CS307-slides02
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other Protection involves ensuring that all access to system resources is controlled Security of ...
... Protection and security - The owners of information stored in a multiuser or networked computer system may want to control use of that information, concurrent processes should not interfere with each other Protection involves ensuring that all access to system resources is controlled Security of ...
Operating system
... (CPU, memory, I/O devices). 2. Operating system – controls and coordinates the use of the hardware among the various application programs for the various users. 3. Applications programs – define the ways in which the system resources are used to solve the computing problems of the users (compilers, ...
... (CPU, memory, I/O devices). 2. Operating system – controls and coordinates the use of the hardware among the various application programs for the various users. 3. Applications programs – define the ways in which the system resources are used to solve the computing problems of the users (compilers, ...
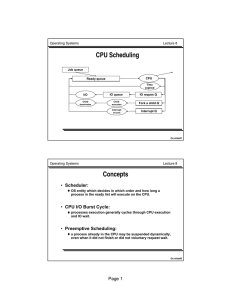
Page 1 • Scheduler: • CPU I/O Burst Cycle: • Preemptive Scheduling:
... • CPU I/O Burst Cycle: processes execution generally cycles through CPU execution and IO wait. ...
... • CPU I/O Burst Cycle: processes execution generally cycles through CPU execution and IO wait. ...
QNX OS for Security
... memory-protected user space. Virtually any component can fail and be automatically restarted without affecting other components or the kernel. Further, the QNX OS provides an optional high-availability framework for ensuring critical software is monitored and kept running even after faults. No other ...
... memory-protected user space. Virtually any component can fail and be automatically restarted without affecting other components or the kernel. Further, the QNX OS provides an optional high-availability framework for ensuring critical software is monitored and kept running even after faults. No other ...
Cheese Factory
... – TCP provides reliable data delivery and the disappearance of a neighbor can be detected with TCP timeout • The neighbor list is updated based on heuristics such as number of relayed query replies and the actual query replies provided by the neighbor to form an efficient topology for resource disco ...
... – TCP provides reliable data delivery and the disappearance of a neighbor can be detected with TCP timeout • The neighbor list is updated based on heuristics such as number of relayed query replies and the actual query replies provided by the neighbor to form an efficient topology for resource disco ...
Chapter 1 - PowerPoint
... Each processor runs an identical copy of the operating system. Many processes can run at once without performance deterioration. Most modern operating systems support SMP Asymmetric multiprocessing Each processor is assigned a specific task; master processor schedules and allocated work to ...
... Each processor runs an identical copy of the operating system. Many processes can run at once without performance deterioration. Most modern operating systems support SMP Asymmetric multiprocessing Each processor is assigned a specific task; master processor schedules and allocated work to ...
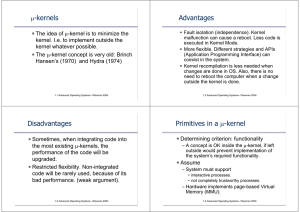
μ-kernels Advantages Disadvantages Primitives in a μ
... The µ-kernel design is extensively depending on the CPU structure. The only µ-kernel feature that can be portable is the scheduler. Large monolithic kernel can have many more portable features. In the early 70's, large portions of the kernel have been started to be written in C, so they could be por ...
... The µ-kernel design is extensively depending on the CPU structure. The only µ-kernel feature that can be portable is the scheduler. Large monolithic kernel can have many more portable features. In the early 70's, large portions of the kernel have been started to be written in C, so they could be por ...
This is a class presentation about A Micropower DSP for Sensor
... memories are implemented using Flip-Flops, rather than SRAM macros. ...
... memories are implemented using Flip-Flops, rather than SRAM macros. ...
Distributed Systems
... Users not aware of multiplicity of machines Access to remote resources similar to access to local resources Data Migration – transfer data by transferring ...
... Users not aware of multiplicity of machines Access to remote resources similar to access to local resources Data Migration – transfer data by transferring ...
Introduction - USC Upstate: Faculty
... – An operating system manages multiple users. – An operating system manages multiple programs (multitasking). ...
