Chapter13 - Website Staff UI
... • Real-time operation • Reactive operation – Respond to external events ...
... • Real-time operation • Reactive operation – Respond to external events ...
AtlasTier3Virtualization - Indico
... • Design a system to be flexible and simple to setup (1 person < 1 week) • Simple to operate - < 0.25 FTE to maintain • Scalable with Data volumes • Fast - Process 1 TB of data over night • Relatively inexpensive • Run only the needed services/process • Devote most resources to CPU’s and Disk ...
... • Design a system to be flexible and simple to setup (1 person < 1 week) • Simple to operate - < 0.25 FTE to maintain • Scalable with Data volumes • Fast - Process 1 TB of data over night • Relatively inexpensive • Run only the needed services/process • Devote most resources to CPU’s and Disk ...
Berkeley NOW
... – ex: faster consumer gets more data – flow equations provide goal, simple error bounds, and react – performance availability ...
... – ex: faster consumer gets more data – flow equations provide goal, simple error bounds, and react – performance availability ...
OperatingSystems
... browser that searches for some information and A word-processing software that is activated to perform the word-processing task are applications. The operating system will switch between tasks based on the tasks current states and their requirements and priorities. Multitasking is only possible when ...
... browser that searches for some information and A word-processing software that is activated to perform the word-processing task are applications. The operating system will switch between tasks based on the tasks current states and their requirements and priorities. Multitasking is only possible when ...
128509655X_397015
... to share common transmission hardware and software effectively • The two transport protocol models (OSI and TCP/IP) and how the layers of each one compare ...
... to share common transmission hardware and software effectively • The two transport protocol models (OSI and TCP/IP) and how the layers of each one compare ...
Fatema Nafa`s presentation on "Measures to
... mechanisms within the kernel. Good development practices and security are more synonymous than most people believe. The role of this fundamental securityenforcement mechanism is : Validating all access attempts made to resources (data, programs, etc.) by any given process. ...
... mechanisms within the kernel. Good development practices and security are more synonymous than most people believe. The role of this fundamental securityenforcement mechanism is : Validating all access attempts made to resources (data, programs, etc.) by any given process. ...
Based Platform for Advanced Studies on Operating Systems
... software (i.e., guest operating systems, guest applications), while the software running outside the virtual machine – typically the host operating system – is identified as host software. All guest software (including the guest OS) runs in user mode, having a limited control over the real system ha ...
... software (i.e., guest operating systems, guest applications), while the software running outside the virtual machine – typically the host operating system – is identified as host software. All guest software (including the guest OS) runs in user mode, having a limited control over the real system ha ...
p2p_3
... local node join/create a Pastry network. Credentials are used for authorization. An object used for callbacks is passed through the Application parameter route(msg, key): routes a message to the live node D with nodeId numerically closest to the key (at the time of delivery) Application interface to ...
... local node join/create a Pastry network. Credentials are used for authorization. An object used for callbacks is passed through the Application parameter route(msg, key): routes a message to the live node D with nodeId numerically closest to the key (at the time of delivery) Application interface to ...
DecentralizedP2P - Department of Computer Science
... has approximately 30,000 SNs Each SN is like a traffic hub that processes requests from ONs Each SN serves approximately 60-150 ONs at a time Each SN keeps a database of all the files that it’s ONs are sharing ...
... has approximately 30,000 SNs Each SN is like a traffic hub that processes requests from ONs Each SN serves approximately 60-150 ONs at a time Each SN keeps a database of all the files that it’s ONs are sharing ...
Discovering Network Neighborhoods Using Peer-to-Peer Lookups
... Center for Educational Computing Initiatives Massachusetts Institute of Technology ...
... Center for Educational Computing Initiatives Massachusetts Institute of Technology ...
MODERN OPERATING SYSTEMS Third Edition ANDREW S. …
... Features common to removable media: 1. All devices must be inserted and removed. 2. All removable media can be removed ‘‘hot,’’ that is, while being used. 3. Each medium can report its capabilities. 4. Incompatible cards must be rejected. 5. Each card needs power. Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems ...
... Features common to removable media: 1. All devices must be inserted and removed. 2. All removable media can be removed ‘‘hot,’’ that is, while being used. 3. Each medium can report its capabilities. 4. Incompatible cards must be rejected. 5. Each card needs power. Tanenbaum, Modern Operating Systems ...
