IoT - L4
... The Arduino’s ability to sense digital and analog inputs allows it to respond to you and to the world around you Digital input pins sense the presence and absence of voltage on a pin Analog input pins measure a range of voltages on a pin ...
... The Arduino’s ability to sense digital and analog inputs allows it to respond to you and to the world around you Digital input pins sense the presence and absence of voltage on a pin Analog input pins measure a range of voltages on a pin ...
Lab 3
... using a small screwdriver or the adjustment tool in your kit. Purists might want to buy an IC puller which hooks under the ends and pulls both up at the same time. 1.a (20 points) Use the circuit of Figure P1-1 to fill out Table P1-1. For each combination of resistor values, use the ideal op amp mod ...
... using a small screwdriver or the adjustment tool in your kit. Purists might want to buy an IC puller which hooks under the ends and pulls both up at the same time. 1.a (20 points) Use the circuit of Figure P1-1 to fill out Table P1-1. For each combination of resistor values, use the ideal op amp mod ...
Experiment 1.
... 1. Calculate the voltage on the resistors in Figure 2.1 as a ratio of the source voltage Voltage ratio on the 330 Ohm resistor: Voltage ratio on the 470 Ohm resistor: 2. Calculate the current on the resistors in Figure 2.1 as a ratio of the source current Current ratio on the 330 Ohm resistor: Curre ...
... 1. Calculate the voltage on the resistors in Figure 2.1 as a ratio of the source voltage Voltage ratio on the 330 Ohm resistor: Voltage ratio on the 470 Ohm resistor: 2. Calculate the current on the resistors in Figure 2.1 as a ratio of the source current Current ratio on the 330 Ohm resistor: Curre ...
Circuit electricity
... From the diagram below, determine: a) The total resistance, and the supply current. b) The voltage across the R1 resistor. c) The current through R2 , and the power dissipated in it. ...
... From the diagram below, determine: a) The total resistance, and the supply current. b) The voltage across the R1 resistor. c) The current through R2 , and the power dissipated in it. ...
FE3110411050
... without any additional components. 2. The output voltage is controlled by varying the modulation index instead of varying the amplitude of the carrier signal. With this type of control, lower order harmonics can be eliminated or minimized along with its output voltage control. The filtering requirem ...
... without any additional components. 2. The output voltage is controlled by varying the modulation index instead of varying the amplitude of the carrier signal. With this type of control, lower order harmonics can be eliminated or minimized along with its output voltage control. The filtering requirem ...
LectNotes5-Superposition
... The basic idea behind superposition is that you can take a circuit with several independent sources (voltage or current), and find a particular circuit value (voltage or current) by adding the effects of each source considered separately. It's a powerful opportunistic circuit solution method that ca ...
... The basic idea behind superposition is that you can take a circuit with several independent sources (voltage or current), and find a particular circuit value (voltage or current) by adding the effects of each source considered separately. It's a powerful opportunistic circuit solution method that ca ...
FAN2012 1.5 A Low-Voltage, Current-Mode Synchronous PWM Buck Regulator
... The FAN2012 is a step-down pulse width modulated (PWM) current mode converter with a typical switching frequency of 1.3 MHz. At the beginning of each clock cycle, the P-channel transistor is turned on. The inductor current ramps up and is monitored via an internal circuit. The P-channel switch is tu ...
... The FAN2012 is a step-down pulse width modulated (PWM) current mode converter with a typical switching frequency of 1.3 MHz. At the beginning of each clock cycle, the P-channel transistor is turned on. The inductor current ramps up and is monitored via an internal circuit. The P-channel switch is tu ...
DUAL LOW-VOLTAGE POWER AMPLIFIER
... Figure 20 : Low Cost Application in Portable Players (using only one 100µF output capacitor) ...
... Figure 20 : Low Cost Application in Portable Players (using only one 100µF output capacitor) ...
LF451 Wide-Bandwidth JFET-Input Operational Amplifier
... The LF451 is biased by a zener reference which allows normal circuit operation on g 4V power supplies. Supply voltages less than these may result in lower gain bandwidth and slew rate. The LF451 will drive a 2 kX load resistance to g 10V over the full temperature range of 0§ C to a 70§ C. If the amp ...
... The LF451 is biased by a zener reference which allows normal circuit operation on g 4V power supplies. Supply voltages less than these may result in lower gain bandwidth and slew rate. The LF451 will drive a 2 kX load resistance to g 10V over the full temperature range of 0§ C to a 70§ C. If the amp ...
Section G8: Non-Inverting Amplifier
... ¾ A KVL about the input loop indicates that R1 is much less than either 2Rcm or Rin (we will explicitly prove this shortly). This allows us to neglect R1 (essentially replace with a short circuit) in the simplifications below. With this information, the equivalent circuit (above, right) may be simp ...
... ¾ A KVL about the input loop indicates that R1 is much less than either 2Rcm or Rin (we will explicitly prove this shortly). This allows us to neglect R1 (essentially replace with a short circuit) in the simplifications below. With this information, the equivalent circuit (above, right) may be simp ...
Document
... constant output voltage under dynamically changing load conditions. In successive approximation converters, the input current is compared to a series of switched trial currents. The comparison point is diode clamped but may deviate several hundred millivolts resulting in high frequency modulation of ...
... constant output voltage under dynamically changing load conditions. In successive approximation converters, the input current is compared to a series of switched trial currents. The comparison point is diode clamped but may deviate several hundred millivolts resulting in high frequency modulation of ...
555 Timer As Mono Stable Multi Vibrator
... 7) Here you can see that the R pin in SR flip flop is connected with the output of the comparator c(U).So the input of SR flip flop is S=0 and R=1 and output is Q=0 and Q-bar=1. 8) As shown in picture Q ia connected with the output so, output becomes low shown in green color in output graph. 9) Agai ...