... – An operating system manages multiple users. – An operating system manages multiple programs (multitasking). ...
CS 330 – Operating Systems
... 1. Describe the basic components of a computer and how they interact with an operating system. 2. Describe classes of operating systems, roles of an operating system, and the services an operating system provides under each role to applications and users. 3. Understand process and thread concept ...
... 1. Describe the basic components of a computer and how they interact with an operating system. 2. Describe classes of operating systems, roles of an operating system, and the services an operating system provides under each role to applications and users. 3. Understand process and thread concept ...
How do all these components work together - Metal
... Fax: 0800 864 865 E-mail: [email protected] Web: www.instant.org.nz ...
... Fax: 0800 864 865 E-mail: [email protected] Web: www.instant.org.nz ...
Figure 15.1 A distributed multimedia system
... A running programming including both code and data that travels from one computer to another in a network carrying out a task on someone’s behalf, such as collecting information, eventually returning with the results. It is a potential security threat to the resources in computers that they visit. ...
... A running programming including both code and data that travels from one computer to another in a network carrying out a task on someone’s behalf, such as collecting information, eventually returning with the results. It is a potential security threat to the resources in computers that they visit. ...
Chapter 3 Operating Systems
... Operating system (OS): • A collection of programs that manages resources of a computer, such as - processors - memory - input/output devices • ... like the conductor of an orchestra. • A virtual machine that lets a user accomplish tasks that would be difficult to perform directly with the underlying ...
... Operating system (OS): • A collection of programs that manages resources of a computer, such as - processors - memory - input/output devices • ... like the conductor of an orchestra. • A virtual machine that lets a user accomplish tasks that would be difficult to perform directly with the underlying ...
1.01 - University of South Florida
... System goals –easy to design, implement, and maintain, as well as flexible, reliable, error-free, and efficient ...
... System goals –easy to design, implement, and maintain, as well as flexible, reliable, error-free, and efficient ...
Abstract View of System Components
... local memory; processors communicate with one another through various communications lines, such as highspeed buses or telephone lines Advantages of distributed systems ...
... local memory; processors communicate with one another through various communications lines, such as highspeed buses or telephone lines Advantages of distributed systems ...
Kernel Control Path
... • Kernel control path can preempt a running process; however, when an interrupt handle terminates, the process resumes. • Only kernel control path can interrupt another kernel control path. ...
... • Kernel control path can preempt a running process; however, when an interrupt handle terminates, the process resumes. • Only kernel control path can interrupt another kernel control path. ...
CST1215 Operating System Fundamentals
... 16. Identify the design goals of Windows operating systems. 17. Identify the use of the device, processor, and network managers in recent versions of Windows. 18. Identify the design goals for Windows vs. open source operating systems 19. Identify the services provided by operating systems. 20. Solv ...
... 16. Identify the design goals of Windows operating systems. 17. Identify the use of the device, processor, and network managers in recent versions of Windows. 18. Identify the design goals for Windows vs. open source operating systems 19. Identify the services provided by operating systems. 20. Solv ...
Operating Systems History
... • Some OS use the microkernel concept, this have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
... • Some OS use the microkernel concept, this have the function to coordinate to the other parts of an OS such as : I/O Devices, Process, Memory and File Systems. • The structure of and OS could be different but in most of the time are very similar because some OS use Open Standards. ...
Operating Systems - Chulmleigh ICT Department
... letting you enter more data on the keyboard printing sheet one displaying what is going on via your monitor. The operating system helps to manage which tasks take priority. ...
... letting you enter more data on the keyboard printing sheet one displaying what is going on via your monitor. The operating system helps to manage which tasks take priority. ...
Operating Systems - Glyndwr University
... Single-user, multi-tasking - Type of operating system most people use on their desktop and laptop computers today. Multi-user - A multi-user operating system allows many different users to take advantage of the computer's resources simultaneously. The operating system must make sure that the require ...
... Single-user, multi-tasking - Type of operating system most people use on their desktop and laptop computers today. Multi-user - A multi-user operating system allows many different users to take advantage of the computer's resources simultaneously. The operating system must make sure that the require ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.