Enabling Innovation inside the Network
... – Efficient, generic support for traffic monitoring – Good for many problems, rather than perfect for one ...
... – Efficient, generic support for traffic monitoring – Good for many problems, rather than perfect for one ...
Introduction to Object Technology
... • Takes less time to create a new thread than a process • Less time to terminate a thread than a process • Less time to switch between two threads within the same process • Since threads within the same process share memory and files, they can communicate with each other without invoking the kernel ...
... • Takes less time to create a new thread than a process • Less time to terminate a thread than a process • Less time to switch between two threads within the same process • Since threads within the same process share memory and files, they can communicate with each other without invoking the kernel ...
Swarm Intelligence on Graphs
... To reach an agreement Depend on their shared state information Information exchange among the agents ...
... To reach an agreement Depend on their shared state information Information exchange among the agents ...
View
... permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
... permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
Peer-to-peer architecture for collaborative intrusion and malware
... and new malware as soon as possible, hierarchical architectures for intrusion detection have been proposed, such as [1]. They are able to gather information from a wide network space and allow early detection of emerging threats because they are based on multiple sensors placed in different network ...
... and new malware as soon as possible, hierarchical architectures for intrusion detection have been proposed, such as [1]. They are able to gather information from a wide network space and allow early detection of emerging threats because they are based on multiple sensors placed in different network ...
Implementing Processes, Threads, and Resources
... • MS-DOS - written to provide the most functionality in the least space – not divided into modules – Although MS-DOS has some structures, its interfaces and levels of functionality are not well separated. • application programs are able to access BIOS routines directly (bypassing DOS). ...
... • MS-DOS - written to provide the most functionality in the least space – not divided into modules – Although MS-DOS has some structures, its interfaces and levels of functionality are not well separated. • application programs are able to access BIOS routines directly (bypassing DOS). ...
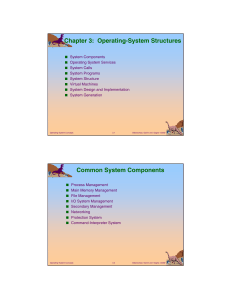
Chapter 3: Operating-System Structures Common System
... permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. ■ Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. ■ The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
... permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. ■ Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. ■ The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
Module 3: Operating
... permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
... permanently, the computer system must provide secondary storage to back up main memory. Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle on-line storage medium, for both programs and data. The operating system is responsible for the following activities in connection with disk management: ...
Lecture 1 - Department of Computer Science
... computer system’s hardware, the physical machine and its electronic components, which include: – Main memory: where data and instructions must reside in order to be processed – Input/Output (IO) devices: the peripheral units in the system, e.g., printers, keyboards, CD drives, modems etc. – The C ...
... computer system’s hardware, the physical machine and its electronic components, which include: – Main memory: where data and instructions must reside in order to be processed – Input/Output (IO) devices: the peripheral units in the system, e.g., printers, keyboards, CD drives, modems etc. – The C ...
Workshop Report for IPTPS`02, 1st International Workshop on Peer
... Mojo Nation was an ambitious and complex system that incorporated digital cash as payment for resources. The digital cash worked and most of the rest did not. It didn’t scale (never reaching 10,000 simultaneous nodes). 20,000 new people tried it each month, but its half-life was less than an hour. T ...
... Mojo Nation was an ambitious and complex system that incorporated digital cash as payment for resources. The digital cash worked and most of the rest did not. It didn’t scale (never reaching 10,000 simultaneous nodes). 20,000 new people tried it each month, but its half-life was less than an hour. T ...
Distributed operating system
A distributed operating system is a software over a collection of independent, networked, communicating, and physically separate computational nodes. Each individual node holds a specific software subset of the global aggregate operating system. Each subset is a composite of two distinct service provisioners. The first is a ubiquitous minimal kernel, or microkernel, that directly controls that node’s hardware. Second is a higher-level collection of system management components that coordinate the node's individual and collaborative activities. These components abstract microkernel functions and support user applications.The microkernel and the management components collection work together. They support the system’s goal of integrating multiple resources and processing functionality into an efficient and stable system. This seamless integration of individual nodes into a global system is referred to as transparency, or single system image; describing the illusion provided to users of the global system’s appearance as a single computational entity.