... 7) Here you can see that the R pin in SR flip flop is connected with the output of the comparator c(U).So the input of SR flip flop is S=0 and R=1 and output is Q=0 and Q-bar=1. 8) As shown in picture Q ia connected with the output so, output becomes low shown in green color in output graph. 9) Agai ...
Input Leakage Current in High Speed Applications
... input consisting of two inputs, one of which is at V 1 = 1.25 V and the other at V2 = 3.75 V. On the multiplexer output is a capacitor CLOAD. The capacitance CLOAD will depend on the number of channels, the size of the switches in the multiplexer, the pin capacitance of the multiplexer, if it connec ...
... input consisting of two inputs, one of which is at V 1 = 1.25 V and the other at V2 = 3.75 V. On the multiplexer output is a capacitor CLOAD. The capacitance CLOAD will depend on the number of channels, the size of the switches in the multiplexer, the pin capacitance of the multiplexer, if it connec ...
Example 16 - Rose
... Design an op amp circuit such that vout 3v1 5v 2 4v3 . In this problem, we want to design a circuit having three inputs v1 , v 2 , and v 3 , and one output v out .The output must be related to the inputs by vout 3v1 5v 2 4v3 . This required circuit must multiply each input by a number ...
... Design an op amp circuit such that vout 3v1 5v 2 4v3 . In this problem, we want to design a circuit having three inputs v1 , v 2 , and v 3 , and one output v out .The output must be related to the inputs by vout 3v1 5v 2 4v3 . This required circuit must multiply each input by a number ...
Single Channel Operational Amplifier
... are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC) or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent ...
... are registered trademarks of Semiconductor Components Industries, LLC (SCILLC) or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. SCILLC owns the rights to a number of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and other intellectual property. A listing of SCILLC’s product/patent ...
Direct Current Circuits - GTU e
... The current through each resistor connected in parallel is variable (path of least resistance) The voltage across each resistor connected in parallel is constant. ...
... The current through each resistor connected in parallel is variable (path of least resistance) The voltage across each resistor connected in parallel is constant. ...
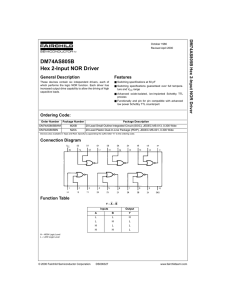
DM74AS805B Hex 2-Input NOR Driver
... These devices contain six independent drivers, each of which performs the logic NOR function. Each driver has increased output drive capability to allow the driving of high capacitive loads. ...
... These devices contain six independent drivers, each of which performs the logic NOR function. Each driver has increased output drive capability to allow the driving of high capacitive loads. ...
AD628 High Common-Mode Voltage Programmable Gain
... ±5 V, ±10 V, and 4–20 mA input signals to a single-ended output within the input range of single-supply ADCs. The AD628 has an input common-mode and differential mode operating range of ±120 V. The high common-mode input impedance makes the device well suited for high voltage measurements across a s ...
... ±5 V, ±10 V, and 4–20 mA input signals to a single-ended output within the input range of single-supply ADCs. The AD628 has an input common-mode and differential mode operating range of ±120 V. The high common-mode input impedance makes the device well suited for high voltage measurements across a s ...
MAXREFDES24 - Digi-Key
... developed to meet the requirements of PLCs and other industrial control and automation applications. The MAX15500 operates from a ±15V to ±32.5V power-supply range. The MAX15500 can generate both unipolar and bipolar current and voltage outputs. In current mode, the device produces currents of -1.2m ...
... developed to meet the requirements of PLCs and other industrial control and automation applications. The MAX15500 operates from a ±15V to ±32.5V power-supply range. The MAX15500 can generate both unipolar and bipolar current and voltage outputs. In current mode, the device produces currents of -1.2m ...
Two Page Summary
... Explain which diodes conduct when Capacitors Draw a RC charging circuit and sketch voltage vs time graphs for voltages across C and also R, also current vs time graph. Draw a discharging RC circuit and sketch voltage vs time graphs for voltages across C and also R, also current vs time graph. ...
... Explain which diodes conduct when Capacitors Draw a RC charging circuit and sketch voltage vs time graphs for voltages across C and also R, also current vs time graph. Draw a discharging RC circuit and sketch voltage vs time graphs for voltages across C and also R, also current vs time graph. ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... We disconnect the load impedance from the circuit and find the Thévenin equivalent circuit. VTH is the equivalent voltage. ZTH is the equivalent impedance. Then we set the load impedance equal to the conjugate of ZTH. The maximum power transferred to the load resistance should be ¼ times the magnitu ...
... We disconnect the load impedance from the circuit and find the Thévenin equivalent circuit. VTH is the equivalent voltage. ZTH is the equivalent impedance. Then we set the load impedance equal to the conjugate of ZTH. The maximum power transferred to the load resistance should be ¼ times the magnitu ...
Integrating ADC
An integrating ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that converts an unknown input voltage into a digital representation through the use of an integrator. In its most basic implementation, the unknown input voltage is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp for a fixed time period (the run-up period). Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the integrator and is allowed to ramp until the integrator output returns to zero (the run-down period). The input voltage is computed as a function of the reference voltage, the constant run-up time period, and the measured run-down time period. The run-down time measurement is usually made in units of the converter's clock, so longer integration times allow for higher resolutions. Likewise, the speed of the converter can be improved by sacrificing resolution.Converters of this type can achieve high resolution, but often do so at the expense of speed. For this reason, these converters are not found in audio or signal processing applications. Their use is typically limited to digital voltmeters and other instruments requiring highly accurate measurements.