests involved a great deal more than simply turning the new routing algorithm on to see whether it would run. The tests were specifi ...
Operating System Structures
... reserved by Wiley. These lecture notes should only be used for internal teaching purposes at the Linköping University. Christoph Kessler, IDA, Linköpings universitet. ...
... reserved by Wiley. These lecture notes should only be used for internal teaching purposes at the Linköping University. Christoph Kessler, IDA, Linköpings universitet. ...
A Classification and Comparison of Data Mining Algorithms for
... Communication pattern in a Wireless Sensor Network of the type CluME Legend: • Nx – A WSN node parameterized by a couple [NxG, NxL] • NxG – Node’s global parameter: The cluster a node belongs to • NxL – Node’s local parameter: Set of features observable through the node’s sensors • Ax – An arch den ...
... Communication pattern in a Wireless Sensor Network of the type CluME Legend: • Nx – A WSN node parameterized by a couple [NxG, NxL] • NxG – Node’s global parameter: The cluster a node belongs to • NxL – Node’s local parameter: Set of features observable through the node’s sensors • Ax – An arch den ...
Part 4b: DataMining in WSNs - Algorithams and Architectures
... Communication pattern in a Wireless Sensor Network of the type CluME Legend: • Nx – A WSN node parameterized by a couple [NxG, NxL] • NxG – Node’s global parameter: The cluster a node belongs to • NxL – Node’s local parameter: Set of features observable through the node’s sensors • Ax – An arch den ...
... Communication pattern in a Wireless Sensor Network of the type CluME Legend: • Nx – A WSN node parameterized by a couple [NxG, NxL] • NxG – Node’s global parameter: The cluster a node belongs to • NxL – Node’s local parameter: Set of features observable through the node’s sensors • Ax – An arch den ...
Codes for a Distributed Caching based Video-On
... a tiny fraction of the catalog content, or have the bandwidth to satisfy the streaming demands of more than a small subset of all users, or have the ability to open up connections to more than a small subset of the users in the system. Given this architecture, our system goal is to effectively use t ...
... a tiny fraction of the catalog content, or have the bandwidth to satisfy the streaming demands of more than a small subset of all users, or have the ability to open up connections to more than a small subset of the users in the system. Given this architecture, our system goal is to effectively use t ...
Chap. 2, Operating System Structures
... Programming interface to the OS services Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level ...
... Programming interface to the OS services Typically written in a high-level language (C or C++) Mostly accessed by programs via a high-level ...
Facility Monitoring System Design Recommendations
... is simply writing data to two separate databases at the same time. ...
... is simply writing data to two separate databases at the same time. ...
ZigBee, ZDO, and ZDP
... Device discovery services have a few things in common: ◦ They provide additional information about a node. ◦ They are all optional from the client side, but some server side processing is mandatory (a common subset among all ZigBee devices). ◦ They are node-wide, and do not represent any particular ...
... Device discovery services have a few things in common: ◦ They provide additional information about a node. ◦ They are all optional from the client side, but some server side processing is mandatory (a common subset among all ZigBee devices). ◦ They are node-wide, and do not represent any particular ...
CS 111 Processes
... A process may be create several new processes, via a create-process system call, during the course of execution. The creating process is called a Parent process, and new processes are called the Children of that process. Each of these new processes may in turn create other processes forming a tree o ...
... A process may be create several new processes, via a create-process system call, during the course of execution. The creating process is called a Parent process, and new processes are called the Children of that process. Each of these new processes may in turn create other processes forming a tree o ...
HPDC - Pitt Computer Science
... is capable of providing fully isolated OS/Rs, or enclaves, to local workloads. This approach allows a user to dynamically compose independent enclaves from arbitrary sets of local hardware resources at runtime based on a coupled applications’ resource and isolation requirements. While others have ex ...
... is capable of providing fully isolated OS/Rs, or enclaves, to local workloads. This approach allows a user to dynamically compose independent enclaves from arbitrary sets of local hardware resources at runtime based on a coupled applications’ resource and isolation requirements. While others have ex ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) routing is a routing protocol for mobile ad hoc networks and other wireless ad-hoc networks. It is jointly developed in Nokia Research Centre of University of California, Santa Barbara and University of Cincinnati by C. Perkins and S. Das. It is an on-demand a ...
... Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) routing is a routing protocol for mobile ad hoc networks and other wireless ad-hoc networks. It is jointly developed in Nokia Research Centre of University of California, Santa Barbara and University of Cincinnati by C. Perkins and S. Das. It is an on-demand a ...
Mobile Computing (ECS-087)
... frequencies according to a certain pattern, i.e., FDMA combined with TDMA. The latter example is the common practice for many wireless systems to circumvent narrowband interference at certain frequencies, known as frequency hopping. Sender and receiver have to agree on a hopping pattern, otherwise t ...
... frequencies according to a certain pattern, i.e., FDMA combined with TDMA. The latter example is the common practice for many wireless systems to circumvent narrowband interference at certain frequencies, known as frequency hopping. Sender and receiver have to agree on a hopping pattern, otherwise t ...
Introduction
... Processes - a key concept Resource container for “program in execution” Timesharing, process suspension/preemption Process Table Process Groups Signals ...
... Processes - a key concept Resource container for “program in execution” Timesharing, process suspension/preemption Process Table Process Groups Signals ...
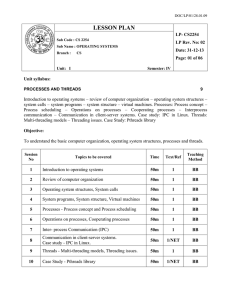
CS2254 os
... system calls – system programs – system structure – virtual machines. Processes: Process concept – Process scheduling – Operations on processes – Cooperating processes – Interprocess communication – Communication in client-server systems. Case study: IPC in Linux. Threads: Multi-threading models – T ...
... system calls – system programs – system structure – virtual machines. Processes: Process concept – Process scheduling – Operations on processes – Cooperating processes – Interprocess communication – Communication in client-server systems. Case study: IPC in Linux. Threads: Multi-threading models – T ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.